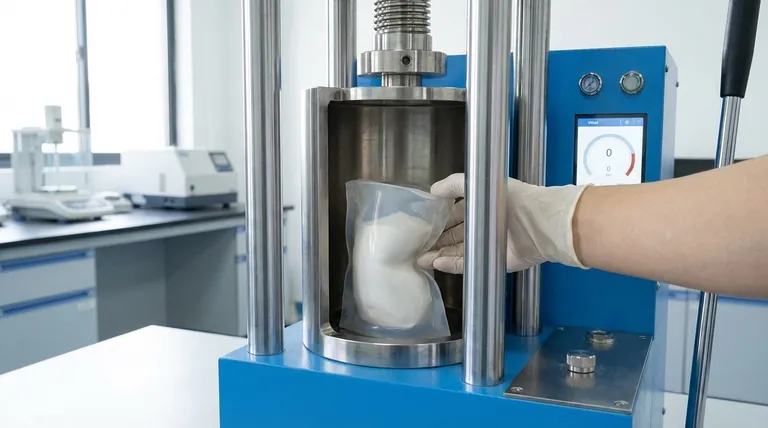
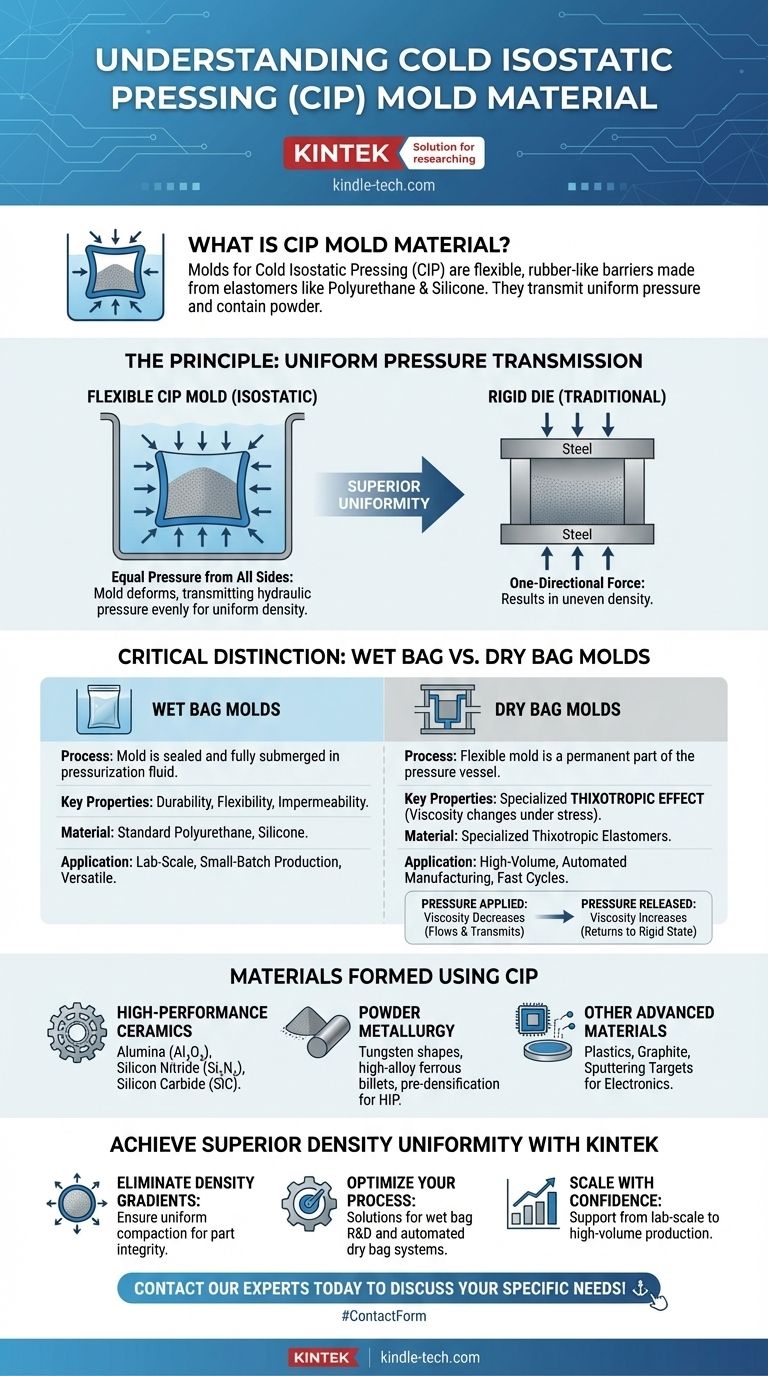
In short, molds for Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) are made from flexible, rubber-like materials designed to act as a barrier that transmits pressure uniformly. The most common materials are polyurethane, silicone, and other elastomers. Unlike the rigid steel molds used in traditional pressing, these pliable materials are essential for the isostatic process.
