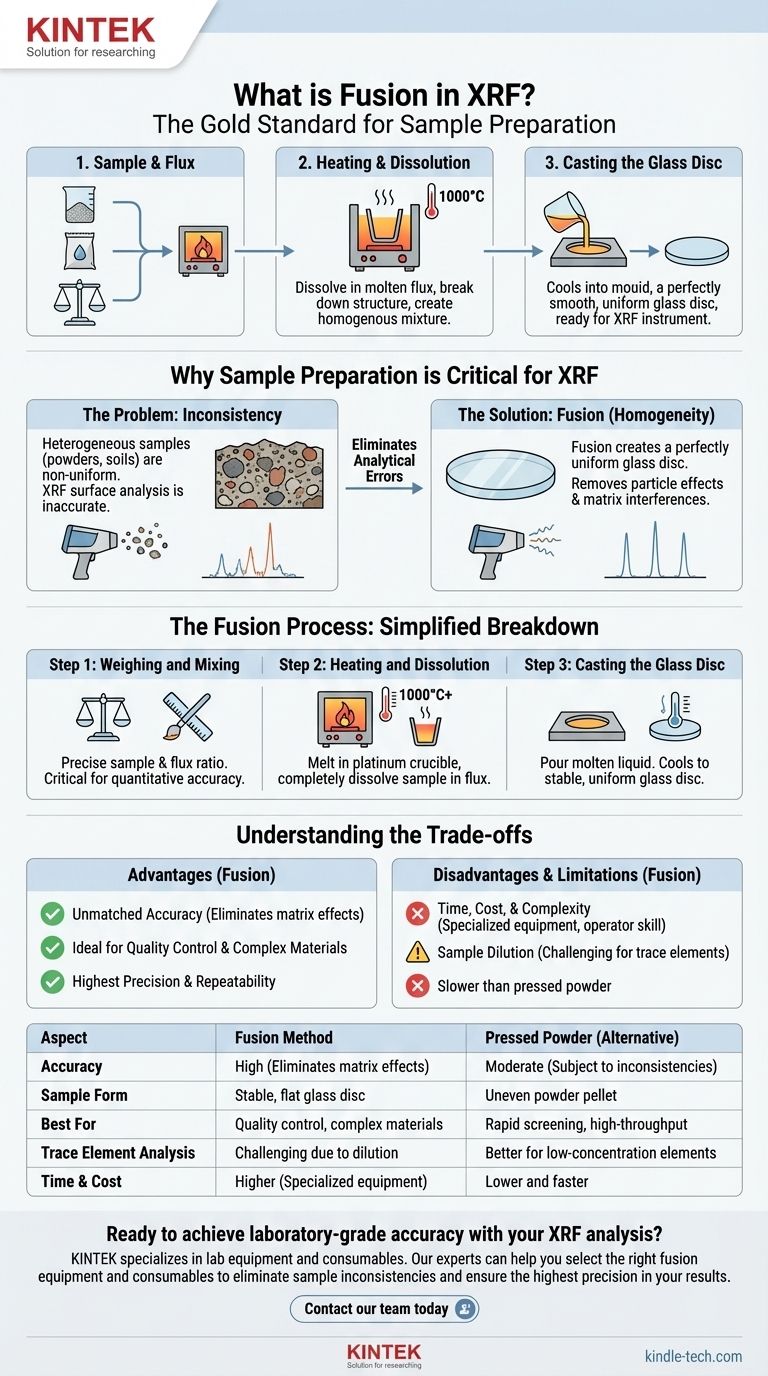
Fusion in X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is an advanced sample preparation technique. It involves dissolving a finely ground sample in a molten solvent, called a flux, at extremely high temperatures. This process breaks down the sample's original structure and chemical bonds, creating a perfectly homogenous molten mixture which is then cast into a flat, stable glass disc for analysis.
The core purpose of fusion is to eliminate analytical errors caused by the physical and chemical inconsistencies within a sample. By creating a perfectly uniform glass disc, fusion removes inaccuracies from particle size differences and inter-element interference, ensuring the highest possible precision and repeatability in XRF results.

Why Sample Preparation is Critical for XRF
X-Ray Fluorescence is a powerful analytical method, but its accuracy is fundamentally dependent on the quality of the sample presented to the instrument. The X-rays emitted by the spectrometer interact with only a very thin layer of the sample's surface.
