In short, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process for creating thin, solid films by reacting gases on a surface, while polymerization is a chemical reaction that links small molecules together to form long chains or networks. CVD builds a material layer by layer from a gas, whereas polymerization creates large molecules, which then make up a bulk material like plastic.
The core difference lies in the final product's structure. CVD is fundamentally about surface coating and film growth, building a solid from gaseous precursors, while polymerization is about creating massive molecules (polymers) by linking smaller building blocks (monomers).

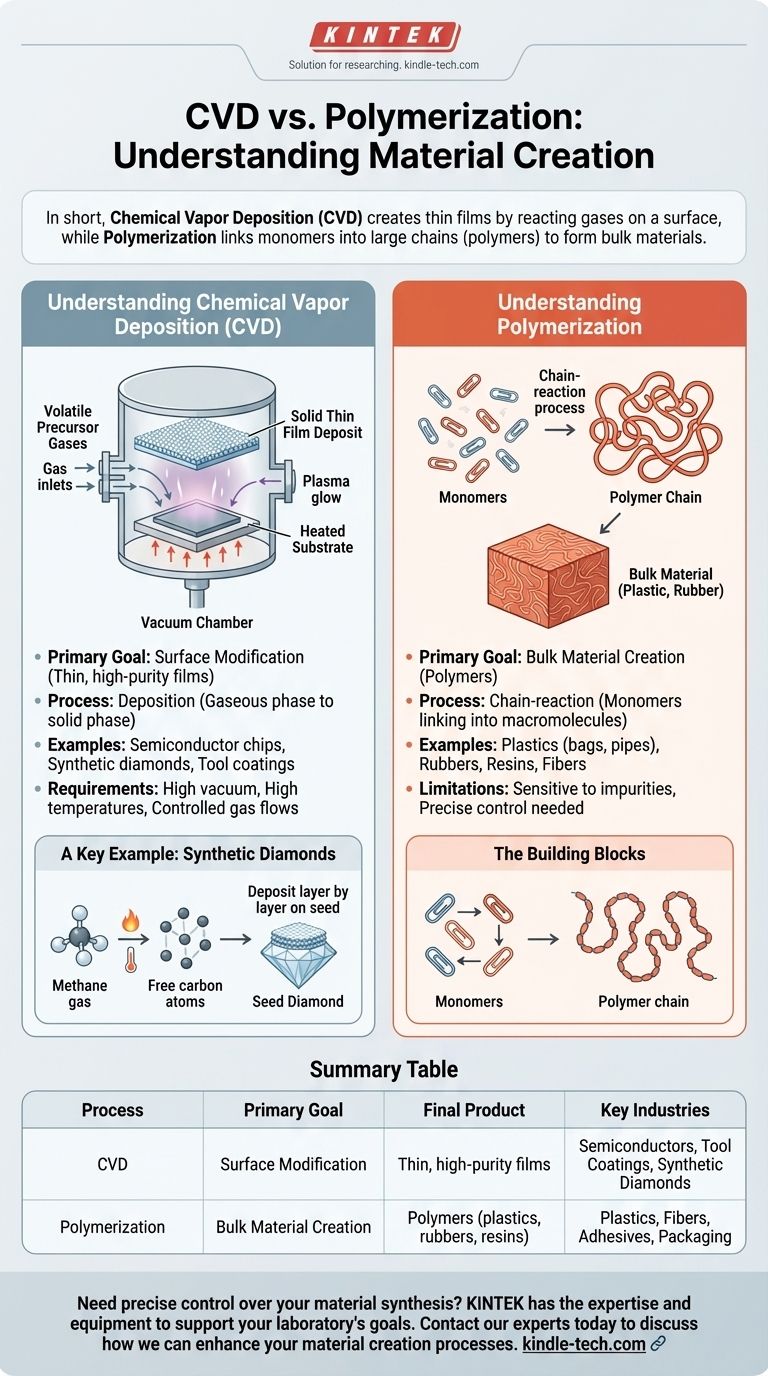
Understanding Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a highly controlled method used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. It is a cornerstone of industries like semiconductor manufacturing and synthetic gem creation.
The Core Mechanism
The process begins by introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a vacuum chamber. These gases contain the elements you want to deposit.
Inside the chamber, a substrate (the material to be coated) is heated. This high temperature provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction among the gas molecules.
As the gases react, a solid material is produced and deposits onto the substrate, forming a thin, uniform film.
A Key Example: Synthetic Diamonds
CVD is famously used to create lab-grown diamonds. A vacuum chamber is filled with a carbon-rich gas, like methane.
This gas is then heated and ionized, breaking it down and freeing carbon atoms.
These carbon atoms slowly deposit onto a small "seed" diamond, meticulously arranging themselves into the crystal lattice and growing a larger, pure diamond layer by layer.
Understanding Polymerization
Polymerization is a process that forms the basis for nearly all plastics, rubbers, and resins we use today. It's about building big things from small, repeating units.
The Building Blocks: Monomers and Polymers
The process starts with monomers, which are small, simple molecules. Think of them as individual paper clips.
A chemical reaction is initiated, causing these monomers to link together in a repeating chain. This process of linking is polymerization.
The resulting large molecule, made of many repeating monomer units, is called a polymer. This is the long chain you get after linking all the paper clips together.
The Result: Bulk Materials
Unlike CVD, which creates a thin film on a surface, polymerization typically creates a bulk material. The long polymer chains entangle and interact to form a solid or viscous liquid with unique properties like elasticity or strength.
Common examples of materials made through polymerization include polyethylene (plastic bags), PVC (pipes), and nylon (fabric).
The Critical Distinctions and Limitations
While both are methods for creating materials, their goals, processes, and outputs are fundamentally different. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating their specific applications.
Goal: Surface vs. Substance
The primary goal of CVD is to modify a surface by adding a thin, highly controlled film. The bulk properties of the original substrate remain.
The goal of polymerization is to create an entirely new bulk material. The final substance is composed entirely of the polymers that were formed.
Process: Deposition vs. Chain Reaction
CVD is a deposition process. Material is transferred from a gaseous phase to a solid phase on a surface.
Polymerization is a chain-reaction or step-growth process. The reaction happens throughout a volume of monomers, linking them together into macromolecules.
Limitations and Requirements
CVD typically requires a high vacuum, high temperatures, and precisely controlled gas flows, making the equipment complex and expensive. The deposition rates can also be quite slow.
Polymerization reactions can be highly sensitive to impurities, which can halt the process. Controlling the length of the polymer chains, which dictates the material's properties, requires precise control over temperature, pressure, and catalysts.
How to Think About These Processes
To determine which process is relevant, consider the final state of the desired material.
- If your primary focus is creating an ultra-pure thin film or a crystalline coating on a substrate: You are in the realm of CVD. This is for applications like semiconductor chips, protective tool coatings, and synthetic diamonds.
- If your primary focus is creating a bulk material from small molecular building blocks: You are talking about polymerization. This is the foundation for creating plastics, fibers, adhesives, and rubbers.
Ultimately, these two processes represent distinct and powerful strategies for engineering materials from the molecular level up.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Final Product | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Surface Modification | Thin, high-purity films | Semiconductors, Tool Coatings, Synthetic Diamonds |
| Polymerization | Bulk Material Creation | Polymers (plastics, rubbers, resins) | Plastics, Fibers, Adhesives, Packaging |
Need precise control over your material synthesis?
Whether your work requires high-purity thin films via CVD techniques or specialized polymer development, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory's goals. We specialize in providing the right solutions for semiconductor, research, and industrial applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your material creation processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















