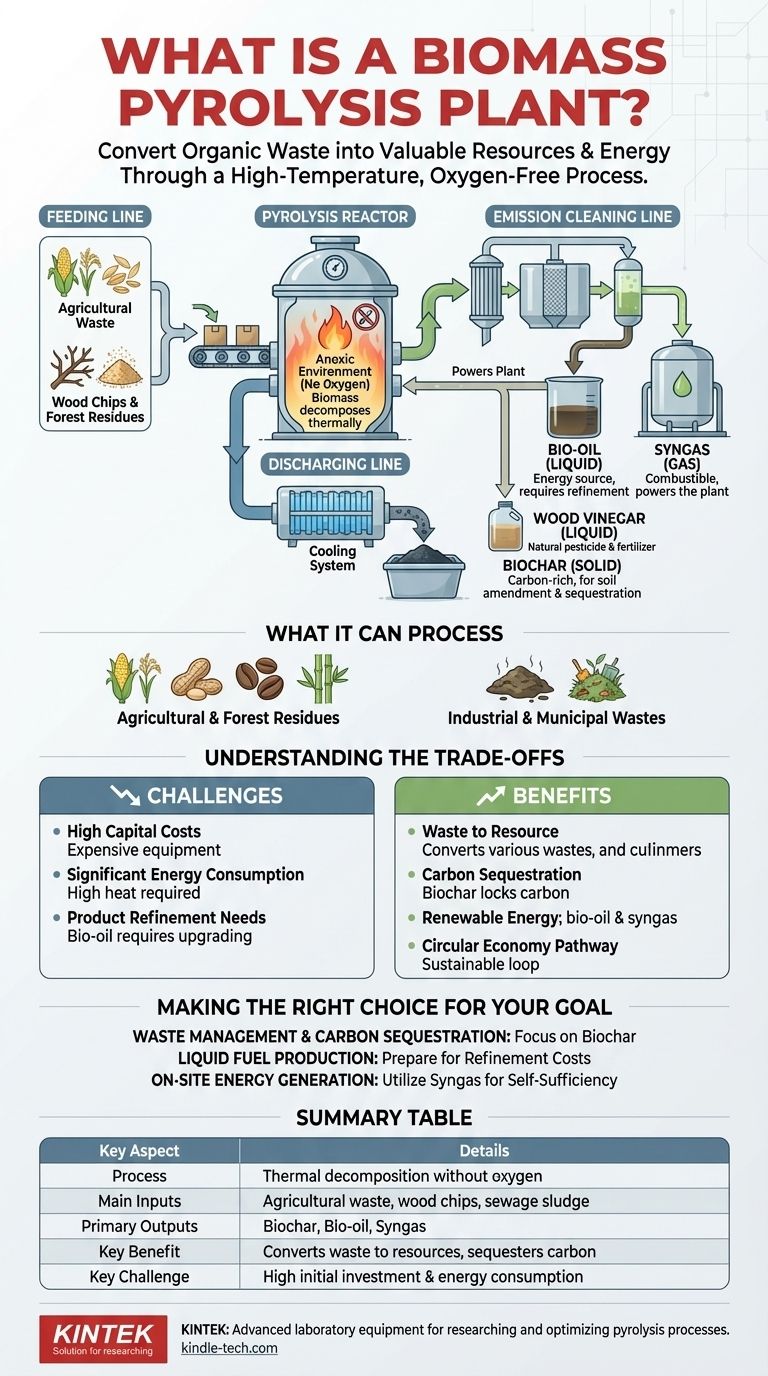
At its core, a biomass pyrolysis plant is a facility that converts organic materials, such as agricultural waste or wood chips, into valuable products through a high-temperature process without oxygen. It is composed of four main systems—feeding, pyrolysis, discharging, and emission cleaning—that work together to transform biomass into biochar (a charcoal-like solid), bio-oil, and syngas.
Biomass pyrolysis offers a powerful method for converting waste into renewable energy and sequestering carbon. However, its practical viability hinges on balancing its significant environmental benefits against high capital costs and the energy required to operate the system.
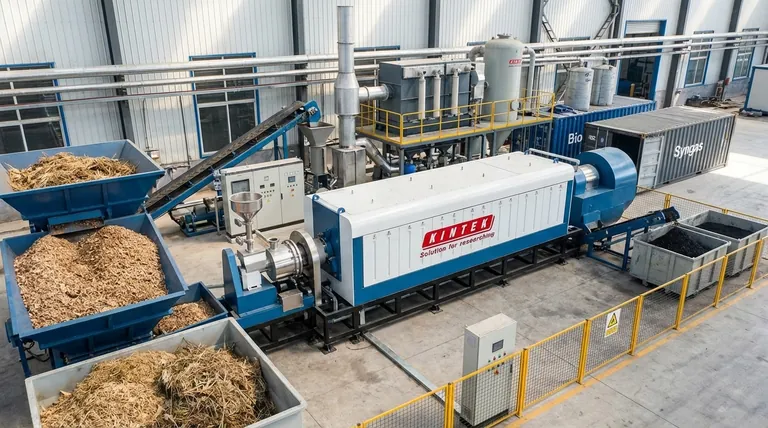

How a Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Works
A biomass pyrolysis plant functions by facilitating a chemical reaction called pyrolysis. This process breaks down organic matter using heat in an anoxic (oxygen-free) environment, ensuring the material does not combust but rather decomposes into different substances.
