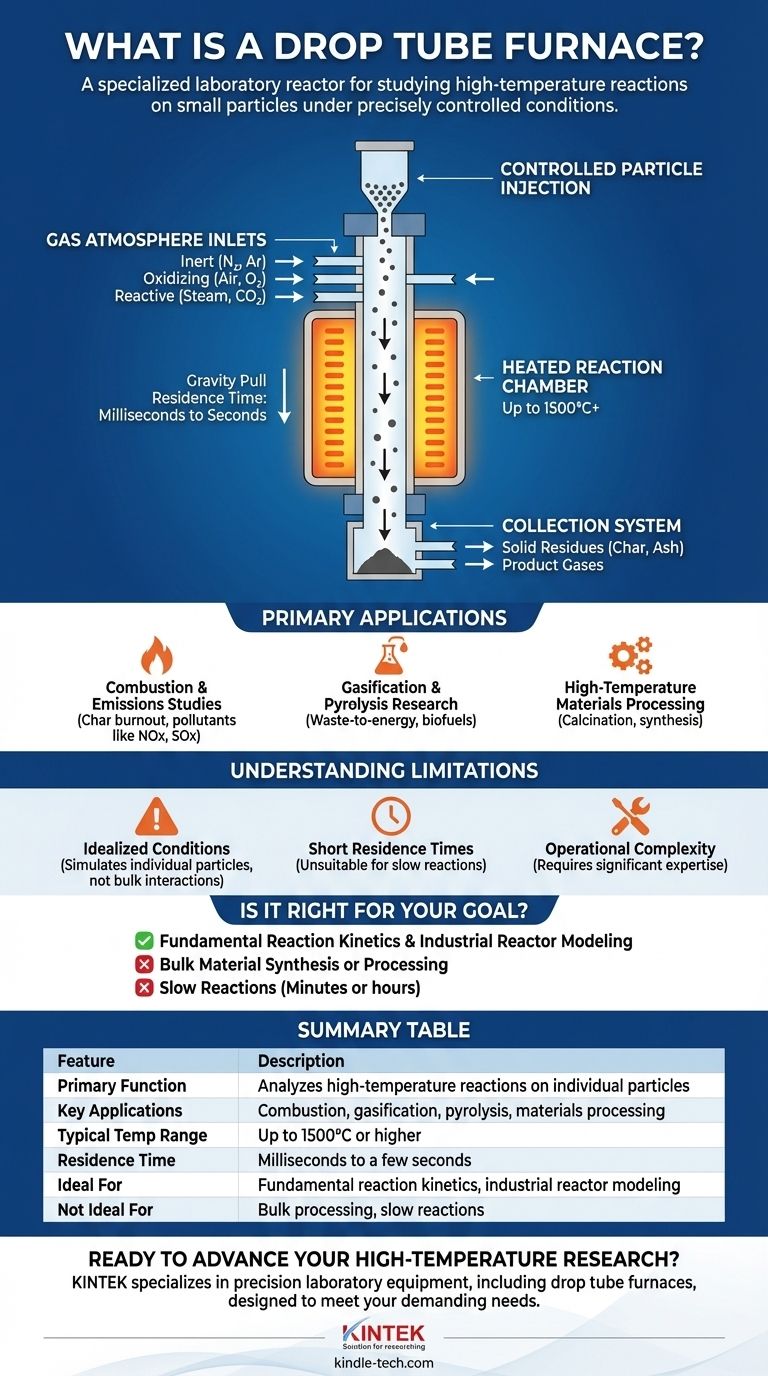
At its core, a drop tube furnace (DTF) is a specialized laboratory reactor designed to study high-temperature reactions on small particles under precisely controlled conditions. It consists of a vertical heated tube where solid particles are dropped from the top, allowing them to react in a specific atmosphere as they fall. This setup closely mimics the environment individual fuel particles experience inside large-scale industrial systems like power plant boilers or gasifiers.
A drop tube furnace is not for bulk processing; it is a powerful analytical tool. Its primary value is in isolating and studying the behavior of individual particles during rapid, high-temperature events like combustion or gasification, providing data that is essential for designing and optimizing large-scale industrial reactors.

How a Drop Tube Furnace Works
A DTF is an assembly of precision components, each serving a critical function in simulating a high-temperature reactive environment. Understanding its operation reveals why it is so valuable for specific types of research.
