A classic example of thermal evaporation is the process used to create the thin, highly reflective metallic layer inside a car's headlight assembly. In a vacuum chamber, a small piece of aluminum is heated until it evaporates, and the resulting aluminum vapor travels in a straight line until it coats the inner surface of the plastic headlight housing, forming a brilliant mirror finish. This same fundamental process is used for countless other applications.
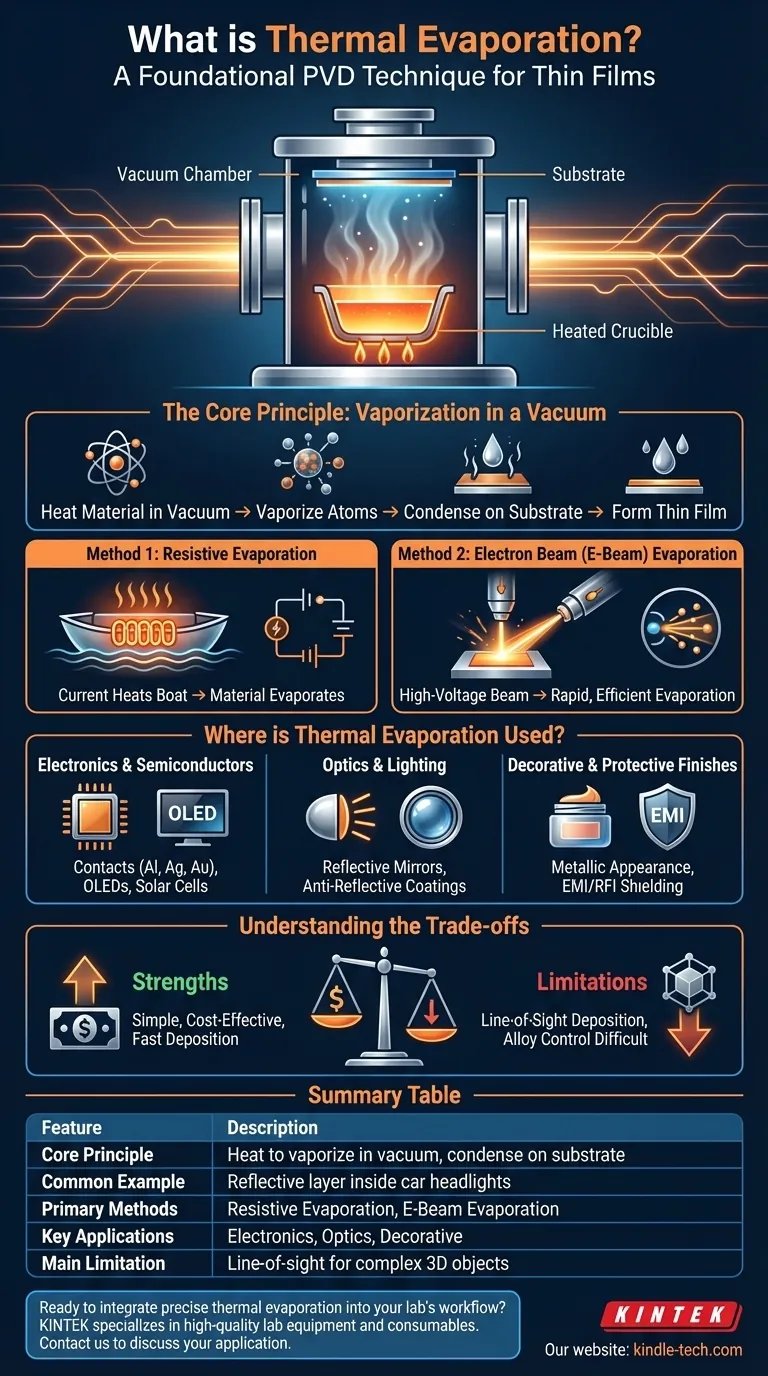
Thermal evaporation is not a single application but a foundational manufacturing technique. It involves heating a material in a high vacuum until it turns into a vapor, which then condenses onto a target surface to form an extremely thin, high-purity film.
