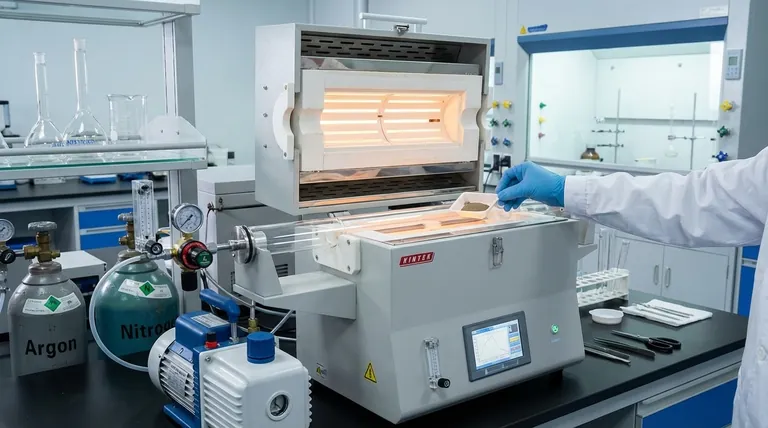
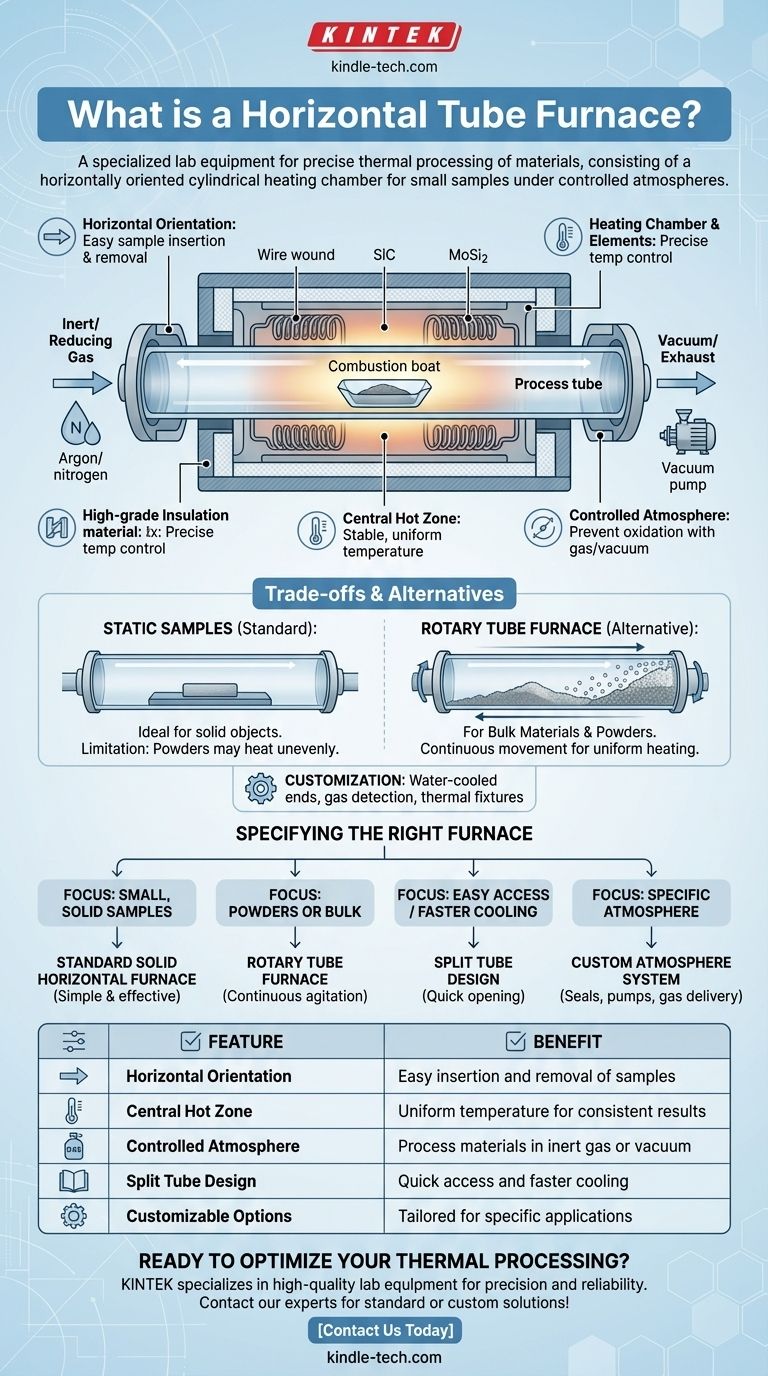
At its core, a horizontal tube furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory or industrial equipment designed for precise thermal processing of materials. It consists of a cylindrical heating chamber oriented horizontally, which allows for controlled heating of small samples, often within a specific atmosphere like a vacuum or an inert gas.
