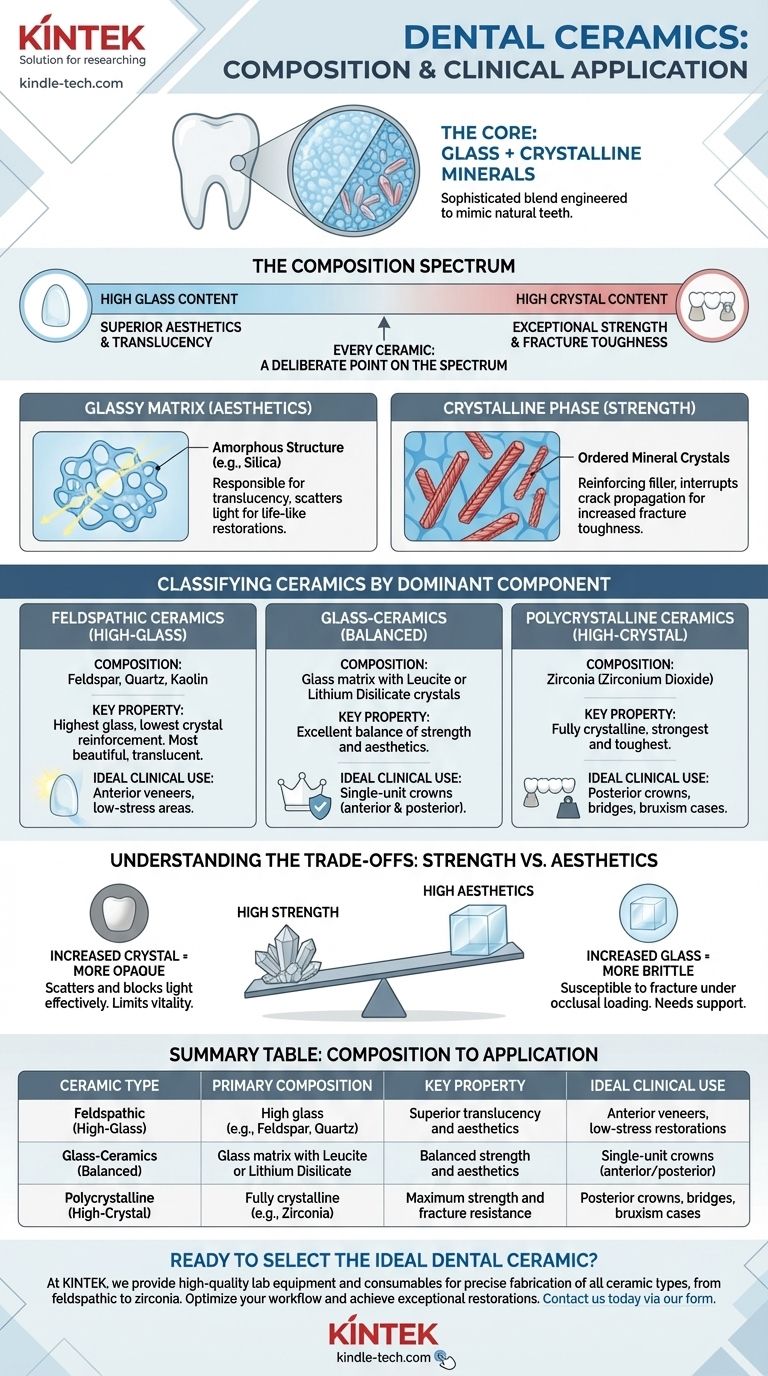
At their core, dental ceramics are a sophisticated blend of glass and crystalline minerals. This composition is precisely engineered to mimic the optical and mechanical properties of natural teeth. However, the specific ratio and type of these components vary dramatically depending on the ceramic's intended clinical use, from a delicate anterior veneer to a robust multi-unit bridge.
The key to understanding dental ceramics is to see their composition as a spectrum. At one end, a high glass content provides superior aesthetics and translucency. At the other, a high crystalline content, like zirconia, provides exceptional strength at the cost of that translucency. Every modern ceramic represents a deliberate point on this spectrum.
The Two-Part System: Glass and Crystal
Virtually all dental ceramics are composites, but on a microscopic scale. They combine a glass matrix with a crystalline filler, and the balance between these two phases dictates the final material properties.
The Glassy Matrix: The Key to Aesthetics
The glass phase is an amorphous, non-crystalline structure, typically based on silicon dioxide (silica). This matrix is responsible for the material's translucency.
It acts as a transparent medium that allows light to pass through and scatter in a way that closely resembles natural tooth enamel, making it indispensable for life-like restorations.
The Crystalline Phase: The Source of Strength
Dispersed within the glassy matrix are various types of ordered mineral crystals. These crystals function as a reinforcing filler.
Think of them as the rebar in concrete. Their primary role is to interrupt crack propagation, which dramatically increases the material's fracture toughness and overall strength. The type and amount of crystal define the ceramic's classification and strength profile.
Classifying Ceramics by Their Dominant Component
Dental ceramics are best understood by their primary crystalline content, which directly correlates to their strength and ideal application.
