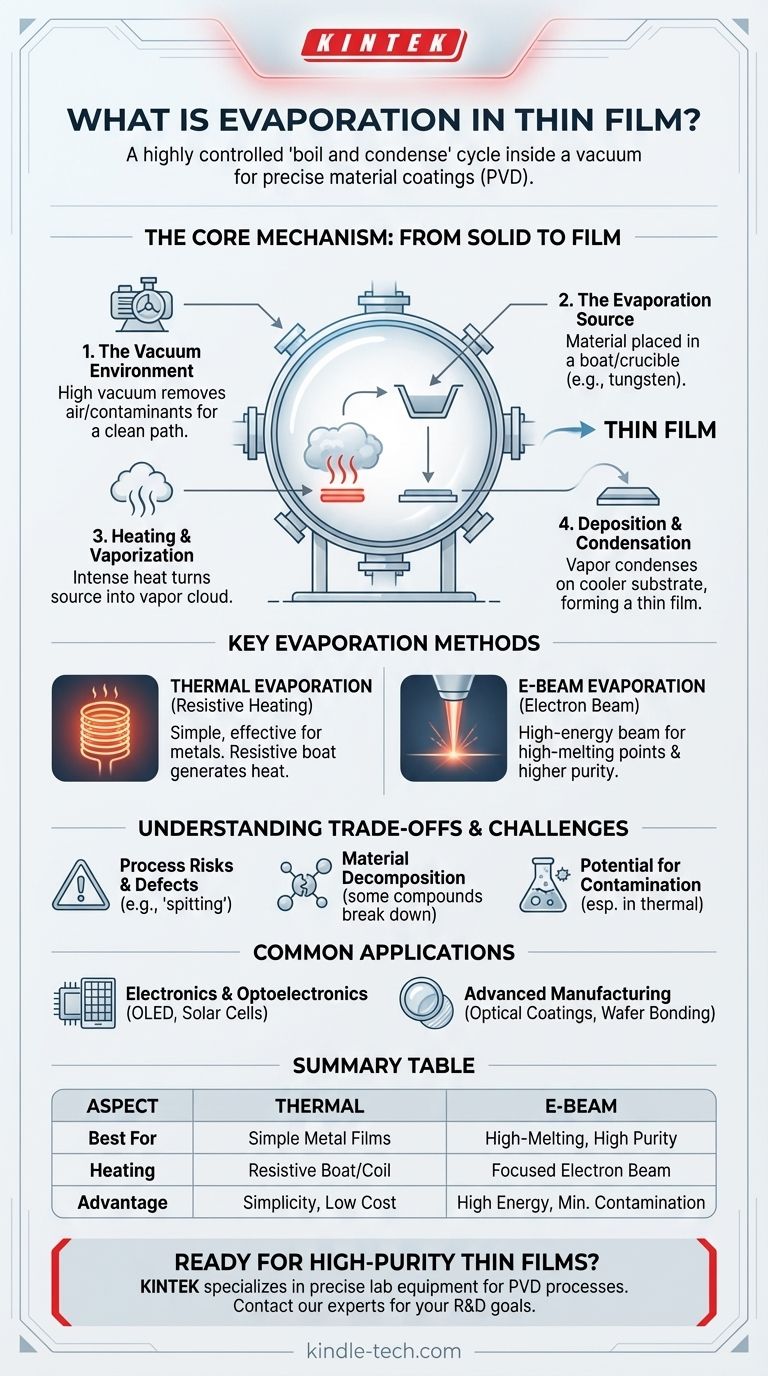
In essence, thin-film evaporation is a manufacturing process that functions like a highly controlled "boil and condense" cycle inside a vacuum. A source material is heated until it turns into a vapor, which then travels and coats a target surface (called a substrate), condensing back into an ultra-thin solid layer. This technique is a fundamental type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) used to create precise material coatings.
Evaporation is a direct method for creating high-purity thin films by vaporizing a source material in a vacuum. The core decision in this process lies in choosing the heating method—either simple resistive heating for common materials or a high-energy electron beam for more demanding applications.