The core function of a CIP mold is not to shape by force, but to serve as a flexible, impermeable membrane. It contains the powder and perfectly transmits hydraulic pressure from all directions, which is the defining advantage of isostatic pressing for creating highly uniform, dense parts.

The Principle Behind Flexible Molds
Transmitting Pressure Uniformly
Isostatic means "equal pressure." The goal is to squeeze a powder compact from all sides simultaneously. A flexible, elastomeric mold is the only way to achieve this. As the hydraulic fluid in the pressure vessel is pressurized, the mold deforms and transmits that pressure evenly onto the powder within it.
Containing the Powder
The mold acts as a "bag" that holds the loose powder in its initial shape. It must be completely impermeable to the pressurization fluid (typically water or specialized oil) to prevent contamination and ensure the process works correctly.
The Contrast with Rigid Dies
Traditional axial or die pressing uses rigid steel molds. These molds only apply force along one axis (e.g., from the top and bottom). This often results in density gradients, where the part is denser at the ends and less dense in the middle. The flexible nature of CIP molds eliminates this problem.
Critical Distinction: Wet Bag vs. Dry Bag Molds
The specific type of CIP process—wet bag or dry bag—imposes different requirements on the mold material.
Molds for Wet Bag Pressing
In wet bag CIP, the powder-filled mold is sealed and fully submerged in the pressurization fluid. For this process, the primary material requirements are durability, flexibility, and fluid impermeability. Standard polyurethane or silicone is perfectly suitable.
Molds for Dry Bag Pressing
In dry bag CIP, the flexible mold is a permanent part of the pressure vessel itself, allowing for faster, more automated cycles. This demands a more specialized material.
The Special Requirement: Thixotropy
Dry bag molds often require a material with a thixotropic effect. This means the material's viscosity changes under stress.
When pressure is applied, the mold material's viscosity decreases, allowing it to flow slightly and transmit pressure perfectly. When the pressure is released, its viscosity increases, and it returns to its original, more rigid state, ready for the next cycle.
What Materials Are Formed Using CIP?
The versatility of CIP allows it to be used for a wide range of advanced materials where uniform density is critical.
High-Performance Ceramics
CIP is essential for forming complex ceramic components like alumina (Al₂O₃), silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), and silicon carbide (SiC) before they are sintered.
Powder Metallurgy
The process is used to form parts from metal powders, including tungsten shapes and high-alloy ferrous billets, often as a pre-densification step before Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP).
Other Advanced Materials
Its applications extend to forming plastics, graphite, and sputtering targets used in the electronics industry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal mold material is dictated entirely by your manufacturing process and goals.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale work or versatile, small-batch production: Standard polyurethane or silicone molds for a wet bag process offer the most flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated manufacturing: A specialized, thixotropic elastomeric mold designed for a dry bag system is essential for achieving the necessary speed and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is creating complex geometries: The key benefit is the inherent flexibility of elastomers, which allows for shapes that are impossible to produce with rigid tooling.
Ultimately, selecting the correct flexible mold material is the key to unlocking the primary benefit of isostatic pressing: the creation of complex parts with outstanding density uniformity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Wet Bag Molds | Dry Bag Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyurethane, Silicone | Specialized Thixotropic Elastomers |
| Key Property | Flexibility, Impermeability | Thixotropic Effect (Viscosity Changes Under Stress) |
| Application | Lab-Scale, Small-Batch Production | High-Volume, Automated Manufacturing |
| Primary Use | Versatile Powder Containment | Fast, Repeatable Cycles in Permanent Vessels |
Achieve Superior Density Uniformity in Your Materials with KINTEK
Are you working with advanced ceramics, powder metallurgy, or complex geometries that demand perfect density? The right Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) mold material is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the precise elastomeric molds needed for reliable CIP processes.
Our expertise helps you:
- Eliminate Density Gradients: Ensure uniform compaction for superior part integrity.
- Optimize Your Process: Whether you need durable wet bag molds for R&D or specialized thixotropic materials for automated dry bag systems, we have the solution.
- Scale with Confidence: From lab-scale experiments to high-volume production, our products support your growth.
Don't let mold material limitations compromise your results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your CIP operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between sintering and pressing? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy Processes
- What are the disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Key Limitations in Strength and Size
- What are the applications of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- How much does an isostatic press cost? A Guide to Lab vs. Industrial Pricing
- What is a cold isostatic press? Achieve Uniform Powder Compaction for Complex Parts



















