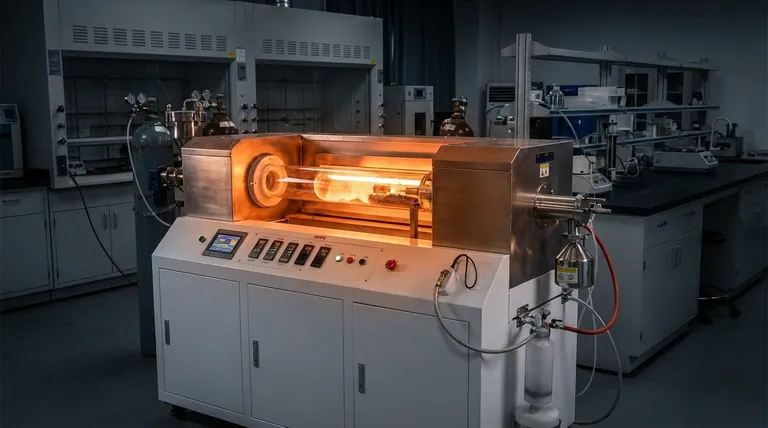
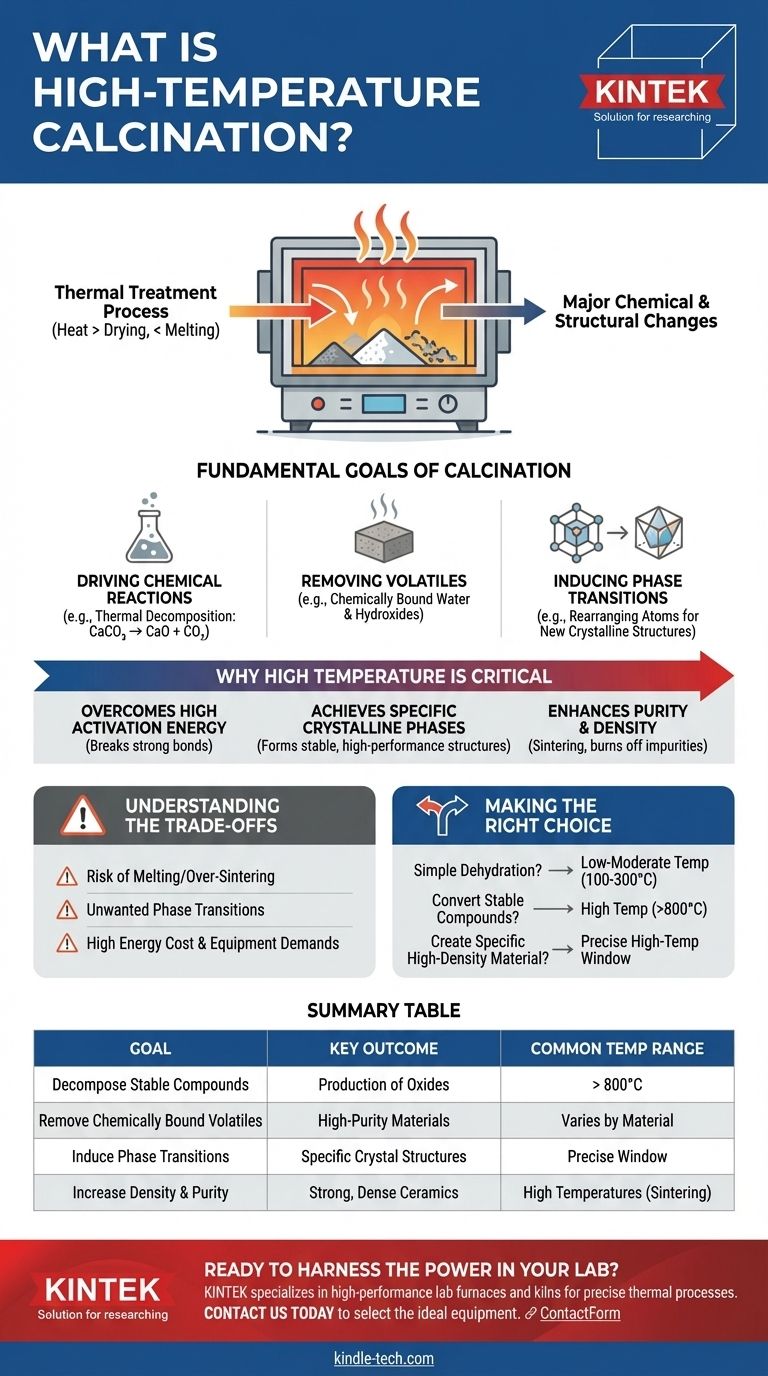
In essence, high-temperature calcination is a thermal treatment process that uses significant heat—well above what's needed for simple drying but below the material's melting point—to induce major chemical or structural changes. Unlike lower-temperature variants, its purpose is to overcome high energy barriers, typically to decompose highly stable compounds, create new crystalline structures, or significantly increase a material's density and purity.
