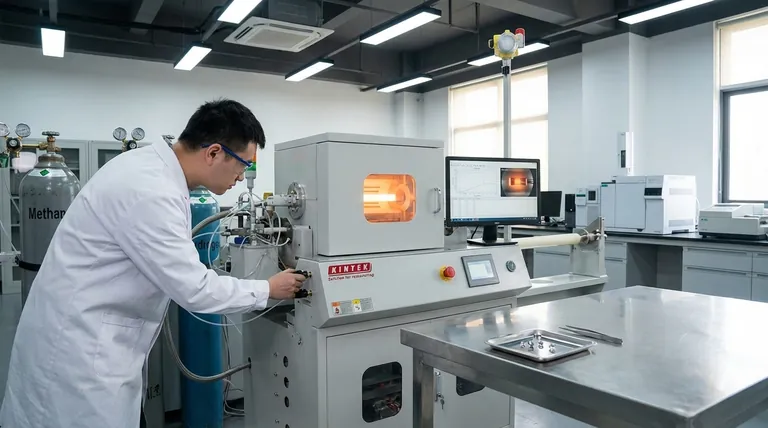
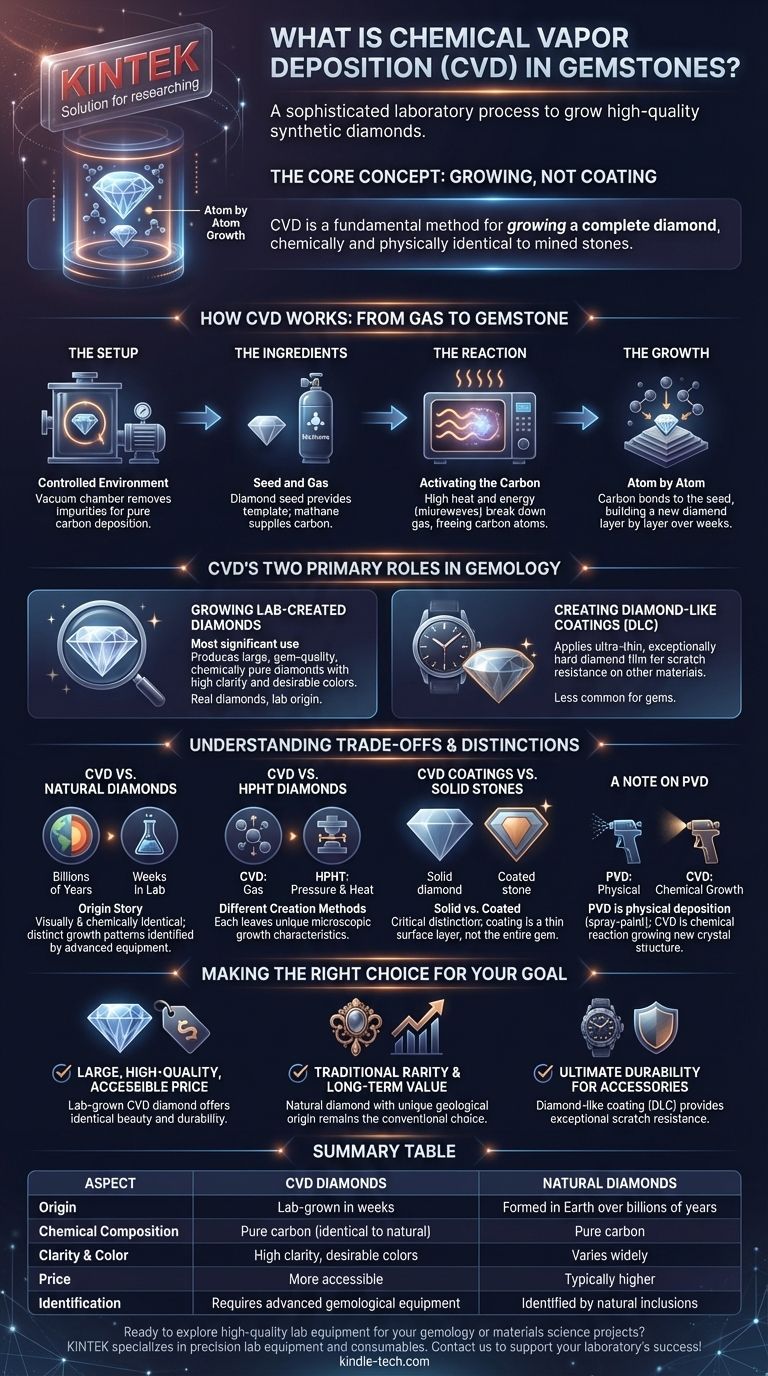
In the world of gemstones, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated laboratory process used to grow high-quality synthetic diamonds from a carbon gas. In a vacuum chamber, gases like methane are broken down by energy, causing carbon atoms to deposit onto a small diamond "seed" crystal. This process meticulously builds a new, larger diamond layer by layer, resulting in a gemstone that is chemically and physically identical to one mined from the earth.
