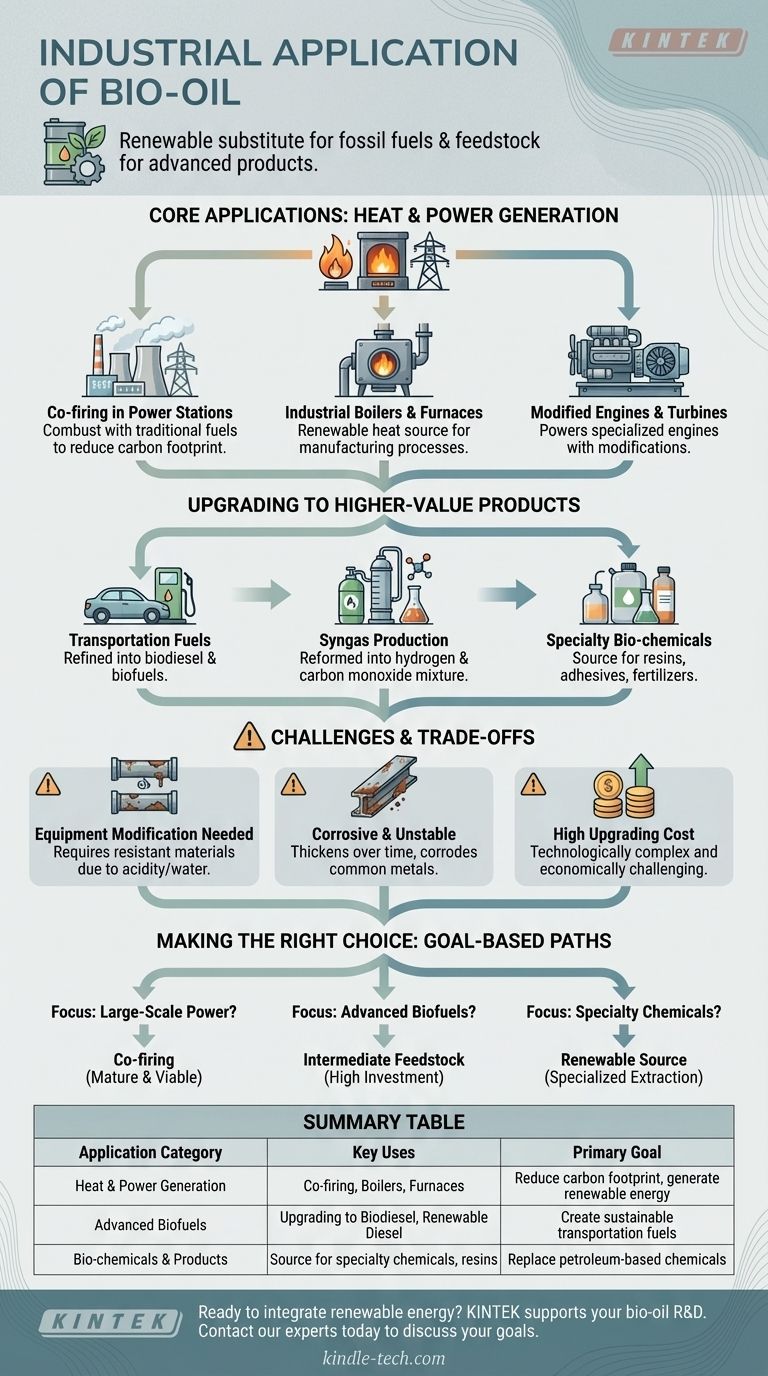
In industrial settings, bio-oil is primarily used as a renewable substitute for fossil fuels in applications like boilers, furnaces, and power plants. It also serves as a valuable feedstock for producing advanced transportation fuels and a wide range of specialty bio-chemicals, though these applications often require significant upgrading and processing.
While bio-oil is a dense and easily transportable liquid energy carrier, its direct use is limited. Its true industrial value is unlocked either through co-firing in existing power infrastructure or by upgrading it into higher-value fuels and chemical products.
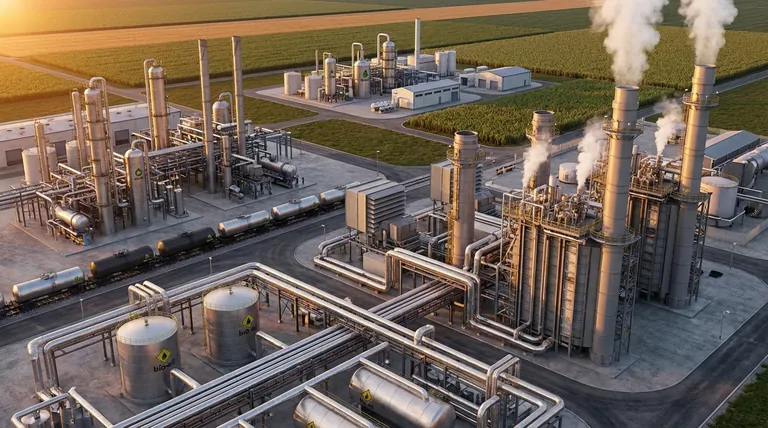

Core Applications: Heat and Power Generation
The most immediate industrial use for bio-oil is leveraging its energy content for heat and power. Its liquid form gives it a significant logistical advantage over raw, solid biomass like wood chips.
