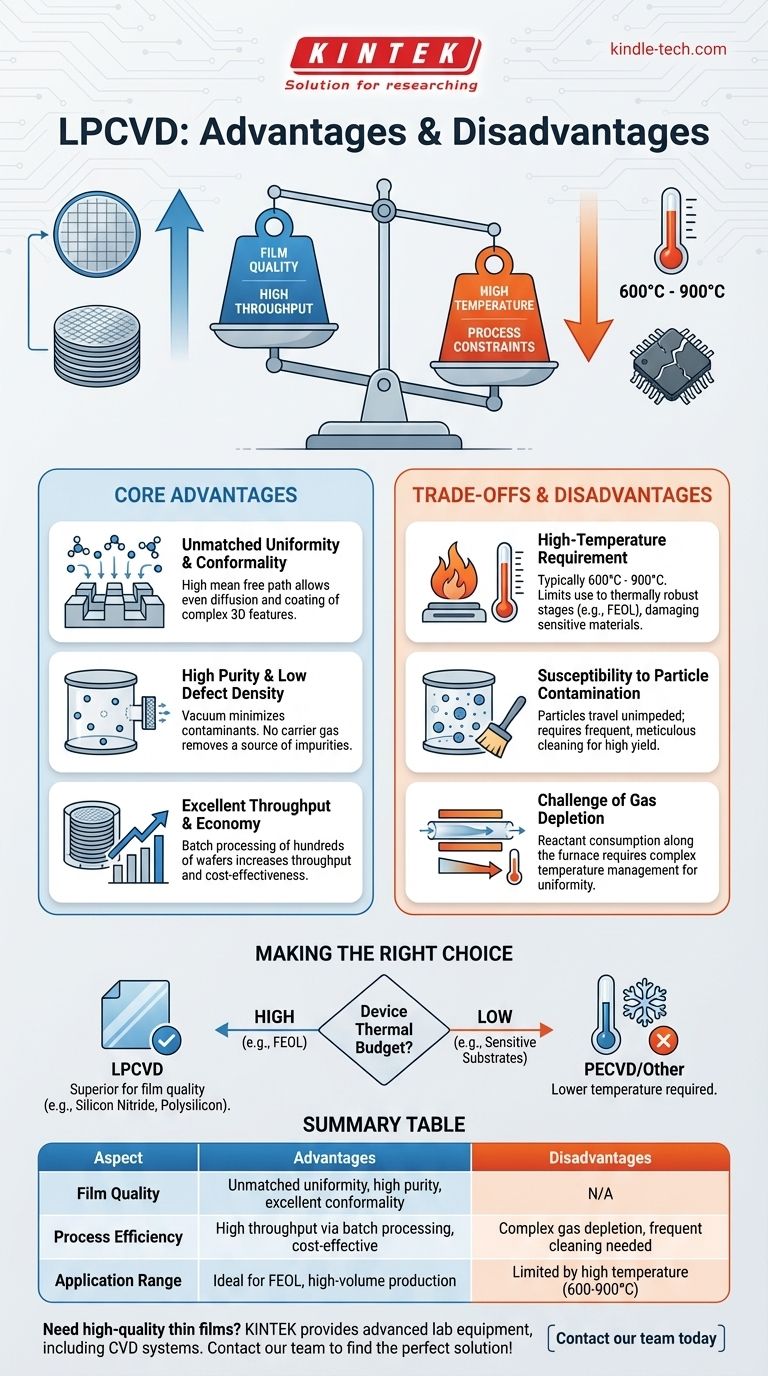
In short, LPCVD's primary advantage is its ability to produce exceptionally uniform and pure thin films at high throughput, making it highly economical. Its main disadvantage is the high processing temperature required, which can damage other components on a device and limits where it can be used in a manufacturing sequence.
The decision to use Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) is almost always a direct trade-off between film quality and temperature. It is the preferred method when superior film properties are critical and the underlying device can withstand the high thermal budget.

The Core Advantages of LPCVD
LPCVD became a cornerstone of semiconductor manufacturing because it excels in areas critical for building microscopic, high-performance devices. Its benefits stem directly from its low-pressure operating environment.
Unmatched Film Uniformity and Conformality
At low pressures (vacuum), gas molecules can travel much farther before colliding with each other. This increased mean free path is the key to LPCVD's success.
Reactant gases can diffuse freely and evenly across all wafer surfaces, including the complex vertical sidewalls of microscopic trenches. This results in a film that is highly uniform across the wafer and highly conformal over 3D structures.
High Purity and Low Defect Density
The deposition process occurs in a vacuum, which inherently minimizes the presence of unwanted contaminants.
Furthermore, LPCVD does not require a carrier gas to transport the reactive chemicals. This eliminates a major source of potential impurities, leading to films with higher purity and fewer defects compared to atmospheric pressure methods.
Excellent Throughput and Economy
Because the film deposition is so uniform, wafers don't need to lie flat facing the gas source. Instead, they can be stacked vertically in cassettes, standing on edge and packed tightly together.
This "batch processing" allows hundreds of wafers to be coated in a single run, dramatically increasing throughput and making LPCVD a very cost-effective solution for high-volume manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
While powerful, LPCVD is not a universal solution. Its drawbacks are significant and must be carefully considered by process engineers.
The High-Temperature Requirement
LPCVD is a thermally-driven process, often requiring temperatures between 600°C and 900°C to initiate the chemical reactions. This high thermal budget is its single greatest limitation.
Many devices have components, such as aluminum or copper interconnects, that cannot tolerate such high temperatures. Therefore, LPCVD is often restricted to the front-end-of-line (FEOL) fabrication stages, before temperature-sensitive materials are deposited.
Susceptibility to Particle Contamination
While the vacuum environment is inherently clean, any particles that do form within the chamber can travel unimpeded and deposit onto the wafers, causing killer defects.
This means LPCVD systems require frequent and meticulous cleaning cycles to maintain high yields, which adds to operational overhead.
The Challenge of Gas Depletion
In a long furnace tube used for batch processing, the reactant gases get consumed as they flow from the front of the tube to the back. This gas depletion can cause wafers at the end of the line to receive a thinner film.
To compensate, engineers must create a temperature gradient along the furnace—running it hotter at the back—to speed up the reaction rate and achieve uniform thickness across the entire batch. This adds a layer of process complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a deposition method requires balancing the need for film quality against the process constraints of your device.
- If your primary focus is the highest film quality and conformality for foundational layers: LPCVD is the superior choice for materials like silicon nitride or polysilicon when a high thermal budget is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates: LPCVD is unsuitable. A lower-temperature process like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the necessary alternative.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective production for a thermally robust device: LPCVD's batch processing capability makes it an excellent economic choice, as seen in both semiconductor and solar cell manufacturing.
Ultimately, selecting LPCVD hinges on whether your device's thermal budget can accommodate its high-temperature operation to gain its superior film properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Film Quality | Unmatched uniformity, high purity, excellent conformality | N/A |
| Process Efficiency | High throughput via batch processing, cost-effective | Complex gas depletion management, frequent cleaning needed |
| Application Range | Ideal for FEOL, high-volume production (e.g., semiconductors, solar cells) | Limited by high temperature (600-900°C), unsuitable for temperature-sensitive materials |
Need to deposit high-quality thin films for your lab? The choice between LPCVD and other methods depends on your specific thermal and quality requirements. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including CVD systems, to meet your precise research and production needs. Our experts can help you select the right technology to optimize your process. Contact our team today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















