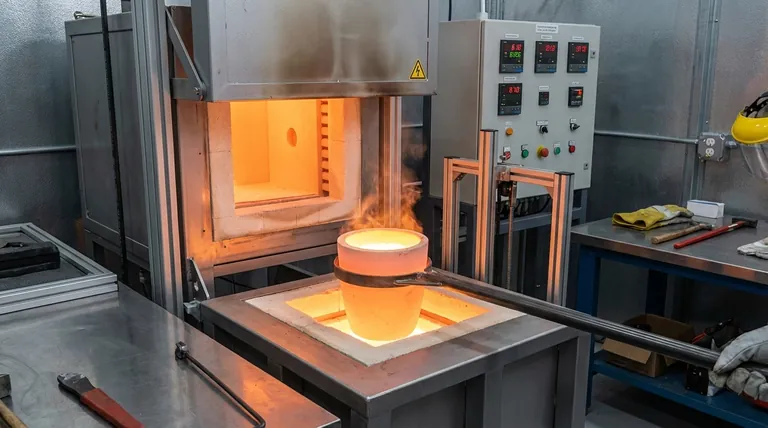
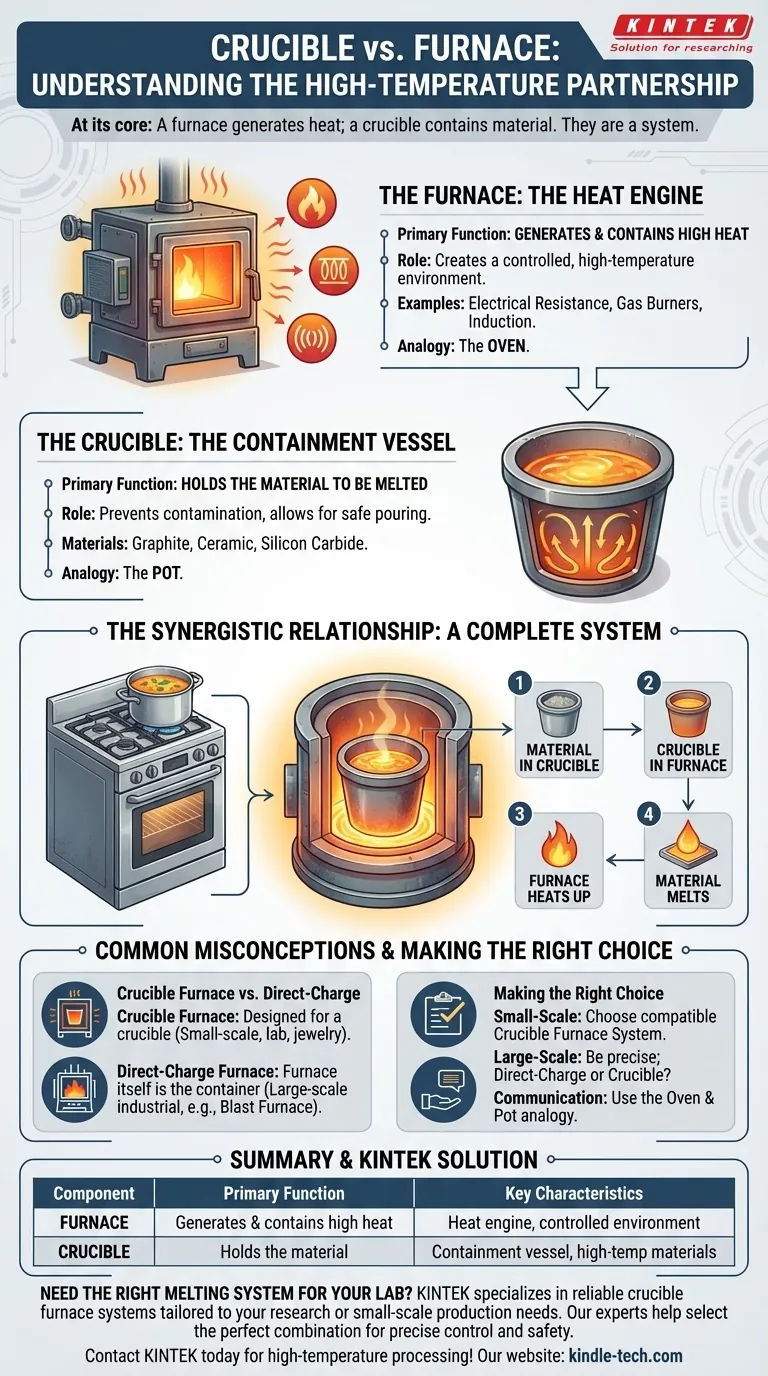
At its core, the distinction is one of function: a furnace is the equipment that generates heat, while a crucible is the pot-like container that holds the material to be melted inside the furnace. They are not alternatives to each other; rather, they work together as a system to melt materials.