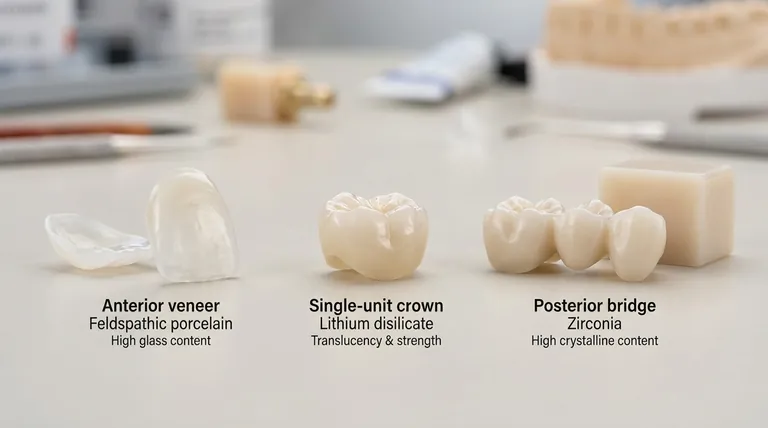
Feldspathic Ceramics (High-Glass)
These are the traditional dental porcelains, composed primarily of feldspar, quartz (silica), and kaolin.
With the highest glass content and lowest crystal reinforcement, they are the most beautiful and translucent of all ceramics. This makes them ideal for anterior veneers, but their relative weakness restricts their use in high-stress areas.
Glass-Ceramics (Balanced)
This broad category represents a significant step up in strength by increasing the volume of crystalline fillers.
Materials like leucite-reinforced ceramics and, most notably, lithium disilicate (e.g., IPS e.max), contain a higher density of strong crystals within the glass matrix. This creates an excellent balance of strength and aesthetics, making them a go-to material for single-unit crowns in any part of the mouth.
Polycrystalline Ceramics (High-Crystal)
This class is dominated by zirconia (zirconium dioxide). It is unique because it is a fully crystalline material with little to no intervening glass phase.
This composition makes zirconia the strongest and toughest dental ceramic available. Its exceptional resistance to fracture makes it the material of choice for posterior crowns, long-span bridges, and cases involving patients with heavy biting forces (bruxism).
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Aesthetics
The choice of a ceramic is never without compromise. The fundamental relationship between the glass and crystal phases creates an inherent trade-off.
The Opacity of Strength
As the crystalline content increases to boost strength, the material becomes more opaque. The dense, ordered structure of the crystals scatters and blocks light more effectively than a glassy matrix.
Early forms of zirconia were very opaque and chalky, limiting their use to posterior teeth or as substructures. While modern "translucent" zirconias have improved, they still do not fully replicate the vitality of high-glass ceramics.
The Brittleness of Beauty
Conversely, materials prized for their beauty are inherently more brittle. The high proportion of glass in feldspathic porcelain makes it susceptible to fracture under occlusal loading.
This is why these materials are often restricted to non-stress-bearing applications or must be bonded to a stronger underlying tooth structure that provides support.
Matching Composition to Clinical Goal
The ideal ceramic does not exist; the optimal choice is always dictated by the specific mechanical and aesthetic demands of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics for an anterior veneer: A high-glass feldspathic porcelain or a high-translucency lithium disilicate offers the most natural and vital appearance.
- If you need a versatile balance of strength and beauty for a single crown: Lithium disilicate provides a reliable, strong, and highly aesthetic solution for both anterior and posterior applications.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength for a posterior bridge or a patient with bruxism: A monolithic restoration milled from a high-strength zirconia block is the most durable and predictable option.
Understanding the fundamental composition of these materials empowers you to move beyond brand names and make predictable, evidence-based clinical decisions.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Primary Composition | Key Property | Ideal Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feldspathic (High-Glass) | High glass content (e.g., feldspar, quartz) | Superior translucency and aesthetics | Anterior veneers, low-stress restorations |
| Glass-Ceramics (Balanced) | Glass matrix with leucite or lithium disilicate crystals | Balanced strength and aesthetics | Single-unit crowns (anterior/posterior) |
| Polycrystalline (High-Crystal) | Fully crystalline (e.g., zirconia) | Maximum strength and fracture resistance | Posterior crowns, bridges, bruxism cases |
Ready to select the ideal dental ceramic for your practice?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to dental laboratories. Whether you're working with delicate feldspathic porcelain or high-strength zirconia, our products support precise fabrication and consistent results.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can help you optimize your ceramic workflows and achieve exceptional restorations for your clients.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the firing temperature of dental porcelain? A Guide to Classes from Ultra-Low to High-Fusing
- What is the difference between dental ceramic and dental porcelain? Choosing the Right Material for Your Restoration
- What does a dental furnace do? Achieve Perfect, Lifelike Dental Restorations
- What is the advantage of firing porcelain in a vacuum? Achieve Denser, Stronger, and More Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- How long does it take to sinter zirconia? A Guide to Optimizing Your Sintering Cycle
- What is a crucial factor to consider when selecting a Dental Press Furnace? Material Compatibility is Key
- Can ceramic crowns be repaired? A Dentist's Guide to Assessing the Damage
- What are the 3 types of materials used for all-ceramic restorations? Master the Aesthetics vs. Strength Trade-Off