The core takeaway is that CVD is not merely a coating, but a fundamental method for growing a complete diamond. Understanding this process is essential for anyone navigating the modern gem market, as it explains the origin and properties of a significant portion of lab-created diamonds available today.

How CVD Works: From Gas to Gemstone
The CVD process is a marvel of material science, essentially recreating a part of the cosmic cycle of carbon formation in a highly controlled laboratory setting. It breaks down into a few key stages.
The Setup: A Controlled Environment
The entire process takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber. Removing all other gases is critical to ensure that only pure carbon is deposited, preventing impurities from disrupting the diamond's crystal structure.
The Ingredients: Seed and Gas
A small, thin slice of a previously grown diamond, known as a "seed crystal," is placed in the chamber. This seed provides the foundational template for the new diamond's crystal lattice. Then, a precise mixture of carbon-rich gas, typically methane, is introduced.
The Reaction: Activating the Carbon
The chamber is heated to a high temperature, and a source of energy, often microwaves, is used to energize the gas. This breaks the methane molecules apart, freeing individual carbon atoms.
The Growth: Atom by Atom
These free carbon atoms are drawn down to the cooler surface of the diamond seed. They bond to the seed's existing crystal structure, perfectly aligning themselves and slowly building up the diamond, one atomic layer at a time, over several weeks.
CVD's Two Primary Roles in Gemology
While most famously used for growing diamonds, the underlying technology of CVD has two distinct applications relevant to jewelry and gemstones.
Growing Lab-Created Diamonds
This is the most significant use of CVD in the industry. The process can produce large, gem-quality diamonds with high clarity and desirable colors. Because they are chemically pure carbon in a diamond lattice, these stones are not "fakes"—they are simply real diamonds with a laboratory origin.
Creating Diamond-Like Coatings (DLC)
The same principle can be used to apply an ultra-thin, exceptionally hard film of diamond or diamond-like carbon onto other materials. This is less common for gemstones but is used to give items like watch parts or even less durable gems a hard, scratch-resistant surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
A CVD diamond is a real diamond, but its origin creates important distinctions that a knowledgeable buyer should understand.
CVD vs. Natural Diamonds
The primary difference is their origin story—billions of years in the earth versus weeks in a lab. While visually and chemically identical, trained gemologists using advanced equipment can identify the unique, subtle growth patterns inherent to the CVD process, distinguishing them from natural stones.
CVD vs. HPHT Diamonds
HPHT (High-Pressure, High-Temperature) is the other primary method for creating lab diamonds. HPHT mimics the earth's mantle with immense pressure and heat to crystallize carbon. CVD, by contrast, builds the diamond from a gas. Each method leaves different microscopic growth characteristics.
CVD Coatings vs. Solid Stones
A critical distinction is whether the entire gem is a solid CVD diamond or if it's a different, less valuable material (like cubic zirconia) with a thin CVD coating for durability. Misrepresenting a coated stone as a solid lab-grown diamond is a significant issue to be aware of.
A Note on PVD
You may also encounter the term Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). This is a different process where a solid material is vaporized and physically deposited onto a surface, often used for colored coatings on jewelry. CVD is a chemical reaction that grows a new crystalline structure, whereas PVD is more like a microscopic spray-painting process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your understanding of CVD should empower you to select a gemstone based on your personal priorities and values.
- If your primary focus is obtaining a large, high-quality diamond at a more accessible price point: A lab-grown CVD diamond offers identical beauty and durability to a natural stone.
- If your primary focus is on traditional rarity and long-term value retention: A natural diamond, with its unique geological origin, remains the conventional choice.
- If your primary focus is the ultimate durability for an accessory or alternative gem: A product with a diamond-like coating (DLC) can provide exceptional scratch resistance where it matters most.
By understanding the science behind the stone, you are empowered to choose the gemstone that truly aligns with your needs and values.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Diamonds | Natural Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Lab-grown in weeks | Formed in Earth over billions of years |
| Chemical Composition | Pure carbon (identical to natural) | Pure carbon |
| Clarity & Color | High clarity, desirable colors | Varies widely |
| Price | More accessible | Typically higher |
| Identification | Requires advanced gemological equipment | Identified by natural inclusions |
Ready to explore high-quality lab equipment for your gemology or materials science projects? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories with reliable solutions for diamond growth, material analysis, and more. Whether you're researching CVD processes or need durable lab supplies, we provide the tools to achieve accurate results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor



















