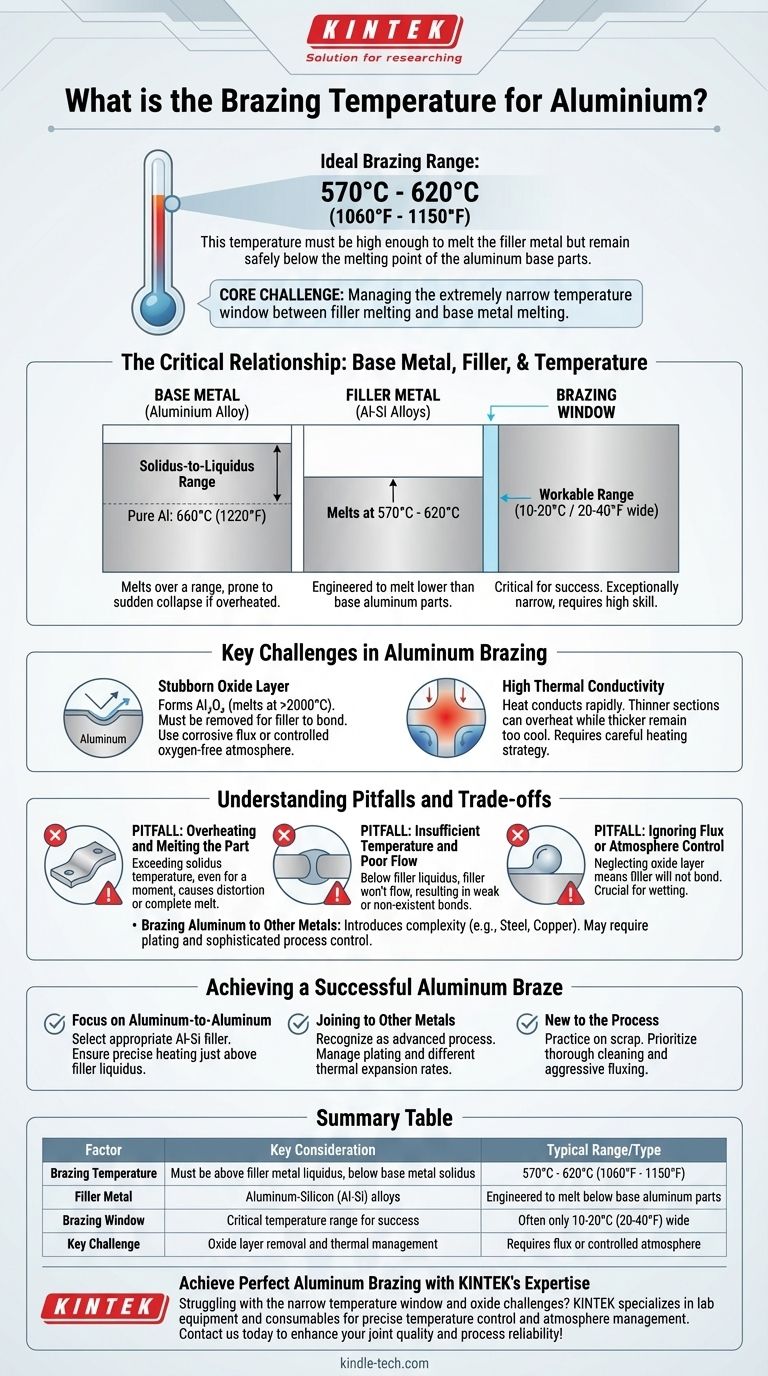
The ideal brazing temperature for aluminum is not a single value, but a narrow range dictated by the specific filler alloy being used. Typically, this process occurs between 570°C and 620°C (1060°F to 1150°F). This temperature must be high enough to melt the filler metal but remain safely below the melting point of the aluminum base parts to prevent them from collapsing.
The core challenge of brazing aluminum is managing the extremely narrow temperature window between the filler metal's melting point and the base metal's melting point. Success depends less on hitting one specific number and more on precise temperature control across the entire joint.

The Critical Relationship: Base Metal, Filler, and Temperature
To braze any metal, you must heat the assembly to a temperature that melts a filler metal, which then flows into the joint by capillary action. For aluminum, this process is particularly sensitive.
Understanding Aluminum's Melting Point
Pure aluminum has a distinct melting point of 660°C (1220°F). However, the alloys used in manufacturing do not; they melt over a solidus-to-liquidus range.
The solidus is the temperature at which the alloy begins to melt. The liquidus is the temperature at which it becomes fully liquid. This range can be very narrow, making the material prone to sudden collapse if overheated.
The Role of the Filler Metal
Aluminum brazing uses filler metals that are typically aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloys. These are engineered to melt at a temperature lower than the base aluminum parts.
