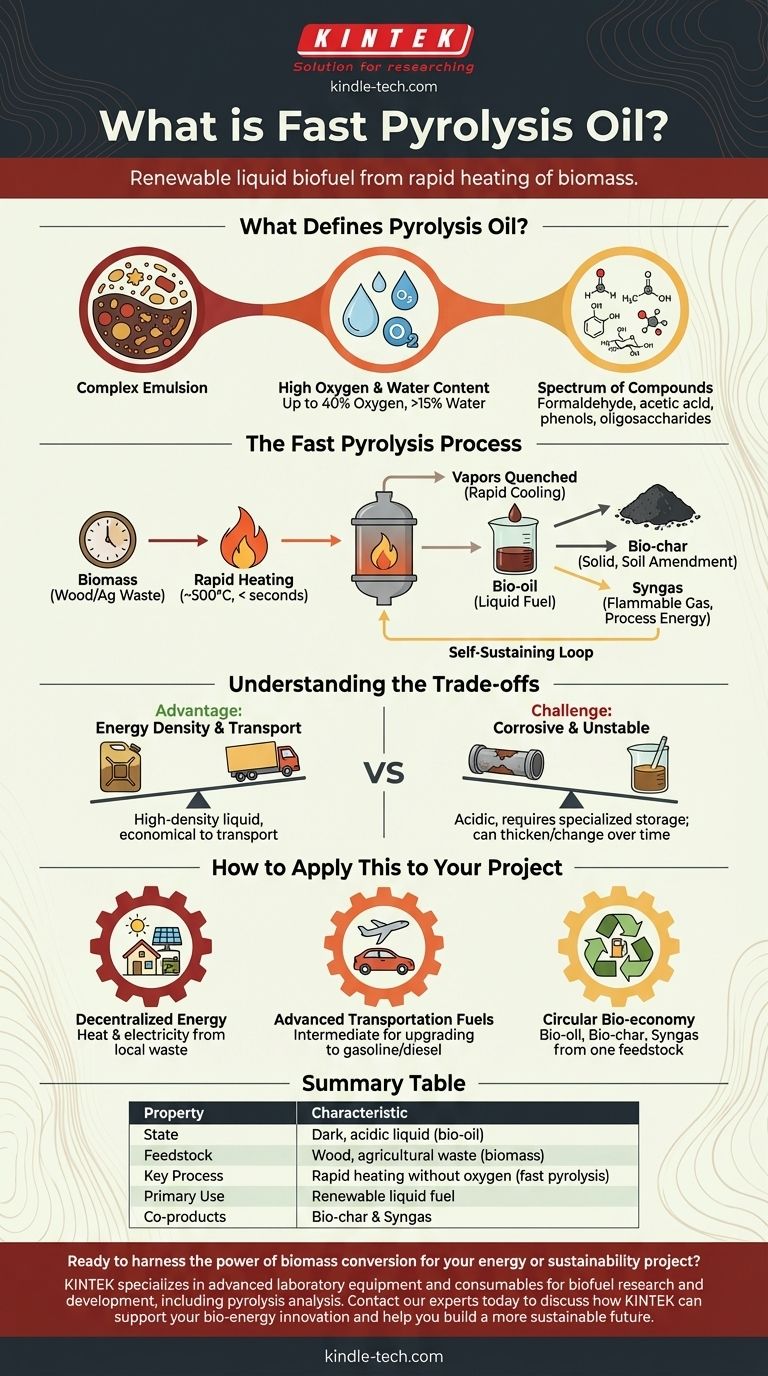
In short, fast pyrolysis oil is a renewable liquid biofuel, also known as bio-oil, created by rapidly heating organic materials like wood or agricultural waste in the absence of oxygen. It is a complex, dark, acidic liquid composed of hundreds of different oxygenated organic compounds, polymers, and a significant amount of water.
The core value of fast pyrolysis is its ability to convert bulky, solid biomass into a dense, liquid fuel that is far easier to transport and store. However, the resulting bio-oil is chemically distinct from conventional petroleum and requires understanding of its unique properties to be used effectively.