1. The Feeding Line
The process begins here. Raw biomass, such as wood chips, rice husks, or sewage sludge, is loaded into the system. This stage ensures a continuous and controlled supply of material into the main reactor.
2. The Biomass Pyrolysis Line
This is the heart of the plant. The biomass enters a fully sealed pyrolysis reactor and is heated to high temperatures. The absence of oxygen prevents burning and instead causes the material to chemically decompose into solids, liquids, and gases.
3. The Discharging Line
After the reaction is complete, the solid end-product, primarily biochar, is cooled and safely discharged from the reactor. This system is designed to handle high-temperature materials efficiently.
4. The Emission Cleaning Line
The gases produced during pyrolysis are captured and processed. This line cleans the emissions, separating valuable products like bio-oil and syngas while ensuring the plant adheres to environmental standards.
What a Pyrolysis Plant Can Process
The technology's versatility is one of its key strengths, as it can handle a wide variety of organic feedstocks that would otherwise be considered waste.
Agricultural and Forest Residues
This includes common byproducts from farming and logging, such as corn stalks, peanut shells, coffee husks, sawdust, tree branches, and bamboo.
Industrial and Municipal Wastes
Pyrolysis is also effective for treating more challenging materials like sewage sludge and organic solid waste from gardens and municipalities.
The Outputs: Turning Waste into Resources
The pyrolysis process yields several valuable products, each with distinct applications.
Biochar (Solid)
The main solid product is a stable, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal. Biochar is highly effective for carbon sequestration, as it locks carbon in the soil for long periods, and can also be used as a soil amendment.
Bio-oil (Liquid)
This dark, viscous liquid is a complex mixture of organic compounds. While it can be used as a source of energy, it often requires further refining before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Syngas (Gas)
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a combustible gas produced during the process. It can be used to power the pyrolysis plant itself, creating a more energy-efficient, self-sustaining operation.
Wood Vinegar (Liquid)
Also known as pyroligneous acid, this liquid byproduct has applications in agriculture as a natural pesticide and fertilizer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While promising, biomass pyrolysis technology is not without its challenges. A clear-eyed view of its limitations is essential for any potential implementation.
High Capital Costs
The equipment and machinery required to build a pyrolysis plant are costly. This significant initial investment can be a major barrier, particularly for small-scale applications.
Significant Energy Consumption
The process requires sustaining high temperatures over long periods, which consumes a substantial amount of energy. While using the produced syngas can offset some of this demand, the initial energy input remains a key consideration.
The Need for Product Refinement
The outputs of pyrolysis are not always ready for immediate use. Bio-oil, for instance, is a mixed product that must be separated, purified, and upgraded before it can serve as a direct replacement for conventional fuels, adding time and expense to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating a biomass pyrolysis plant requires aligning the technology's capabilities with your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is waste management and carbon sequestration: The production of stable biochar makes this a highly effective and environmentally beneficial technology.
- If your primary focus is liquid fuel production: Be prepared for the additional downstream costs and technical complexity associated with refining the raw bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site energy from a specific waste stream: The ability to use the produced syngas to power the operation can create a compelling, self-sufficient energy loop, but you must first overcome the high initial investment.
Ultimately, a biomass pyrolysis plant provides a sophisticated pathway to a circular economy, provided the economic and energy inputs are carefully aligned with the desired outputs.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition of biomass without oxygen. |
| Main Inputs | Agricultural waste, wood chips, sewage sludge. |
| Primary Outputs | Biochar (solid), Bio-oil (liquid), Syngas (gas). |
| Key Benefit | Converts waste into valuable resources and sequesters carbon. |
| Key Challenge | High initial investment and energy consumption. |
Ready to explore how pyrolysis technology can benefit your operation?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for researching and optimizing processes like biomass pyrolysis. Whether you are developing new biofuels, analyzing biochar properties, or scaling up your technology, our precise and reliable solutions support your innovation from lab to pilot plant.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's equipment can help you achieve your renewable energy and waste valorization goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of pyrolysis? Converting Waste into Valuable Fuels and Chemicals
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary kiln incineration? A Guide to High-Temperature Waste Destruction
- What is the composition of pyrolysis oil from plastic waste? Unlocking the Potential of Chemical Recycling
- How is pyrolysis environmentally friendly? A Sustainable Solution for Waste & Carbon Reduction
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How do you purify pyrolysis oil? A Guide to Transforming Bio-Crude into Usable Fuel
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the factors that affect pyrolysis? Mastering Temperature, Feedstock, and Process Control