The Problem of Inconsistency
Most raw samples, such as powders, soils, or crushed rock, are heterogeneous. This means their composition is not uniform throughout.
Analyzing an unprepared sample is like trying to understand a complex recipe by only tasting one random ingredient. The result will not represent the whole.
The Challenge of "Matrix Effects"
The way one element emits (fluoresces) X-rays can be suppressed or enhanced by the other elements surrounding it in the sample's matrix.
These "matrix effects" can severely skew results, making a low-concentration element appear even lower, or vice-versa. Fusion dissolves the sample into a known flux, which standardizes this matrix and minimizes these inter-element interferences.
Ensuring Ideal Physical Form
The XRF process relies on consistent X-ray interaction with the sample's atoms. A rough, uneven surface from a pressed powder can scatter X-rays unpredictably.
A smooth, flat, and dense glass disc created by fusion provides the ideal surface for analysis, guaranteeing that the geometric relationship between the instrument and the sample is perfect and repeatable every time.
The Fusion Process: A Simplified Breakdown
While the chemistry can be complex, the physical steps of the fusion process are straightforward and methodical.
Step 1: Weighing and Mixing
A precise amount of the oxidized sample is weighed and mixed with a specific ratio of a flux, typically a lithium borate compound. This initial step is critical for quantitative accuracy.
Step 2: Heating and Dissolution
The sample-flux mixture is placed in a crucible (often made of platinum) and heated in a furnace to temperatures exceeding 1000°C. The mixture melts, and the crucible is agitated to ensure the sample completely dissolves into the flux.
Step 3: Casting the Glass Disc
Once the solution is perfectly homogenous, the molten liquid is poured into a casting dish or mold. It cools rapidly into a solid, stable, and chemically uniform glass disc, ready for analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Fusion is often considered the gold standard for XRF sample preparation, but it is not the only method. Understanding its advantages and disadvantages is key to making an informed decision.
The Advantage: Unmatched Accuracy
Fusion is the superior method for eliminating matrix effects and sample inconsistencies. For applications requiring the highest degree of accuracy, such as in quality control, geological surveys, or cement production, it is the definitive choice.
The Disadvantage: Time, Cost, and Complexity
Compared to simply pressing a powder into a pellet, fusion is more time-consuming and requires specialized, expensive equipment like automated fusion machines and platinum crucibles. It is a more involved process requiring a higher level of operator skill.
The Limitation: Sample Dilution
Because the sample is dissolved in a flux, its original concentration is diluted. This can be a challenge when analyzing for trace elements, as their diluted concentration may fall below the detection limits of the XRF instrument.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best sample preparation method depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible accuracy and repeatability: Fusion is the correct choice, especially for complex or mineralogically diverse materials.
- If your primary focus is rapid screening or high-throughput analysis: A simpler method, such as preparing a pressed powder pellet, may be sufficient and more efficient.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for elements at very low trace levels: You must carefully consider if the dilution from fusion will compromise your ability to detect the element of interest.
Ultimately, selecting the correct sample preparation method is the foundation upon which all reliable XRF analysis is built.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Fusion Method | Pressed Powder (Alternative) |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (Eliminates matrix effects) | Moderate (Subject to inconsistencies) |
| Sample Form | Stable, flat glass disc | Uneven powder pellet |
| Best For | Quality control, complex materials | Rapid screening, high-throughput |
| Trace Element Analysis | Challenging due to dilution | Better for low-concentration elements |
| Time & Cost | Higher (specialized equipment) | Lower and faster |
Ready to achieve laboratory-grade accuracy with your XRF analysis?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right fusion equipment and consumables to eliminate sample inconsistencies and ensure the highest precision in your results.
Contact our team today to discuss how fusion can enhance your XRF workflow and deliver reliable data you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses facilitate biomass pelletization? Optimize Biofuel Density and Prevent Slagging
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized for electrolyte pelletizing? Unlock High Ionic Conductivity
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press used for LLZTO pellets? Achieve 93% Density in Solid-State Battery Research
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep
- Why is a hydraulic pellet press used for FTIR? Transform Nanofillers into Clear Data



