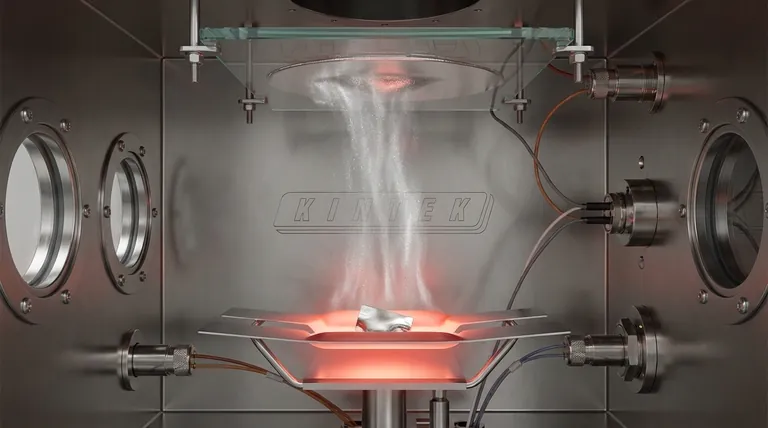

How Thermal Evaporation Works: From Solid to Thin Film
At its core, thermal evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process. It precisely transfers material atom by atom from a source to a substrate.
The Core Principle: Vaporization in a Vacuum
The entire process occurs inside a high-vacuum chamber. A source material, such as a pellet of aluminum or gold, is heated until its atoms gain enough energy to vaporize and become a gas.
These vaporized atoms travel unimpeded through the vacuum until they strike a cooler surface, known as the substrate. Upon contact, they rapidly cool, condense, and adhere to the substrate, building up a uniform thin film.
Method 1: Resistive Evaporation
This is the simplest and most common method. The source material is placed in a small container or "boat" made of a material with a very high melting point, like tungsten.
An electric current is passed through the boat, causing it to heat up due to its electrical resistance. This heat is transferred to the source material, causing it to evaporate.
Method 2: Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
For materials that require extremely high temperatures to evaporate, e-beam evaporation is used. A high-voltage beam of electrons is generated and magnetically guided to strike the source material directly.
This focused energy transfer is incredibly efficient, heating a small spot on the material to thousands of degrees and causing rapid evaporation with minimal contamination from a heating element.
Where is Thermal Evaporation Used?
The ability to create precise, ultra-thin layers makes this technique essential across numerous industries.
Electronics and Semiconductors
Thermal evaporation is a cornerstone of microfabrication. It is used to deposit the thin layers of metal—like aluminum, silver, or gold—that form the electrical contacts and interconnects on integrated circuits. It's also critical in manufacturing OLED displays and solar cells, where specific thin films determine device performance.
Optics and Lighting
Beyond automotive headlights, this process is used to create highly reflective coatings for mirrors used in telescopes and lasers. It can also be used to apply anti-reflective coatings to lenses by depositing materials like magnesium fluoride.
Decorative and Protective Finishes
Many shiny, "chrome-like" finishes on plastic items, such as cosmetic packaging or logos on consumer goods, are created using thermal evaporation. It provides a metallic appearance without the weight or cost of solid metal. It is also used to deposit films that provide EMI/RFI shielding for sensitive electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation has specific strengths and weaknesses that define its ideal use cases.
Strength: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to other deposition methods, resistive thermal evaporation systems are relatively simple, inexpensive to operate, and can deposit material quickly. This makes them ideal for high-volume production of simple coatings.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the vapor atoms travel in straight lines from the source, they cannot coat the "back side" or shadowed areas of a complex, three-dimensional object. This makes achieving a uniform coating on non-flat surfaces challenging.
Limitation: Material and Alloy Control
While e-beam can handle high-temperature materials, depositing a precise alloy can be difficult. If an alloy's components have different evaporation temperatures, one may vaporize faster than the other, changing the composition of the final film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right deposition technique depends entirely on the material, substrate, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metal contacts or simple reflective layers: Resistive thermal evaporation of materials like aluminum or silver is an ideal and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-purity films for advanced electronics like OLEDs: E-beam or resistive evaporation is critical, chosen based on the specific material's properties for each layer.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex 3D object uniformly: You should investigate alternative PVD methods like sputtering, which does not have the same line-of-sight limitation.
Understanding the principles of thermal evaporation empowers you to recognize its critical role in the devices we use every day, from smartphone screens to advanced aerospace components.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heating a material in a vacuum until it vaporizes and condenses on a substrate. |
| Common Example | Applying a reflective aluminum layer inside car headlight assemblies. |
| Primary Methods | Resistive Evaporation, Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation. |
| Key Applications | Semiconductor contacts, OLED displays, optical coatings, decorative finishes. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition makes coating complex 3D objects uniformly difficult. |
Ready to integrate precise thermal evaporation into your lab's workflow?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thin film deposition needs. Whether you are developing advanced electronics, optical coatings, or specialized surface finishes, our expertise and reliable products ensure you achieve high-purity, consistent results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications


