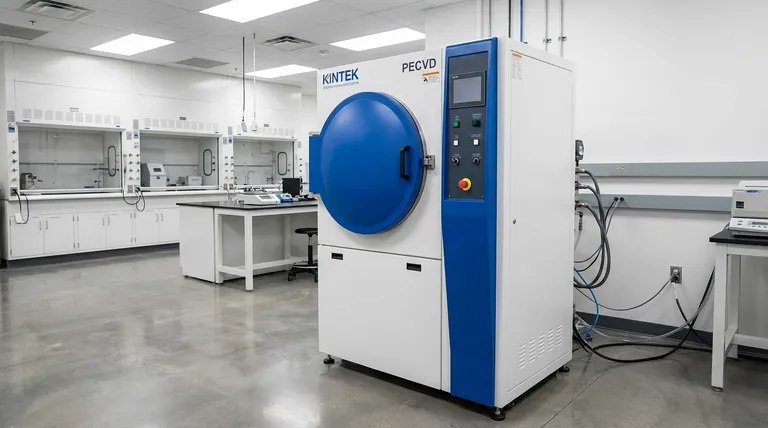

The Core Mechanism: From Solid to Film
To understand evaporation, it's best to break it down into its essential stages. Each step is critical for achieving a high-quality, uniform film.
The Vacuum Environment
A high vacuum (a very low-pressure environment) is the first requirement. This is crucial because it removes air and other particles that could contaminate the film or impede the vapor's path from the source to the substrate.
The Evaporation Source
The material intended for the coating, known as the source material, is placed in a crucible or a holder often called a "boat" or "basket." These holders are made from materials like tungsten that can withstand extreme temperatures.
The Heating and Vaporization
The source material is heated intensely until it evaporates (or sublimates, going directly from solid to gas). This creates a cloud of vapor within the vacuum chamber. The method of heating is the primary distinction between different evaporation techniques.
Deposition and Condensation
The vaporized particles travel in a straight line through the vacuum until they strike the cooler substrate. Upon contact, they rapidly lose energy, condense back into a solid state, and gradually build up to form the desired thin film.
Key Evaporation Methods
While the principle remains the same, the method used to generate the heat defines the process and its capabilities.
Thermal Evaporation (Resistive Heating)
This is the most straightforward method. An electric current is passed through the resistive boat or coil holding the source material. The resistance generates intense heat, causing the material to evaporate. It is simple, effective, and widely used for depositing pure metals and various non-metals.
Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
In this more advanced technique, a high-energy beam of electrons is magnetically guided to strike the source material. This delivers a massive amount of focused energy, making it ideal for materials with very high melting points that are difficult to vaporize with resistive heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Evaporation is a powerful technique, but it is not without its limitations. Understanding them is key to successful implementation.
Simplicity vs. Control
Thermal evaporation is valued for its simplicity and relatively low cost. However, precisely controlling the deposition rate and ensuring perfect film uniformity can be more challenging compared to other PVD methods like sputtering.
Material Decomposition
Not all materials can be evaporated cleanly. Some compounds can decompose or break down into their constituent elements when heated. This means the resulting film may not have the same chemical composition as the source material.
Process Risks and Defects
Overloading a source boat or heating the material too quickly can cause "spitting," where small solid chunks are ejected along with the vapor. These particles create significant defects in the final film.
Potential for Contamination
In resistive thermal evaporation, there is a small risk that the boat material itself can evaporate and contaminate the film. E-beam evaporation avoids this, as the electron beam only heats the source material, not the crucible holding it.
Common Applications of Evaporation
The ability to create high-purity thin layers makes evaporation a critical process in high-tech manufacturing.
Electronics and Optoelectronics
Evaporation is essential for creating the electrically conductive metallic layers in devices like OLED displays, solar cells, and thin-film transistors. The purity of the deposited film is critical for device performance.
Advanced Manufacturing
The technique is also used for more specialized tasks, such as depositing thick layers of indium for wafer bonding in the semiconductor industry or applying optical coatings on glass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine which evaporation method is most suitable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for simple metal films: Resistive thermal evaporation is often the most direct and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-melting-point or ceramic materials: E-beam evaporation provides the necessary energy density to vaporize these demanding sources effectively.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity: E-beam evaporation is superior, as it minimizes contamination from the heating apparatus.
Ultimately, mastering thin-film deposition by evaporation comes down to controlling the fundamental principles of heat, vacuum, and material behavior to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Cost-effective, simple metal films | High-melting-point materials, highest purity |
| Heating Method | Resistive heating (boat/coil) | Focused electron beam |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity, lower cost | High energy, minimal contamination |
| Consideration | Potential for boat contamination | Higher complexity and cost |
Ready to achieve high-purity thin films for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for evaporation and other Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes. Whether you're working on next-generation electronics, solar cells, or optical coatings, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for high-performance results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and how we can support your R&D and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing



