Co-firing in Power Stations
Bio-oil is particularly attractive for co-firing in existing power plants. It can be combusted alongside traditional fuels like coal or natural gas, reducing the facility's overall carbon footprint without a complete overhaul of its infrastructure.
Fuel for Industrial Boilers and Furnaces
As a substitute for heavy fuel oil, bio-oil can power industrial boilers, furnaces, and kilns. This provides a direct path for industries to switch to a renewable heat source for their manufacturing processes.
Powering Engines and Turbines
While raw bio-oil is not suitable for standard combustion engines, it can be used in certain modified diesel engines, generators, and turbines. This typically requires adjustments to account for its different combustion properties and chemical composition.
Upgrading to Higher-Value Products
Beyond direct combustion, bio-oil is a crucial intermediate product in the bio-refinery concept, where it is converted into more refined and valuable materials.
Production of Transportation Fuels
Raw bio-oil cannot be used as a "drop-in" fuel for cars. However, through a process of upgrading and refining, it can be converted into biodiesel and other advanced biofuels that meet stringent transportation fuel standards.
Conversion to Syngas
Bio-oil can be reformed to produce synthesis gas (syngas), a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Syngas is a fundamental chemical building block used to create a wide variety of fuels and chemicals.
A Source for Bio-chemicals
The complex composition of bio-oil makes it a rich source of valuable organic compounds and specialty chemicals. These can be extracted and purified for use in resins, adhesives, fertilizers, and other industrial products, offering a renewable alternative to petroleum-based chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Deploying bio-oil effectively requires a clear understanding of its technical limitations. It is not a simple drop-in replacement for conventional fossil fuels.
The Need for Equipment Modification
Direct use of bio-oil almost always requires modifications to existing equipment. Its high acidity, water content, and viscosity mean that standard burners, pumps, and storage tanks may need to be replaced with more resistant materials.
Corrosive Nature and Instability
Bio-oil is inherently acidic and can corrode common metals like carbon steel. It is also thermally unstable, meaning it can thicken and change its chemical properties over time, which complicates long-term storage.
The Cost of Upgrading
The process of upgrading bio-oil into transportation fuels or purified chemicals is technologically complex and can be economically challenging. These upgrading costs are a significant factor in its widespread adoption for higher-value applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal application for bio-oil depends entirely on your specific industrial objective and available infrastructure.
- If your primary focus is large-scale power generation: Co-firing bio-oil with fossil fuels in existing plants is the most mature and economically viable application.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced biofuels: View bio-oil as an intermediate feedstock that requires significant investment in upgrading and refining technology.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty chemicals: Bio-oil offers a renewable source of valuable compounds, but this requires specialized extraction and purification capabilities.
Ultimately, understanding bio-oil's properties and its necessary processing pathways is the key to unlocking its industrial potential.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Heat & Power Generation | Co-firing in power plants, industrial boilers, furnaces | Reduce carbon footprint, generate renewable energy |
| Advanced Biofuels | Upgrading to biodiesel, renewable diesel | Create sustainable transportation fuels |
| Bio-chemicals & Products | Source for specialty chemicals, resins, fertilizers | Replace petroleum-based chemicals with renewable alternatives |
Ready to integrate renewable energy solutions into your operations? KINTEK specializes in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables essential for researching, developing, and optimizing bio-oil production and upgrading processes. Whether you are scaling up from the lab or need precise analytical tools, our expertise supports your journey in sustainable energy. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific bio-oil application goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced magnetron? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thin-Film Process
- What critical reaction conditions does a shaking incubator provide? Optimize Cassava Cellulose Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- What can you test with a diamond tester? Accurately Identify Genuine Diamonds from Fakes
- Does SEM require sputter coating? Essential Guide to Clear, High-Resolution Imaging
- Are carbon nanotubes safe to use? Understanding the Critical Difference Between Bound and Free CNTs
- Why are cold traps considered essential auxiliary equipment in laboratory-scale plastic pyrolysis research? | KINTEK
- How do Ultra-Low Temperature freezers contribute to public health? Preserving Vaccines and Research for a Healthier World
- Is biomass the best renewable energy source? Weighing Reliability Against Environmental Impact