The most critical takeaway is to stop thinking of a furnace and a crucible as separate choices. Instead, understand their relationship: the crucible is the vessel, and the furnace is the high-temperature environment that heats that vessel.

The Role of the Furnace: The Heat Engine
A furnace's sole purpose is to create and contain a controlled, high-temperature environment. It is the "oven" in any melting or heat-treating operation.
What Defines a Furnace?
A furnace is an enclosed structure that uses a fuel source or electrical energy to generate intense heat. Its design is focused on thermal efficiency—getting its internal chamber to a target temperature and keeping it there.
How Does It Work?
The method of heat generation varies. A furnace might use electrical resistance coils, gas burners, or electromagnetic induction to produce heat. This energy is then transferred to whatever is inside the chamber.
The Role of the Crucible: The Containment Vessel
While the furnace provides the heat, the crucible provides the safe containment for the material being heated, known as the "charge."
What Defines a Crucible?
A crucible is a container made from a material with a much higher melting point than the charge it holds, such as graphite, ceramic, or silicon carbide. It is essentially a high-performance pot designed for extreme temperatures.
Why Is It Necessary?
The crucible serves two critical functions. First, it holds the metal in its solid and liquid states. Second, it prevents the molten material from becoming contaminated by or reacting with the furnace's interior lining. It also allows for the safe pouring of the molten material once the process is complete.
The Synergistic Relationship: How They Work Together
Understanding the process clarifies the relationship instantly. The furnace and crucible are two essential parts of a single system.
Visualizing the Process
Think of cooking a soup on a stove. You would never pour the soup directly onto the burner. The burner (the furnace) provides the heat, while the pot (the crucible) contains the soup and transfers that heat to it.
A Typical Melting Operation
In a typical foundry or lab setting, the process is simple:
- The material to be melted is placed into the crucible.
- The crucible is placed inside the furnace chamber.
- The furnace is turned on, heating the chamber and, by extension, the crucible.
- The crucible absorbs the heat and transfers it to the material inside, causing it to melt.
Common Misconceptions to Avoid
The term "furnace" is sometimes used loosely, which can cause confusion. Clarifying these edge cases demonstrates a deeper understanding of the process.
Is the System Always Called a "Crucible Furnace"?
Yes, when a furnace is designed specifically to heat a crucible, it is correctly called a crucible furnace. This distinguishes it from other types.
Are There Furnaces Without Crucibles?
Yes. In very large-scale industrial operations, like a steel mill's blast furnace or an electric arc furnace, the raw material is often charged directly into a massive, refractory-lined chamber. In this case, the entire furnace body effectively acts as its own containment vessel, eliminating the need for a separate, removable crucible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this distinction is not just academic; it is fundamental to communicating clearly and working safely with high-temperature equipment.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting (jewelry, knives, art): You will be working with a crucible furnace system, and you must select a furnace and crucibles that are compatible in size and temperature rating.
- If you are discussing large industrial metallurgy: Be precise. Specify whether the process uses a crucible furnace or a direct-charge furnace (like a blast or arc furnace) to avoid misunderstanding.
- If your goal is simply clear communication: Use the oven and pot analogy. The furnace is the oven; the crucible is the heat-proof pot you put inside it.
Mastering this core concept of heat source versus containment vessel is the foundation for any work involving the transformation of materials at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace | Generates and contains high heat | Heat engine; creates a controlled, high-temperature environment |
| Crucible | Holds the material being melted | Containment vessel; made of high-temperature materials like graphite or ceramic |
Need the right melting system for your lab?
Understanding the synergy between a furnace and a crucible is key to efficient and safe material processing. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable crucible furnace systems tailored to your specific application—whether for jewelry making, research, or small-scale production.
Our experts can help you select the perfect combination of furnace and compatible crucibles to ensure precise temperature control, material integrity, and operational safety. Let us equip your lab for success.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your high-temperature processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the efficiency of a crucible furnace? A Guide to Thermal Performance & Trade-offs
- When were crucibles used? From Ancient Metallurgy to Modern Labs
- What are the advantages of using a graphite crucible? Maximize Purity and Thermal Stability in Magnesium Reduction
- What is the primary purpose of using alumina crucibles for LLTO ceramics? Optimize Your High-Temperature Sintering
- Why are high-chemical-stability ceramic crucibles essential for molten carbonate impregnation? Secure Pure Membranes
- What is the maximum temperature for clay crucibles? Find the Right Crucible for Your Melting Needs
- What are the advantages of a crucible furnace? Achieve Precision Melting for Labs & Small-Scale Production
- Why are alumina crucibles used for LLZO calcination? Optimize Cubic Phase Stability and Thermal Resilience



