The Vertical Reaction Chamber
The heart of the system is a vertically oriented tube, typically made of alumina or another high-performance ceramic, capable of withstanding extreme temperatures (often up to 1500°C or higher).
This tube is surrounded by multiple, independently controlled heating elements. This allows researchers to create a uniform temperature zone or a specific temperature profile along the length of the furnace.
Controlled Particle Injection
At the top of the furnace, a sophisticated feeder mechanism introduces a very small, steady stream of powdered or granular sample material into the reaction tube. The feed rate is precisely metered to ensure repeatable experimental conditions.
Simulating the Environment: Gas Atmosphere
Gas inlets allow for the precise control of the gaseous environment inside the tube. This could be an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) for pyrolysis studies, an oxidizing atmosphere (air or enriched oxygen) for combustion, or a reactive gas mixture (like steam and CO₂) for gasification.
The Reaction and Collection
Gravity pulls the particles through the heated zone. The time the particles spend in this zone, known as the residence time, is typically very short—from milliseconds to a few seconds.
At the bottom of the furnace, a collection system rapidly cools and captures both the solid residues (like char or ash) and the product gases for subsequent analysis.
Primary Applications: Bridging Lab Research and Industrial Reality
The DTF's ability to replicate the conditions of a single particle in a massive reactor makes it an indispensable tool for engineers and scientists.
Combustion and Emissions Studies
The primary use of a DTF is to study the combustion of solid fuels like pulverized coal and biomass. It allows researchers to measure key parameters like char burnout rates, ignition behavior, and the formation of pollutants such as NOx and SOx under controlled conditions.
Gasification and Pyrolysis Research
By changing the gas atmosphere to be oxygen-free, researchers use the DTF to investigate pyrolysis (thermal decomposition) and gasification. This research is vital for developing advanced waste-to-energy and biofuel technologies.
High-Temperature Materials Processing
The DTF is also used in materials science for processes like the calcination of minerals, the roasting of ores, and the synthesis of advanced ceramic powders. The controlled atmosphere and temperature profile are key to achieving desired material properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a drop tube furnace is a specialized instrument with specific limitations that are critical to understand.
Idealized Conditions vs. Industrial Complexity
A DTF studies the behavior of dispersed, individual particles. It cannot replicate the complex fluid dynamics, particle-particle interactions, or heat transfer from surrounding particles that occur in a densely packed industrial fluid bed or boiler.
Short and Inflexible Residence Times
The residence time is governed by gravity and particle characteristics, making it inherently short and difficult to extend significantly. Therefore, a DTF is unsuitable for studying slow reactions that take many seconds, minutes, or hours to complete.
Operational Complexity
Operating a DTF and its associated analytical equipment (like gas chromatographs or mass spectrometers) requires significant technical expertise. It is a complex research apparatus, not a simple benchtop furnace.
Is a Drop Tube Furnace the Right Tool for Your Goal?
To make an informed decision, align the furnace's capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is on fundamental reaction kinetics: A DTF is the ideal instrument for studying fast, high-temperature reactions on a single-particle level.
- If your primary focus is to simulate industrial solid fuel combustion or gasification: A DTF is an essential tool for generating the data needed to model and optimize large-scale boilers and gasifiers.
- If your primary focus is bulk material synthesis or processing: A DTF is not a production tool; you should consider a rotary kiln, belt furnace, or batch furnace instead.
- If your primary focus is on slow reactions over minutes or hours: A thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) or a standard muffle furnace is a more appropriate choice.
Understanding its role as a precise analytical instrument is the key to leveraging its unique capabilities for your research.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Analyzes high-temperature reactions on individual particles |
| Key Applications | Combustion, gasification, pyrolysis, materials processing |
| Typical Temperature Range | Up to 1500°C or higher |
| Residence Time | Milliseconds to a few seconds |
| Ideal For | Fundamental reaction kinetics, industrial reactor modeling |
| Not Ideal For | Bulk processing, slow reactions (minutes/hours) |
Ready to advance your high-temperature research?
KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory equipment, including drop tube furnaces, designed to meet the demanding needs of researchers studying combustion, gasification, and materials science. Our expertise ensures you get the right analytical tool to generate the critical data needed for your projects.
Let's discuss how a drop tube furnace can power your research. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification



















