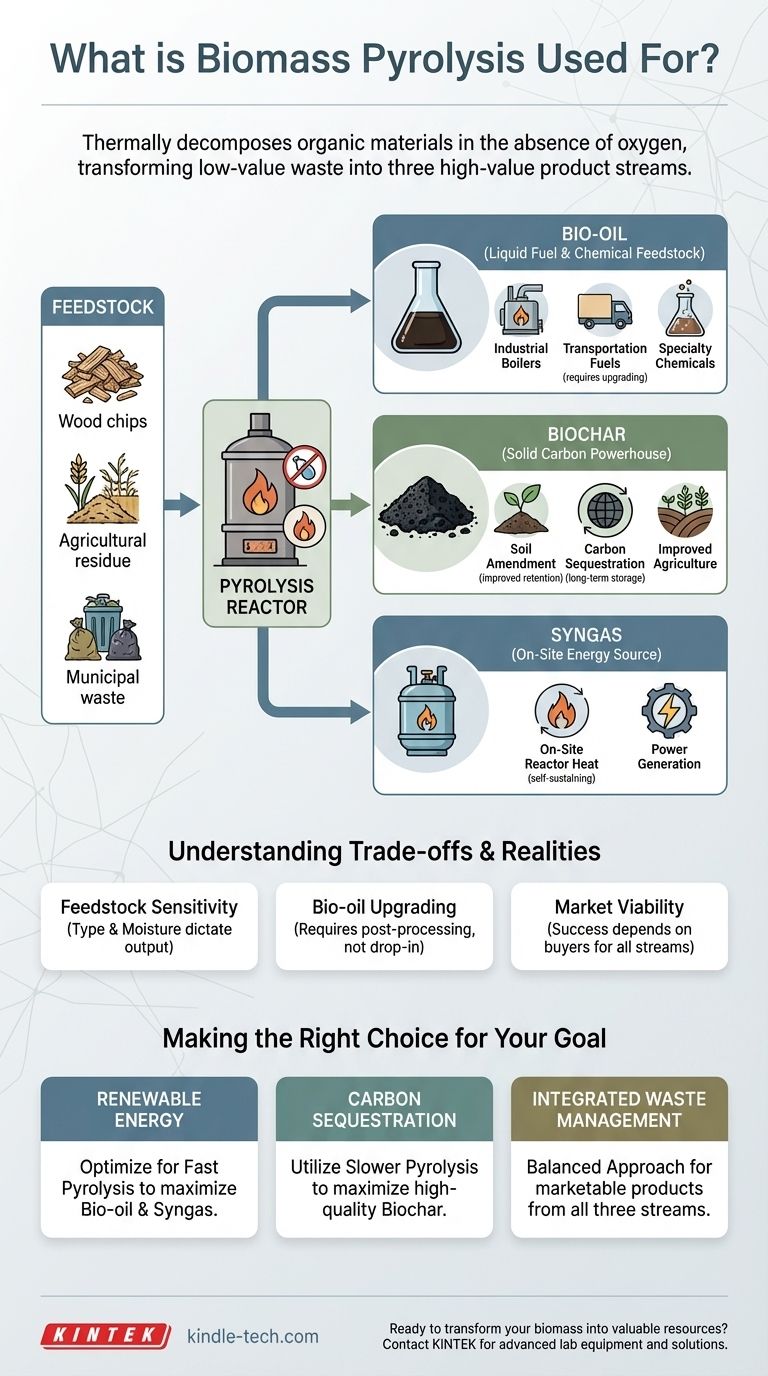
Fundamentally, biomass pyrolysis is used to thermally decompose organic materials like agricultural residue, wood waste, or municipal solid waste in the absence of oxygen. This process transforms low-value or problematic waste into a suite of high-value products: a liquid biofuel (bio-oil), a solid carbon-rich material (biochar), and a combustible gas (syngas).
Biomass pyrolysis is not merely a waste treatment method; it is a versatile refinery process. It unlocks the chemical and energy value stored in organic matter, creating three distinct product streams that can be used for energy generation, chemical production, and environmental remediation.
