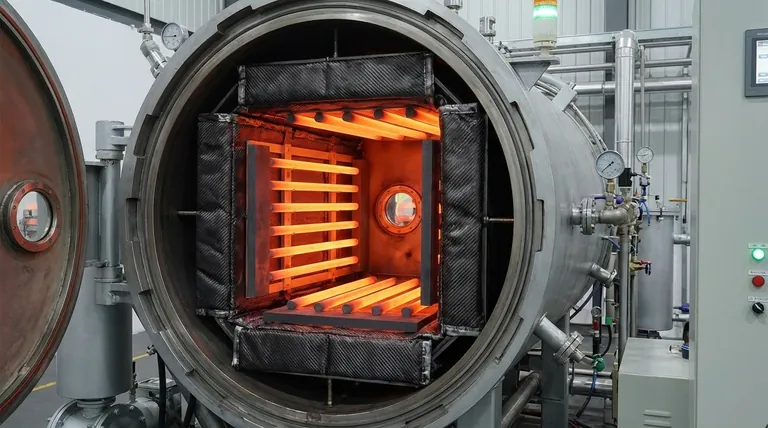
In industrial high-temperature applications, graphite heating refers to the use of components made from pure graphite as the primary heating elements and structural parts within a furnace. This system leverages graphite's excellent electrical conductivity and thermo-mechanical strength to create a durable, low-cost, and efficient environment for processes like high-temperature sintering and heat treatment, especially within vacuum furnaces.
The core principle of graphite heating is using graphite's unique material properties to achieve rapid, high-temperature processing with exceptional durability. It represents a strategic choice for demanding industrial environments where longevity and performance are paramount.
The Core Principles of Graphite Heating
Graphite's role in industrial heating is defined by its fundamental physical properties. It isn't just a passive material; it is an active and integral part of the furnace's thermal system.
How It Works: Electrical Resistance
Graphite heating elements function based on electrical resistance. A high electrical current is passed through the graphite components, which resist the flow of electricity. This resistance converts electrical energy directly into heat, radiating it throughout the furnace's "hot zone."
Key Material Properties
The success of graphite heating hinges on several key characteristics. It possesses excellent thermo-mechanical properties, allowing it to withstand extreme temperature changes without degrading. Furthermore, its high rigidity ensures that structural components, like a furnace hearth, maintain their shape almost indefinitely even under thermal stress.
Common Industrial Applications
Graphite heating systems are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, particularly for processes requiring controlled, high-temperature environments. They are widely used in vacuum furnaces for tasks such as the sintering of powdered metals and the heat treatment of specialized alloys.
Key Advantages in Industrial Processes
Opting for a graphite hot zone is a practical decision driven by clear performance and economic benefits. These advantages make it a default choice for many high-temperature applications.
Durability and Longevity
Furnaces with graphite hot zones are known for being exceptionally durable. Pure graphite demonstrates superior durability compared to metallic mixtures, contributing to a long service life and consistent performance over countless cycles.
Rapid Thermal Cycling
Graphite's ability to heat up and cool down quickly is a significant operational advantage. This capacity for rapid thermal cycling directly reduces overall process times, increasing throughput and operational efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to alternative materials like molybdenum or tungsten, graphite often presents a more low-cost solution. Its widespread availability and established manufacturing processes make it an economical choice for building and maintaining industrial furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is crucial for successful implementation and avoiding costly operational issues.
Brittleness and Physical Damage
The primary drawback of graphite is its brittleness. Components like hearth rails can be prone to chipping or cracking if subjected to sharp impacts during the loading and unloading of furnace materials. Careful handling procedures are essential.
Performance at Lower Temperatures
Although graphite's high thermal conductivity is an asset, its heavier mass can sometimes result in slightly slower heating rates at lower temperatures compared to all-metal designs. This effect is often minor but should be considered for processes sensitive to initial ramp-up speed.
Environmental Requirements
Graphite readily oxidizes at high temperatures when exposed to air. Therefore, graphite heating systems must operate in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon) to prevent the heating elements and insulation from burning away.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate heating system requires aligning the material's properties with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature cycling: Graphite's excellent thermo-mechanical properties make it an ideal choice for reducing process times.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and cost: The proven longevity and lower cost of graphite components provide a reliable and economical solution.
- If your process involves frequent or rough load handling: You must implement strict procedures to mitigate the risk of chipping graphite's brittle components.
Ultimately, leveraging graphite heating effectively comes down to matching its robust high-temperature performance with the specific mechanical and atmospheric demands of your industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| How It Works | Uses electrical resistance to convert energy into heat within a furnace's hot zone. |
| Primary Advantage | Exceptional durability and longevity for long-term, cost-effective operation. |
| Key Application | Ideal for high-temperature sintering and heat treatment in vacuum or inert gas atmospheres. |
| Main Consideration | Requires a protective atmosphere (vacuum/inert gas) to prevent oxidation. |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with a durable, cost-effective heating solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in premium lab equipment, including furnaces with advanced graphite heating systems designed for superior performance in sintering and heat treatment. Our experts can help you select the right system to improve your throughput and operational efficiency.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does an electric oven heating element work? The Science of Resistive Heating Explained
- How are PTC cartridge heaters used? Self-Regulating Precision for Direct Immersion and Contact Heating
- What is the purpose of multi-stage electric heating in tensile testing? Achieve Precision in Grain Boundary Analysis
- What are the properties of a heating element? A Guide to Performance, Lifespan & Cost
- What are the applications of resistance heating? From Toasters to Industrial Furnaces
- What is the life expectancy of a quartz heater element? Maximize Your Heater's Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- How does the heating element work? Mastering Heat Transfer for Your Lab Equipment



















