Contrary to a common misconception, calcination is not a burning process. While both involve high temperatures, they are fundamentally different chemical transformations. Calcination is a process of thermal decomposition, where heat is used to break down a compound, often to drive off a volatile component like carbon dioxide or water.
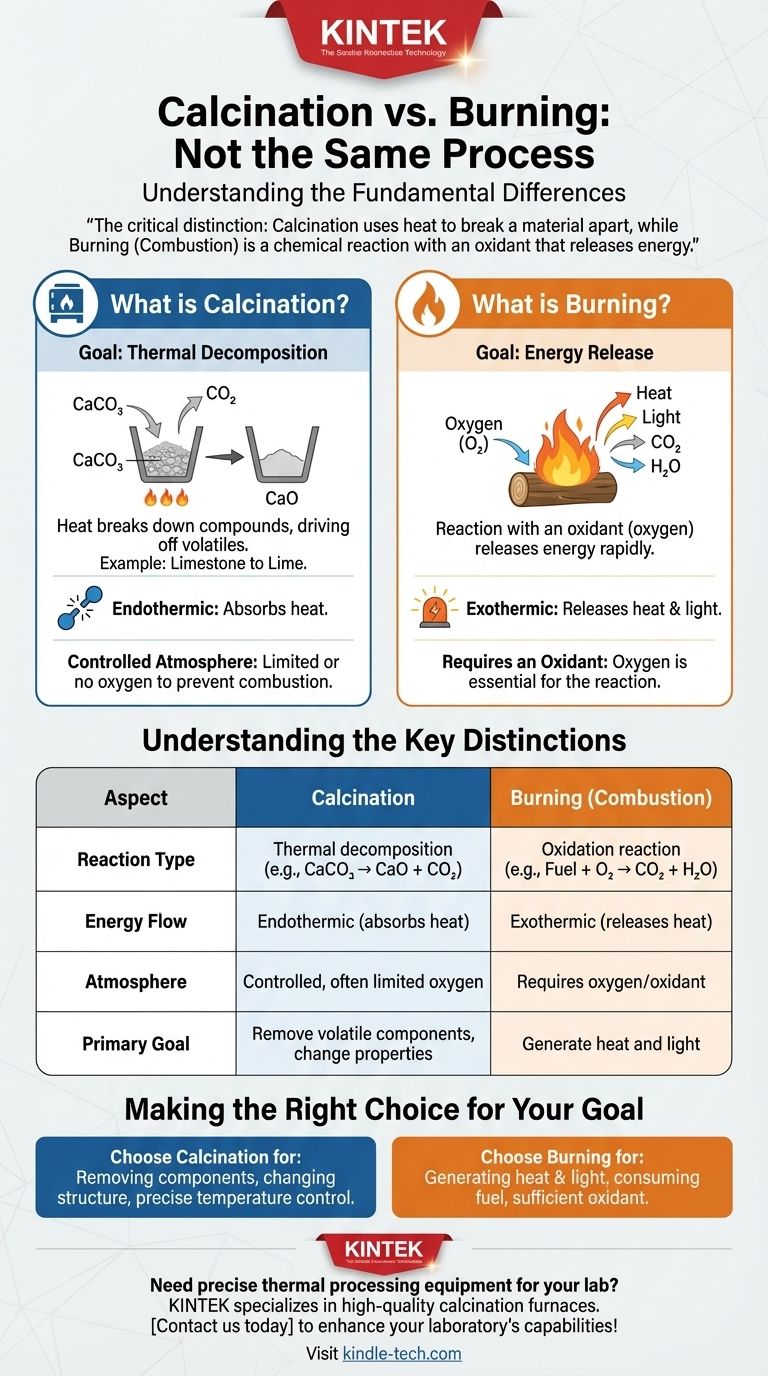
The critical distinction is this: calcination uses heat to break a material apart, often in a controlled atmosphere, while burning (combustion) is a chemical reaction with an oxidant like oxygen that releases energy.
What is Calcination?
Calcination is a precise thermal treatment process used to change the chemical and physical properties of a material. The term is derived from the Latin calcinare, meaning 'to burn lime'.
The Goal: Thermal Decomposition
The primary purpose of calcination is to cause thermal decomposition. Heat provides the energy needed to break chemical bonds within a substance, causing it to separate into simpler components.
A Common Example: Limestone to Lime
The production of lime from limestone is the classic example. When limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is heated to a high temperature, it decomposes.
This process drives off carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, leaving behind lime (calcium oxide, CaO), a crucial component in cement and other industrial materials.
The Role of a Controlled Atmosphere
Crucially, calcination often takes place in an atmosphere with limited or no oxygen. This is done specifically to prevent combustion and ensure that only the desired decomposition reaction occurs.
How is This Different from Burning?
Burning, known chemically as combustion, is a high-temperature exothermic reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, most commonly oxygen from the air.
The Requirement of an Oxidant
Unlike calcination, burning cannot happen without an oxidant. When you burn wood, the wood's organic compounds are not just decomposing; they are actively reacting with oxygen.
The Goal: Energy Release
The primary result of combustion is the rapid release of energy in the form of heat and light. While it also produces new chemical substances (like ash, carbon dioxide, and water vapor), the energy release is its defining characteristic.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Confusing these two processes can lead to significant errors in materials processing, chemistry, and engineering. The differences are clear and absolute.
Reaction Type
Calcination is a decomposition reaction. A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler products (e.g., CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂).
Combustion is an oxidation reaction. A fuel reacts with an oxidant to form new, oxidized products (e.g., CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O).
Energy Flow
Calcination is typically an endothermic process. It requires a continuous input of energy (heat) to sustain the reaction and break the chemical bonds.
Combustion is an exothermic process. Once initiated, it releases far more energy than was required to start it, creating a self-sustaining reaction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding whether you need to calcine or combust is fundamental to achieving the desired outcome in any thermal process.
- If your primary focus is to remove a specific component from a solid (like water or CO₂) or change its crystalline structure: You are performing calcination, where precise temperature control and atmosphere management are critical.
- If your primary focus is to generate heat and light by consuming a fuel: You are performing combustion, where ensuring a sufficient supply of an oxidant like air is the main priority.
Distinguishing between these two foundational processes is essential for controlling chemical reactions and engineering materials effectively.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Calcination | Burning (Combustion) |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Type | Thermal decomposition | Oxidation reaction |
| Energy Flow | Endothermic (absorbs heat) | Exothermic (releases heat) |
| Atmosphere | Controlled, often limited oxygen | Requires oxygen/oxidant |
| Primary Goal | Remove volatile components, change material properties | Generate heat and light |
Need precise thermal processing equipment for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality calcination furnaces and lab equipment designed for controlled thermal decomposition. Our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and atmosphere management for material transformation. Contact us today to enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process



