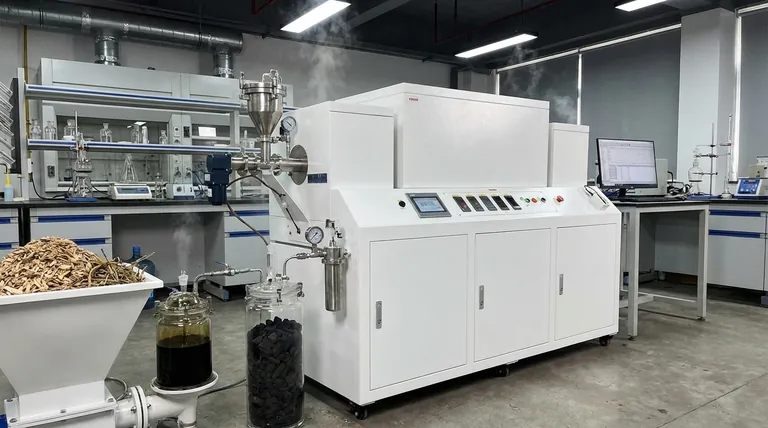

Deconstructing the Outputs: The Core Products
The true utility of pyrolysis lies in its ability to partition a single feedstock into multiple valuable outputs. The specific yields of each product can be controlled by adjusting process conditions like temperature and heating rate.
Bio-oil: The Liquid Fuel and Chemical Feedstock
Bio-oil (also known as pyrolysis oil or tar) is a dark, dense liquid that captures a significant portion of the biomass's original energy content.
Its primary applications include direct combustion in industrial boilers for heat and power generation. With further refining, bio-oil can be upgraded into transportation fuels or serve as a renewable feedstock for producing specialty chemicals.
Biochar: The Solid Carbon Powerhouse
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. It is essentially a form of charcoal.
This material has two globally significant uses. First, as a soil amendment, it improves water retention, soil structure, and nutrient availability. Second, because it is highly resistant to decomposition, it serves as a powerful tool for carbon sequestration, locking carbon in the soil for centuries.
Syngas: The On-Site Energy Source
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is the mix of non-condensable gases (like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane) produced during pyrolysis.
While it can be collected for broader energy generation, its most common use is to be looped back to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor itself. This creates a highly energy-efficient, self-sustaining system.
Other Products
Depending on the feedstock and process, a liquid fraction known as wood vinegar may also be collected. This acidic liquid has niche uses in agriculture and chemical production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a silver bullet. Its successful implementation depends on navigating key operational and economic realities.
Feedstock Determines Output
The process is highly sensitive to the type of biomass used. Wood chips, corn stover, and municipal solid waste will all produce different ratios and qualities of bio-oil, biochar, and syngas. Moisture content is also a critical factor that dictates the energy efficiency of the system.
Bio-oil Requires Upgrading
Raw bio-oil is not a direct, "drop-in" replacement for petroleum fuels. It is typically acidic, corrosive, and less stable. It requires significant post-processing and upgrading to be used as a transportation fuel, which adds cost and complexity to the overall operation.
Market Viability is Essential
The economic success of a pyrolysis plant often depends on having a viable market for all three product streams. An operation may fail if it can produce biochar but has no local buyer, or if the bio-oil cannot be used or sold at a profitable price point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis strategy depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy generation: You should optimize for fast pyrolysis conditions that maximize the yield of bio-oil and syngas for immediate use in heat and power applications.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil health: You should utilize slower pyrolysis conditions to maximize the production of high-quality, stable biochar for agricultural or environmental use.
- If your primary focus is integrated waste management: A balanced approach is best, designed to create marketable products from all three streams to ensure the long-term economic sustainability of the waste conversion process.
Ultimately, leveraging biomass pyrolysis effectively means matching the technology and operating parameters to your specific feedstock and strategic goals.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-oil | Dark liquid fuel from biomass | Industrial heat/power, refined transportation fuels, chemical feedstock |
| Biochar | Solid carbon-rich material | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, improved agriculture |
| Syngas | Mix of combustible gases (H2, CO, CH4) | On-site energy for pyrolysis process, broader power generation |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing bio-oil yields, testing biochar for soil applications, or scaling up syngas production, our precise and reliable solutions help you achieve your goals efficiently.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your biomass conversion projects and drive your sustainability initiatives forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the characteristics of the slipping, slumping, and rolling modes of bed motion? Optimize Your Rotary Process



