What Defines Pyrolysis Oil?
A Complex Chemical Emulsion
Fast pyrolysis oil is not a simple substance but a micro-emulsion. It's a dense mixture of water, polymers derived from cellulose and lignin, and a wide array of other oxygenated organic compounds.
High Oxygen and Water Content
A defining characteristic is its high oxygen content, which can be up to 40% by weight. This is fundamentally different from petroleum fuels, which contain almost no oxygen.
It also contains a notable amount of water, often greater than 15% by weight, which is present from the original biomass and created during the pyrolysis reaction.
A Spectrum of Compounds
The chemical makeup is incredibly varied. It includes low molecular weight compounds like formaldehyde and acetic acid, which contribute to its acidity, alongside high molecular weight substances like phenols and oligosaccharides.
The Fast Pyrolysis Process Explained
How It Works: Rapid Heating, No Oxygen
Fast pyrolysis involves heating biomass to around 500°C in a reactor without oxygen. The key is the speed; the material is heated extremely quickly (in seconds), which vaporizes the biomass before it can char completely.
These vapors are then rapidly cooled, or "quenched," which condenses them into the liquid product known as bio-oil.
A "Whole Biomass" Solution
A major advantage of this process is its efficiency in using the feedstock. All components of the biomass are converted into useful products, minimizing waste.
The Full Product Suite: Oil, Char, and Gas
The main output is bio-oil, but two other valuable co-products are created:
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal that can be used to amend soil or as a feedstock for activated carbon.
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases (methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide) that can be captured.
The Self-Sustaining Loop
The syngas produced during the process can be circled back and burned to provide the heat required for the reactor. This makes the entire fast pyrolysis process highly energy-efficient and potentially self-sustaining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Advantage: Energy Density and Transport
The most significant advantage is logistical. Converting low-density, dispersed biomass into a high-density liquid makes it economically viable to transport the energy from its source (a farm or forest) to a central processing facility.
Challenge: Corrosive and Acidic Nature
The presence of acetic acid and other organic acids makes bio-oil corrosive to many common metals. This means specialized containers and engine components are required for storage and use, preventing it from being a simple "drop-in" replacement for diesel or fuel oil.
Challenge: Chemical Instability
The complex mixture of reactive compounds means that bio-oil can thicken and change over time, especially when heated. It often requires stabilization or further processing, known as "upgrading," to be converted into a more stable transportation fuel like gasoline or diesel.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding the nature of fast pyrolysis oil is the first step to leveraging its potential. Your approach should depend entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is decentralized energy: Fast pyrolysis is an excellent method for converting local biomass waste into a burnable liquid for heating or electricity generation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is advanced transportation fuels: View bio-oil as a crucial intermediate product. The real work involves the subsequent upgrading and refining processes needed to turn it into a stable, high-performance fuel.
- If your primary focus is a circular bio-economy: The process is ideal, as it creates three distinct value streams from a single waste feedstock: a liquid energy carrier (bio-oil), a soil enhancer (bio-char), and process energy (syngas).
By recognizing fast pyrolysis oil as a unique liquid energy carrier, you can effectively harness the value of biomass in a transportable and versatile form.
Summary Table:
| Property | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| State | Dark, acidic liquid (bio-oil) |
| Feedstock | Wood, agricultural waste (biomass) |
| Key Process | Rapid heating without oxygen (fast pyrolysis) |
| Primary Use | Renewable liquid fuel for heat, power, or chemical upgrading |
| Co-products | Bio-char (soil amendment) and Syngas (process energy) |
Ready to harness the power of biomass conversion for your energy or sustainability project?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biofuel research and development, including pyrolysis analysis. Our solutions help you accurately characterize feedstocks, optimize pyrolysis processes, and analyze bio-oil properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your bio-energy innovation and help you build a more sustainable future.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing

