The true value of a horizontal tube furnace lies not just in its ability to heat, but in its capacity to create a highly uniform and controlled environment. Its design is optimized for processing small-diameter samples with exceptional temperature precision and atmospheric purity.

The Core Anatomy of a Horizontal Tube Furnace
A horizontal tube furnace is defined by several key components that work together to create a controlled thermal environment. Understanding these parts is crucial to understanding its function.
The Horizontal Orientation
The term "horizontal" simply refers to the orientation of the long, cylindrical heating chamber. This layout provides a key practical advantage: it allows for very easy insertion and removal of samples, which are typically placed in a container like a "combustion boat" and slid into the tube.
The Heating Chamber and Elements
The central component is the process tube, which is surrounded by heating elements and high-grade insulation. The insulation is often a single, solid piece or can be a "split tube" design, where two semi-cylindrical halves can be opened for easier access.
The heating elements themselves are selected based on the required operating temperature. Common types include:
- Wire wound elements for lower to moderate temperatures.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) for higher temperatures.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) for the highest temperature ranges.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
To ensure the sample is heated evenly, the furnace is designed with a central hot zone. This is the section in the middle of the tube where the temperature is most stable and uniform. More advanced models may feature multiple heating zones that can be controlled independently for even greater precision along the length of the tube.
Controlled Atmosphere Capability
A primary application for these furnaces is processing materials in an environment other than air. By fitting the ends of the tube with sealed end caps, one can introduce an inert or reducing gas (like argon or nitrogen) or pull a vacuum, preventing oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While powerful, the horizontal tube furnace is not a universal solution. Its design comes with specific advantages and limitations that make it ideal for some tasks but less suitable for others.
Key Limitation: Static Samples
The primary limitation is that the sample remains stationary during processing. This is perfectly fine for solid objects but can be a drawback for powders or granular materials, which may not heat with perfect uniformity without being agitated.
The Rotary Tube Furnace Alternative
For processes requiring continuous movement and uniform heating of bulk materials, a rotary tube furnace is the appropriate choice. This design rotates the entire tube, tumbling the material inside. This makes it ideal for applications like calcining, where uniform treatment of every particle is essential.
The Importance of Customization
Standard furnaces provide a baseline, but most applications require specific configurations. Optional components like water-cooled end caps, gas detection systems, and specialized thermal fixtures are often necessary to adapt the furnace for a specific process, such as working with volatile materials or under high vacuum.
Specifying the Right Furnace for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace configuration is critical for achieving your desired outcome. Your decision should be driven entirely by your specific processing requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing small, solid samples: A standard solid horizontal tube furnace provides a simple and effective solution for controlled heating.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of powders or bulk materials: A rotary tube furnace is a superior choice due to its continuous material agitation.
- If your primary focus is easy sample access or faster cooling: A split tube furnace design, which can be opened along its length, is the most practical option.
- If your primary focus is working under a specific atmosphere: You must specify a system with the correct seals, vacuum pumps, or gas delivery and exhaust components.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's temperature range, atmospheric capabilities, and physical design to your material and process goals is the key to successful thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Horizontal Orientation | Easy insertion and removal of samples |
| Central Hot Zone | Uniform temperature for consistent results |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Process materials in inert gas or vacuum |
| Split Tube Design | Quick access and faster cooling |
| Customizable Options | Tailored for specific applications |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including horizontal tube furnaces designed for precision and reliability. Whether you need a standard model for small samples or a custom solution for complex atmospheres, our experts are here to help. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the difference between a tubular furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Application
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- Why use a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Atmosphere Control
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















