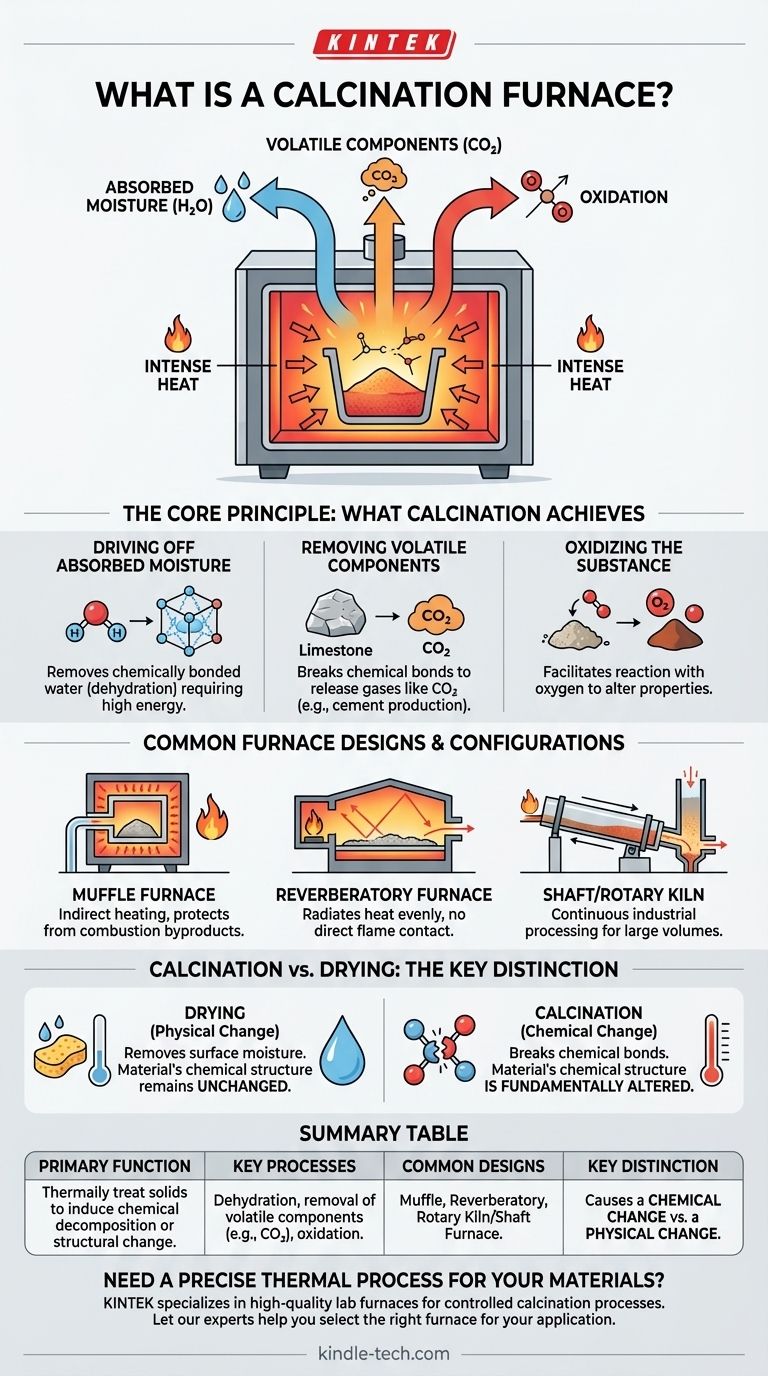
In essence, a calcination furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven designed to heat a solid material to the point where its chemical composition or physical structure changes. Its primary objectives are to drive off absorbed moisture, remove volatile components like carbon dioxide, and oxidize part or all of the substance being treated. The most common industrial application is in cement production, where it decomposes calcium carbonate into calcium oxide (lime).
A calcination furnace is not merely for heating or drying. Its critical function is to use intense heat to break down a solid's chemical structure, fundamentally altering its composition by removing components that are chemically bound within it.
