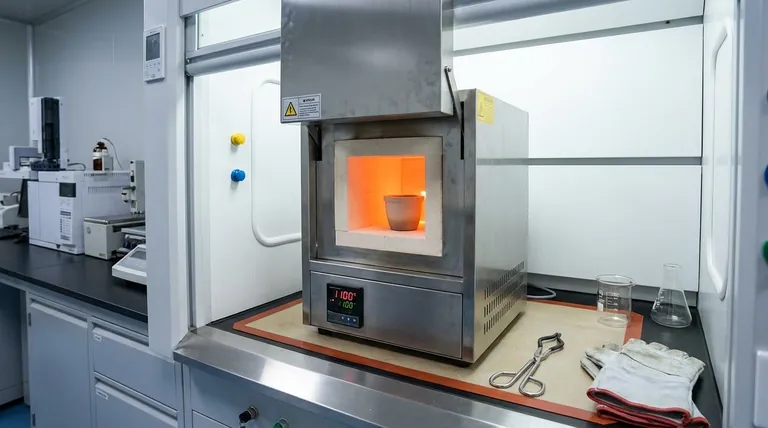
At its core, a laboratory muffle furnace is a specialized high-temperature oven. It is engineered to heat materials to extremely high temperatures—often up to 1200°C (2192°F) or more—within a controlled and isolated chamber. Its primary function is to transform or analyze a material's composition through processes like ashing, heat-treating, and sintering, where direct contact with heating elements would cause contamination.
A muffle furnace is more than just a powerful oven; it is a precision instrument for transforming and analyzing matter. Its defining feature is the "muffle"—an insulating chamber that separates the sample from the heating elements, ensuring pure, radiant heat and preventing chemical contamination.

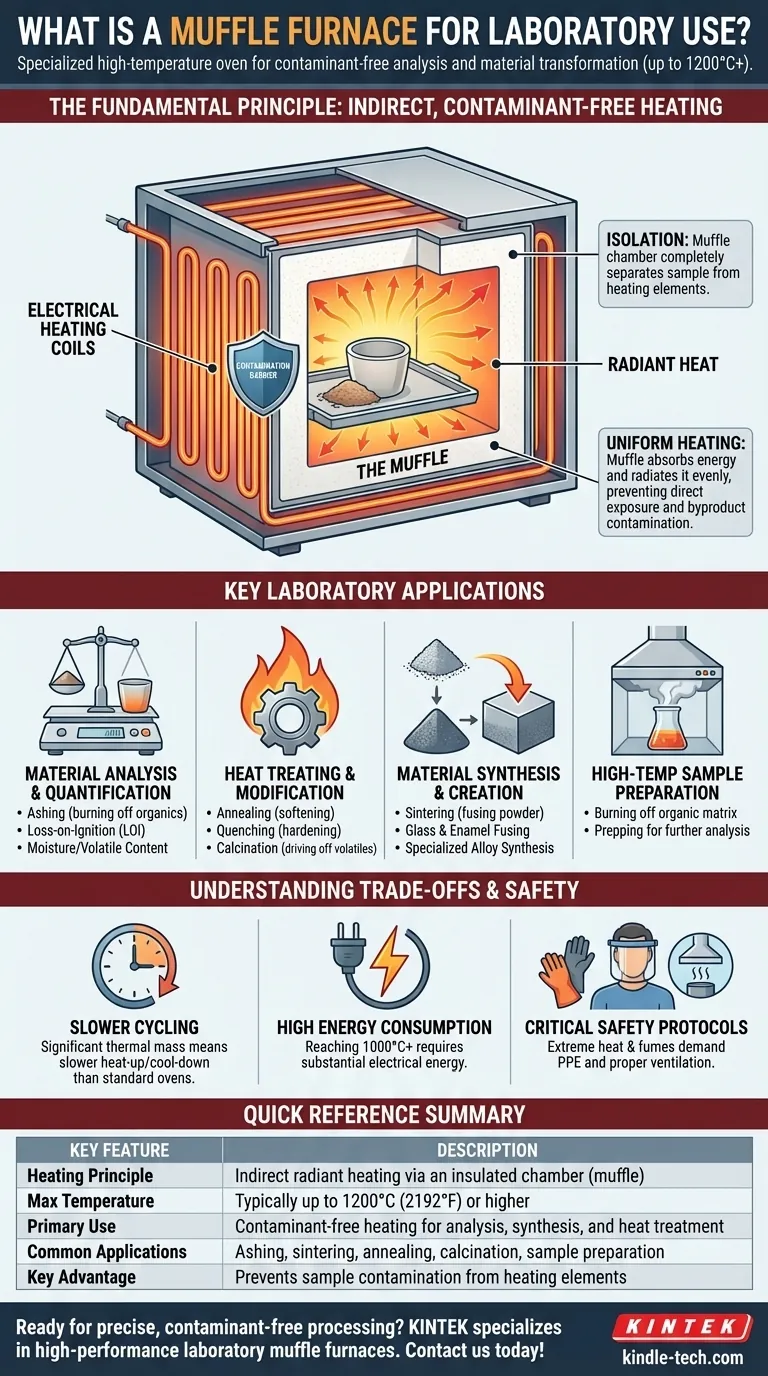
The Fundamental Principle: Indirect, Contaminant-Free Heating
The key to understanding a muffle furnace lies in its name. The design revolves around isolating the sample to ensure the integrity of the process, whether for analysis or materials creation.