The specific temperature used in calcination is not arbitrary; it is the primary control variable that determines the final properties of the material. High temperature is specifically employed when the goal is to force a chemical or physical transformation that requires a substantial energy input.

The Fundamental Goal of Calcination
Calcination is a foundational process in materials science and chemistry. A solid material is heated in a controlled atmosphere (often with limited or no air) to achieve a specific transformation.
Driving Chemical Reactions
The most common purpose of calcination is thermal decomposition. Heat provides the energy to break chemical bonds, converting a compound into a new substance.
A classic industrial example is converting limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) by driving off carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas at temperatures often exceeding 900°C.
Removing Volatiles
This involves removing substances that are volatile at high temperatures but chemically bound at room temperature. This goes beyond simple drying.
It includes removing chemically bound water (hydroxides) or other volatile organic or inorganic compounds locked within the material's structure.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Heat can cause the atoms in a solid to rearrange themselves into a different crystal structure, known as a phase transition.
This is critical because different crystalline phases of the same material can have vastly different properties, such as hardness, reactivity, or color.
Why "High Temperature" is a Critical Distinction
The term "high temperature" is relative, but it signifies that the process requires enough energy to achieve transformations not possible at moderate heat.
Overcoming High Activation Energy
Many stable compounds, like carbonates and sulfates, have very strong chemical bonds. High temperatures provide the necessary activation energy to break these bonds and initiate decomposition. Think of it as needing a much larger "push" to start the reaction.
Achieving Specific Crystalline Phases
Certain high-performance materials, like specific ceramics or catalysts, only form their desired, stable crystalline phase at very high temperatures. The heat allows the atoms enough mobility to settle into the most energetically favorable (and often most robust) structure.
Enhancing Purity and Density
At high temperatures, particles begin to fuse together in a process bordering on sintering. This process burns off residual organic impurities, drives out voids between particles, and significantly increases the material's final density and strength. This is crucial in the manufacturing of ceramics and certain metal powders.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using high temperatures introduces complexities and risks that must be carefully managed. Choosing the wrong temperature can be worse than doing nothing at all.
The Risk of Melting or Over-Sintering
The core principle of calcination is heating below the melting point. If the temperature is too high or poorly controlled, the material can melt or sinter excessively, destroying its desired properties like surface area (for a catalyst) or particle shape.
Unwanted Phase Transitions
Just as high temperatures can create a desired crystal phase, exceeding the optimal temperature can trigger a transition to an unwanted phase. This can render the final product useless for its intended application.
Energy Cost and Equipment Demands
High-temperature processes are inherently energy-intensive and expensive. They demand specialized furnaces (kilns) built with robust refractory materials capable of withstanding extreme thermal stress, which represents a significant operational and capital cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct calcination temperature is dictated entirely by the desired outcome for your specific material.
- If your primary focus is simple dehydration: You likely only need low-to-moderate temperature calcination (e.g., 100-300°C) to remove physically adsorbed water.
- If your primary focus is converting stable compounds like carbonates to oxides: You will require high-temperature calcination (e.g., >800°C) to supply the energy needed to break strong chemical bonds.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific high-density or crystalline material (like a ceramic): You must use precisely controlled high-temperature calcination, often in a specific temperature window, to achieve the target phase and density without melting.
Ultimately, temperature is the most powerful tool you have to define the final chemistry and structure of your material.
Summary Table:
| Goal of High-Temp Calcination | Key Outcome | Common Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Decompose Stable Compounds (e.g., Carbonates) | Production of Oxides (e.g., Lime from Limestone) | > 800°C |
| Remove Chemically Bound Volatiles | High-Purity, Dehydrated Materials | Varies by Material |
| Induce Phase Transitions | Creation of Specific Crystal Structures | Precise, High-Temp Window |
| Increase Density & Purity | Strong, Dense Ceramics & Powders | High Temperatures (Sintering) |
Ready to harness the power of high-temperature calcination in your lab?
The precise temperature control required for successful calcination is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns designed for exacting thermal processes. Whether you are decomposing carbonates, developing new ceramics, or purifying materials, our equipment ensures the accuracy and repeatability you need.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application. Our experts will help you select the ideal furnace to achieve your material transformation goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process



