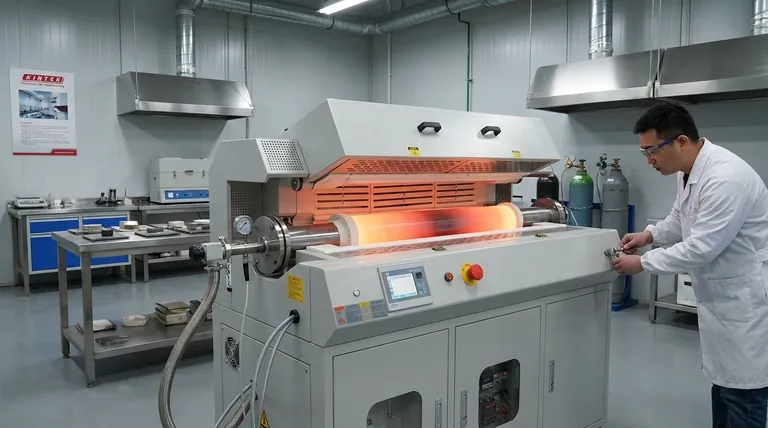

The Core Principle: What Calcination Achieves
Calcination is a precise thermal treatment process. The furnace is the tool that enables this transformation by applying controlled, high temperatures to a material, often just below its melting point.
Driving Off Absorbed Moisture
While a simple oven can dry surface moisture, a calcination furnace removes water that is chemically bonded within a material's crystal structure. This process, often called dehydration, requires significantly more energy and results in a chemically altered substance.
Removing Volatile Components
This is the most common goal of calcination. The furnace's heat breaks chemical bonds, causing certain parts of the material to turn into gas and escape.
A prime example is the production of cement from limestone (calcium carbonate). The furnace heats the limestone, breaking it down into calcium oxide (a key ingredient in cement) and releasing carbon dioxide gas.
Oxidizing the Substance
In some applications, the furnace's high-temperature environment is used to facilitate a reaction between the material and oxygen. This controlled oxidation can change the material's properties for a specific industrial purpose.
Common Furnace Designs and Configurations
Calcination furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all technology. Their design is tailored to the specific material and the desired outcome of the process.
Muffle Furnaces
In a muffle furnace, the material is placed in a chamber (the muffle) that is heated from the outside. This design protects the substance from direct contact with flames or combustion byproducts, allowing for a clean and highly controlled heating environment.
Reverberatory Furnaces
These furnaces work by radiating heat. The heat source is located in one area, and the heat reflects off the furnace's roof and walls onto the material below, ensuring even heating without direct flame contact.
Shaft Furnaces and Kilns
For large-scale, continuous industrial processes like cement manufacturing, rotary kilns or shaft furnaces are common. The material is fed into one end and slowly moves through the heated chamber, ensuring the entire volume is processed efficiently before exiting the other side.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Calcination vs. Drying
Confusing these two processes is a common pitfall. While both involve heat and the removal of water, their fundamental purpose and impact on the material are entirely different.
Drying is a Physical Change
Drying removes unbound water (surface moisture) from a material, typically at relatively low temperatures. The chemical formula and structure of the material itself remain unchanged.
Calcination is a Chemical Change
Calcination uses much higher temperatures to break chemical bonds. It removes substances, like carbon dioxide or chemically-bound water, that are an integral part of the material's molecular structure, creating a new substance.
How to Identify the Need for Calcination
Choosing the right thermal process depends entirely on your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is to remove surface water without altering the material's chemistry: You require a standard drying oven, not a calcination furnace.
- If your primary focus is to decompose a material like limestone or remove chemically-bound water: Calcination is the correct process to drive off volatile gases and create a new chemical compound (an oxide).
- If your primary focus is to fundamentally transform a material's molecular structure using heat: You are in the realm of calcination, which demands a furnace capable of precise, high-temperature control.
Ultimately, understanding the specific chemical transformation you need to achieve is the key to selecting the right thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Thermally treat solids to induce chemical decomposition or structural change. |
| Key Processes | Dehydration, removal of volatile components (e.g., CO₂), oxidation. |
| Common Designs | Muffle, Reverberatory, Rotary Kiln/Shaft Furnace. |
| Key Distinction | Causes a chemical change (calcination) vs. a physical change (drying). |
Need a precise thermal process for your materials?
Calcination is a critical step in many laboratory and industrial workflows. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces, including muffle furnaces ideal for controlled calcination processes. Whether you are developing new materials or processing industrial minerals, our equipment ensures the precise temperature control and clean environment required for consistent, reliable results.
Let our experts help you select the right furnace for your application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your calcination needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision



















