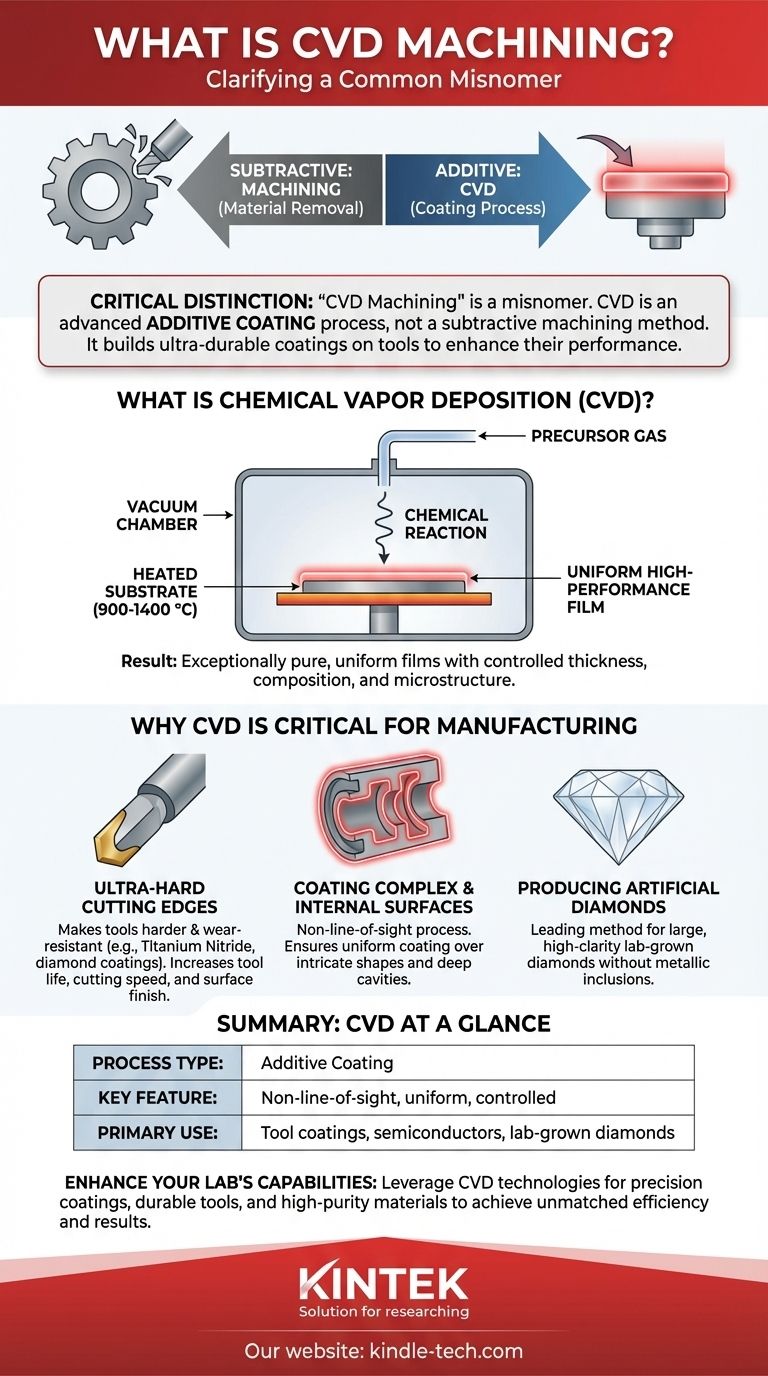
Critically, "CVD machining" is a misnomer. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not a machining process, which involves removing material. Instead, CVD is a highly advanced additive coating process used to deposit exceptionally thin, hard, and high-performance films onto a surface, making it indispensable for creating the modern tools used in machining.
The core misunderstanding is between an additive process (CVD) and a subtractive one (machining). CVD doesn't cut or shape parts; it builds an ultra-durable coating on a tool's surface, which then allows that tool to machine other materials more effectively.

What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)?
CVD is a sophisticated manufacturing process used to produce high-quality, high-performance solid materials, typically in the form of a thin film or coating.
The Core Process: Gas, Heat, and Reaction
The process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. A precursor gas (or a mix of gases) containing the desired coating elements is introduced into the chamber, which holds a heated component, known as the substrate.
The high temperature (often 900-1400 °C) triggers a chemical reaction on or near the hot substrate's surface. This reaction causes the atoms to settle and form a solid, bonded layer on the substrate.
The Result: A High-Performance Film
This process results in an exceptionally pure and uniform film. Manufacturers can precisely control the film's thickness, chemical composition, and microstructure.
This level of control allows for the creation of coatings with specific properties, such as extreme hardness, corrosion resistance, or tailored electrical conductivity.
The Key Distinction: CVD vs. PVD
CVD is often compared to Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The primary difference is that CVD relies on chemical reactions to form the film.
PVD, in contrast, uses physical processes like evaporation or sputtering to transfer coating material onto the substrate.
Why CVD is Critical for Modern Manufacturing
While not a machining process itself, CVD is a foundational technology that enables next-generation machining, tooling, and material science.
Creating Ultra-Hard Cutting Edges
The most common application related to "machining" is coating cutting tools, drills, and end mills. A CVD coating, like Titanium Nitride or diamond, makes the tool vastly harder and more resistant to wear.
This allows the tool to cut faster, last longer, and produce a better surface finish on the machined part.
Coating Complex and Internal Surfaces
Because CVD relies on a gas that fills the entire chamber, it is a non-line-of-sight process. This is a significant advantage.
It allows for a perfectly homogeneous coating to be applied over intricate shapes, contoured surfaces, and even inside cavities—something impossible for many line-of-sight coating methods.
Producing High-Purity Artificial Diamonds
Beyond tool coatings, CVD is a leading method for producing lab-grown diamonds. It enables the creation of large, high-clarity (VVS-VS) diamonds without the metallic inclusions often found in diamonds made with other methods like HPHT (High-Pressure/High-Temperature).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
No technology is a universal solution. Understanding the unique benefits of CVD clarifies its role in the industry.
Advantage: Unmatched Film Quality
CVD produces films of extremely high purity with excellent control over thickness and uniformity across large areas.
Advantage: Application Versatility
The process can be used to coat a wide variety of substrates and complex geometries, making it suitable for everything from semiconductor wafers to automotive components and medical implants.
Advantage: Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to some alternatives, CVD can be a highly scalable and controllable process, offering high production rates and relatively low waste generation.
The Key Consideration: Heat
The high temperatures required for many CVD processes mean the substrate material must be able to withstand them without deforming or being damaged. This is a critical design and material selection constraint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this distinction helps you select the right technology to solve your engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is superior tool life and cutting performance: Seek out tools with CVD coatings, leveraging their extreme hardness and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity materials like semiconductors or diamonds: CVD is a leading technology for its precise control over film composition and structure.
- If your primary focus is coating complex parts with uniform durability: CVD's non-line-of-sight nature makes it the ideal choice for intricate geometries.
By recognizing CVD as an essential additive coating technology, you can better specify and utilize the advanced tools and components it helps create.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Additive Coating |
| Key Feature | Non-line-of-sight, uniform coating |
| Primary Use | Tool coatings, semiconductors, lab-grown diamonds |
| Key Advantage | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, complex geometry coating |
| Consideration | High process temperatures required |
Enhance your lab's capabilities with precision coatings. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including technologies that leverage CVD coatings for superior performance. Whether you need durable cutting tools, high-purity materials, or components with complex coatings, our expertise can help you achieve unmatched efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor



