Common Al-Si filler alloys melt in the range of 570°C to 620°C (1060°F to 1150°F). The exact brazing process temperature is chosen to be slightly above the liquidus temperature of the specific filler you are using.
Defining the "Brazing Window"
The "brazing window" is the workable temperature range above the filler's melting point but below the base metal's solidus point.
For aluminum, this window is exceptionally narrow, often only 10-20°C (20-40°F). This unforgiving nature is the primary reason aluminum brazing is considered a highly skilled process.
Key Challenges in Aluminum Brazing
Achieving the correct temperature is only part of the solution. You must also overcome aluminum's inherent chemical and physical properties.
The Stubborn Oxide Layer
Aluminum instantly forms a tough, transparent layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) on its surface. This oxide melts at over 2000°C (3600°F), far above the brazing temperature.
This oxide layer must be removed for the filler metal to wet and bond with the base aluminum. This is accomplished using a corrosive flux or by brazing in a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere (vacuum or inert gas).
High Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum conducts heat very rapidly and efficiently. This can make it difficult to bring the entire joint assembly to a uniform brazing temperature.
Thinner sections can easily overheat and melt while thicker sections remain too cool for the filler metal to flow properly. This requires a carefully planned heating strategy.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Precise temperature control is non-negotiable. Even small deviations can lead to complete failure.
Pitfall: Overheating and Melting the Part
This is the most common and catastrophic failure mode. Exceeding the base metal's solidus temperature, even for a moment, can cause the part to distort or melt entirely, especially given the narrow working range.
Pitfall: Insufficient Temperature and Poor Flow
If the assembly is not brought up to a temperature slightly above the filler's liquidus point, the filler will not become fluid enough. It will fail to flow into the joint via capillary action, resulting in a partial, weak, or non-existent bond.
Pitfall: Ignoring Flux or Atmosphere Control
Focusing only on temperature while neglecting the oxide layer is a recipe for failure. Without proper fluxing or atmosphere control, the filler metal will simply ball up on the surface and will not bond to the aluminum.
Brazing Aluminum to Other Metals
While possible, joining aluminum to dissimilar metals like steel or copper introduces significant complexity. As the references note, metals like titanium and nickel can be brazed directly, but others require pre-plating. This changes the thermal properties and requires even more sophisticated process control.
Achieving a Successful Aluminum Braze
Your approach should be determined by the materials you are joining and your experience level. Base your strategy on the principles, not just a single temperature value.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum-to-aluminum: Select the appropriate Al-Si filler alloy and ensure your heating process can precisely maintain a temperature just above that filler's liquidus point.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum to other metals: Recognize this is an advanced process where plating the dissimilar metal and managing different thermal expansion rates are as critical as temperature control.
- If you are new to the process: Practice on scrap material to develop a feel for how quickly aluminum absorbs heat, and prioritize thorough cleaning and aggressive fluxing to manage the oxide layer.
Ultimately, a successful aluminum braze is a demonstration of control—over temperature, chemistry, and heat distribution.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Typical Range/Type |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing Temperature | Must be above filler metal liquidus, below base metal solidus | 570°C to 620°C (1060°F to 1150°F) |
| Filler Metal | Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) alloys | Engineered to melt below base aluminum parts |
| Brazing Window | Critical temperature range for success | Often only 10-20°C (20-40°F) wide |
| Key Challenge | Oxide layer removal and thermal management | Requires flux or controlled atmosphere |
Achieve Perfect Aluminum Brazing with KINTEK's Expertise
Struggling with the narrow temperature window and oxide challenges of aluminum brazing? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables that deliver the precise temperature control and atmosphere management your laboratory needs for flawless brazing results. Our solutions help you avoid common pitfalls like part melting and poor filler flow.
Contact us today to discuss how our specialized brazing equipment can enhance your joint quality and process reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum chamber and heating system maintained at 300°C during deposition? Optimize Coating Adhesion
- Is a furnace endothermic or exothermic? Uncover the Science of Home Heating
- Can you temper any metal? No, and here’s why the process is exclusive to certain steels.
- What is the necessity of vacuum annealing for sponge zirconium? Ensure Stability in EBM Refinement
- Why is a vacuum drying oven utilized for AlCrFeNiTix powders? Prevent Oxidation & Preserve High-Entropy Alloy Purity
- What materials are used in quenching? Choosing the Right Quenchant for Hardness & Toughness
- What impact do high-temperature drying and calcination equipment have on apatite-nepheline waste properties?
- How does high-temperature heating equipment facilitate corrosion research? Replicating Nuclear Reactor Environments



