What is the "Muffle"?
The "muffle" is the furnace's inner chamber, typically constructed from high-temperature refractory ceramic. This chamber acts as a complete barrier, or shield, between the sample being heated and the actual heating elements of the furnace.
How It Works
The furnace's electric heating elements heat the outside of the muffle chamber. The chamber absorbs this energy and then radiates it uniformly to the interior.
This method of indirect heating ensures that the sample is heated evenly without any direct exposure to the electrical components.
The Importance of Isolation
This isolation is critical. It prevents byproducts from the heating elements from contaminating the sample. This is essential for accurate analytical work, such as determining the precise ash content of a material, where any added residue would skew the results.
Key Laboratory Applications
Muffle furnaces are versatile tools used across numerous scientific and industrial fields. Their applications can be grouped into several main categories.
Material Analysis and Quantification
This is one of the most common uses. The furnace allows for precise measurement of a sample's composition by burning away specific components.
Key processes include ashing (burning off all organic matter to weigh the remaining inorganic ash), determining moisture or volatile content, and loss-on-ignition (LOI) analysis.
Heat Treating and Materials Modification
In materials science, a muffle furnace is essential for altering the physical properties of metals, alloys, and ceramics.
Processes like annealing (softening metal), quenching (hardening), and calcination (heating solids to drive off volatiles) are performed in a controlled environment to achieve desired characteristics like strength and durability.
Material Synthesis and Creation
The high, uniform temperatures are ideal for creating new materials.
This includes sintering (fusing powdered materials like ceramics or metals together without melting), creating enamel coatings, fusing glass, and synthesizing specialized alloys.
High-Temperature Sample Preparation
In fields like environmental analysis or medicine, samples often need to be prepared for further testing.
A muffle furnace can cleanly burn off the organic matrix of a soil or biological sample, leaving behind inorganic elements for analysis by other instruments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable for high-temperature work, a muffle furnace is a specialized piece of equipment with specific operational characteristics.
Slower Than a Standard Oven
Due to the significant thermal mass of the refractory muffle, these furnaces heat up and cool down much more slowly than a standard laboratory oven. They are designed for steady, high-temperature operation, not rapid temperature cycling.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or higher requires a substantial amount of electrical energy. This is a significant operational consideration compared to lower-temperature equipment.
Critical Safety Protocols
The extreme temperatures pose a serious hazard. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including heat-resistant gloves and face shields, is mandatory. Additionally, processes like ashing produce smoke and fumes that require proper ventilation, often necessitating placement under a fume hood.
When to Choose a Muffle Furnace
Your specific goal determines whether a muffle furnace is the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Use a muffle furnace for ashing to precisely determine the inorganic or non-combustible content of a sample.
- If your primary focus is materials science: This furnace is essential for heat-treating metals to modify their properties or for sintering ceramics to create dense, solid parts.
- If your primary focus is synthesis: It provides the clean, high-temperature environment needed to create specialized materials like technical ceramics, glass, or enamel coatings.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace provides the controlled, high-temperature environment necessary to fundamentally alter or analyze the composition of materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Indirect radiant heating via an insulated chamber (muffle) |
| Max Temperature | Typically up to 1200°C (2192°F) or higher |
| Primary Use | Contaminant-free heating for analysis, synthesis, and heat treatment |
| Common Applications | Ashing, sintering, annealing, calcination, sample preparation |
| Key Advantage | Prevents sample contamination from heating elements |
Ready to achieve precise, contaminant-free high-temperature processing in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory muffle furnaces designed for accurate ashing, heat-treating, and sintering. Our equipment ensures uniform heating and sample integrity for your most demanding applications. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heating element of a muffle furnace? The Engine for High-Temp Precision
- How do you check the temperature of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Monitoring
- How does heat treatment affect surface roughness? Minimize Surface Degradation for Precision Parts
- What is the introduction of muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature, Contamination-Free Heating
- Is a muffle furnace an oven? A Guide to High-Temperature vs. Low-Temperature Heating



















