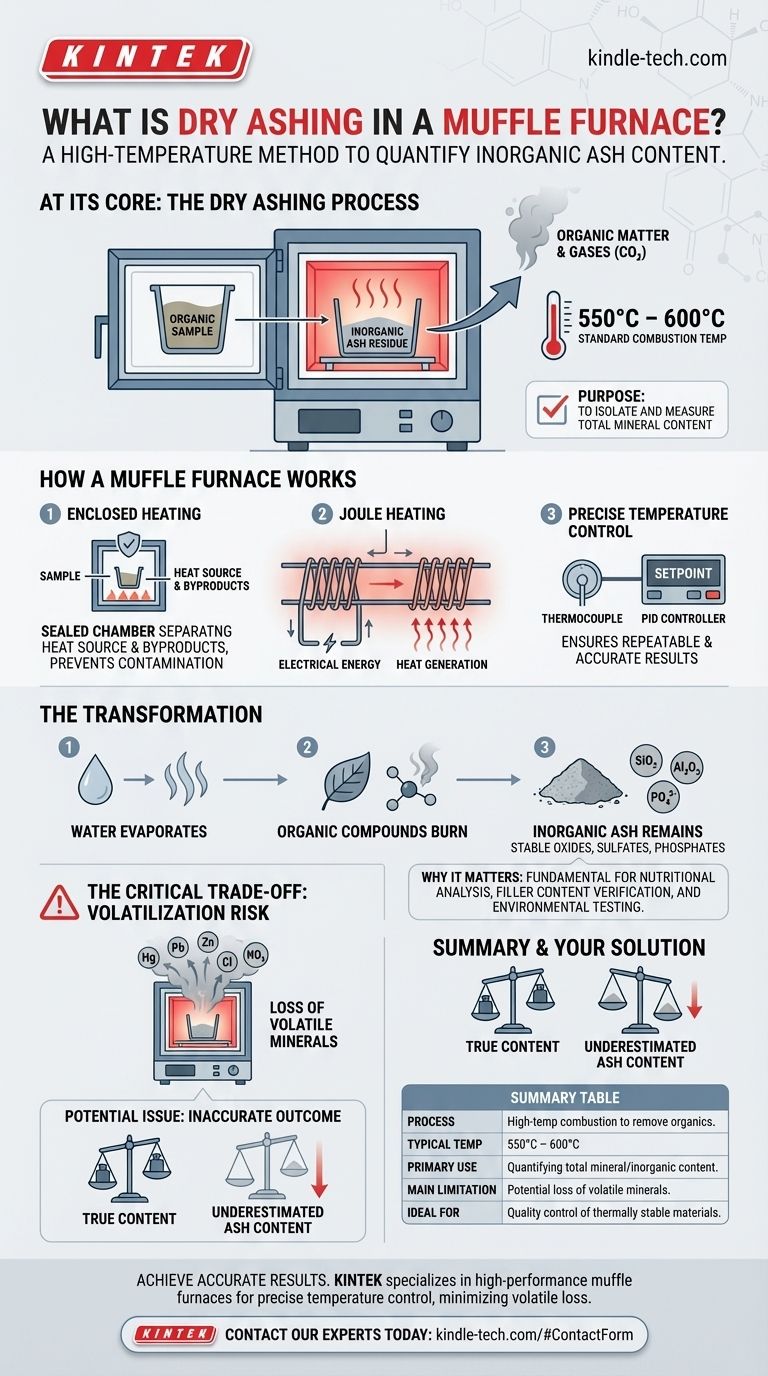
At its core, dry ashing is a high-temperature combustion method used to remove all organic matter from a sample, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue known as ash. This process is performed in a muffle furnace, a specialized oven that can reach and maintain the very high temperatures required, typically between 550°C and 600°C, to ensure complete combustion.
Dry ashing is the standard technique for quantifying the total mineral (inorganic) content of a sample. However, its accuracy hinges on a critical trade-off: the high temperatures necessary for combustion can also cause certain volatile minerals to be lost, potentially skewing the results.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
A muffle furnace is not simply a high-temperature oven; its design is critical for achieving a clean and controlled analysis.
The Principle of Enclosed Heating
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's design, which separates the sample being heated from the byproducts of the heat source. In modern electric furnaces, this means the sample sits inside a refractory chamber that is heated externally by electric coils.
This separation prevents any contamination and ensures the only chemical reaction occurring is the combustion of the sample itself.
Achieving and Controlling High Temperatures
A muffle furnace converts electrical energy into heat via Joule heating, where current is passed through high-resistance heating elements.
These elements, often made of materials like Nichrome, heat the chamber through radiation and convection. A thermocouple measures the internal temperature, which is regulated by a PID controller to maintain a precise setpoint. This control is essential for repeatable and accurate ashing procedures.
The Purpose of Dry Ashing
The goal of this process is to isolate and quantify the non-organic components of a substance.
The Transformation Process
When a sample is heated in the furnace, any water is the first thing to evaporate. As the temperature rises, all organic compounds (those containing carbon) are burned away, reacting with oxygen in the air to form gases like carbon dioxide.
The remaining material is the ash, which consists of stable inorganic compounds such as oxides, sulfates, and phosphates. The weight of this ash relative to the original sample weight gives you the total ash content.
Why Ash Content Matters
Measuring ash content is a fundamental quality control and analytical procedure in many fields. It serves as a direct measure of the total mineral content in a sample.
This is critical for nutritional analysis in food, verifying filler content in polymers and rubbers, and for geological or environmental testing.
Understanding the Key Limitation
While effective, dry ashing is not a perfect method for all scenarios. Its primary drawback is a direct consequence of the high temperatures it uses.
The Risk of Volatilization
The most significant limitation of dry ashing is the potential for loss of volatile minerals.
Elements like mercury, lead, and zinc, as well as certain mineral salts like chlorides and nitrates, can turn into vapor at the high temperatures used in the furnace (550-900°C). When these minerals volatilize, they are lost along with the combusted organic matter.
This leads to an inaccurate outcome, specifically an underestimation of the sample's true total mineral content. The final ash weight will be lower than it should be because these elements have escaped.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of dry ashing depends entirely on your material and your analytical objectives.
- If your primary focus is a general quality check on thermally stable materials (like polymers or rubber): Dry ashing is a reliable, efficient, and straightforward method for determining the total inorganic filler content.
- If your primary focus is precise elemental analysis, especially for samples with potentially volatile minerals (common in food or environmental testing): You must account for the potential loss of these elements and understand that dry ashing may provide an incomplete mineral profile.
Ultimately, recognizing the principles and inherent limitations of dry ashing is the first step toward achieving accurate and meaningful analytical results.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature combustion to remove organic matter, leaving inorganic ash. |
| Typical Temperature | 550°C to 600°C. |
| Primary Use | Quantifying total mineral/inorganic content in a sample. |
| Main Limitation | Potential loss of volatile minerals (e.g., lead, zinc), leading to underestimation. |
| Ideal For | Quality control of thermally stable materials like polymers and rubbers. |
Achieve accurate and reliable results in your lab.
Dry ashing is a fundamental technique, but its success depends on using the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces and lab consumables designed for precise temperature control and repeatable analysis, helping you avoid the pitfalls of volatile mineral loss.
Whether you're in food science, materials testing, or environmental analysis, our solutions are built to meet your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application and ensure the integrity of your data.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a high-temperature muffle furnace? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- What is the difference between electric oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right High-Temp Lab Equipment
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food analysis? Master Ashing for Accurate Mineral Content



















