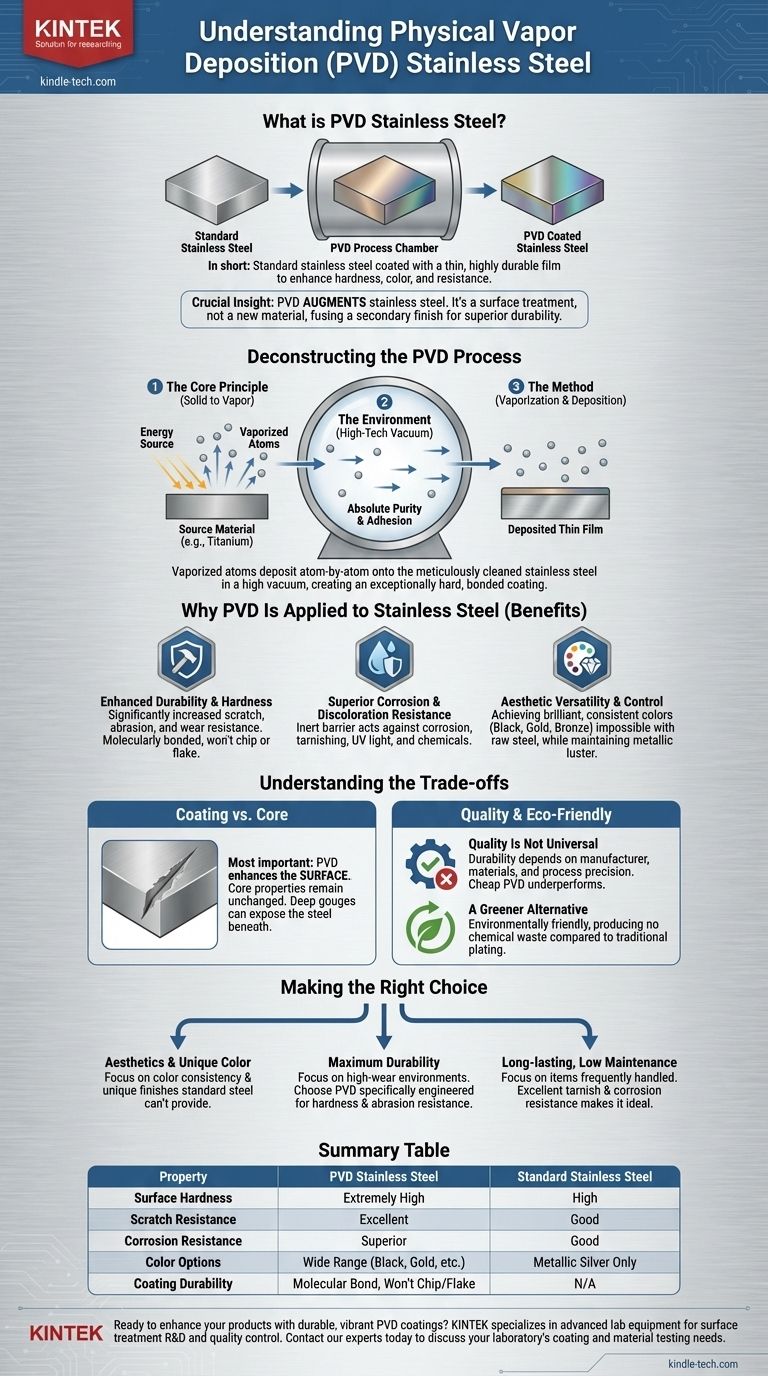
In short, PVD stainless steel is standard stainless steel that has been coated with a thin, highly durable film using a process called Physical Vapor Deposition. This sophisticated vacuum coating technique is not a type of steel itself, but rather a surface treatment used to enhance its properties by adding color, increasing hardness, and improving resistance to scratches and corrosion.
The most critical thing to understand is that PVD is a process that augments stainless steel, not a material you can buy on its own. It fuses a secondary material to the steel's surface, creating a finish that is significantly harder and more durable than the base steel alone.

Deconstructing the PVD Process
To understand the final product, you must first understand the manufacturing process. Physical Vapor Deposition is a high-tech procedure that takes place inside a vacuum chamber to ensure absolute purity and adhesion.
The Core Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Solid
At its heart, the PVD process involves three phases. A solid source material—often a metal like titanium or a ceramic compound—is converted into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto the stainless steel part, forming a thin, tightly bonded film.
The Environment: A High-Tech Vacuum
The entire process is performed under a high vacuum. This is critical because it removes other atoms and molecules that could contaminate the film or interfere with the coating process, ensuring a pure and dense final layer.
The Method: Vaporization and Deposition
First, the stainless steel component is meticulously cleaned to guarantee the coating will bond perfectly. Inside the chamber, high-power electricity or a specialized plasma discharge bombards the source material. This energizes the material, causing its atoms to vaporize. These vaporized atoms are then deposited atom-by-atom onto the surface of the stainless steel, creating an extremely thin but exceptionally hard coating.
Why PVD Is Applied to Stainless Steel
While stainless steel is already known for its strength, PVD coating elevates its performance and aesthetic possibilities to a new level. The result is a hybrid material that combines the best of both the substrate and the coating.
Enhanced Durability and Hardness
The primary benefit of PVD is a dramatic increase in surface hardness. This makes the product far more resistant to scratches, abrasions, and daily wear and tear than uncoated stainless steel. The coating is molecularly bonded to the steel, so it won't chip, flake, or peel off.
Superior Corrosion and Discoloration Resistance
The PVD film acts as an inert barrier, protecting the underlying stainless steel from environmental factors. This provides an additional layer of resistance against corrosion, tarnishing, and discoloration from things like UV light or chemicals.
Aesthetic Versatility and Control
PVD allows manufacturers to achieve a wide spectrum of consistent, brilliant colors—from black and gold to bronze and even bold blues or greens. This offers a level of design freedom that is impossible with raw stainless steel, while maintaining a metallic luster.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, it's crucial to see PVD as a specific tool with its own set of considerations. It is not a magical solution for all applications.
It's a Coating, Not a Core Property
The most important distinction is that PVD enhances the surface. The core properties of the stainless steel underneath remain unchanged. If a PVD-coated object sustains an extremely deep gouge that penetrates the coating, the exposed steel beneath can still be scratched or corrode.
Quality Is Not Universal
The durability, color consistency, and longevity of a PVD finish depend heavily on the manufacturer's quality control, the specific coating materials used, and the precision of the process. A cheap, poorly applied PVD coating will not perform as well as one from a high-end, controlled process.
A Greener Alternative
Compared to traditional coating methods like electroplating, which involve hazardous chemical baths and produce toxic waste, PVD is a significantly more environmentally friendly process. It produces no chemical waste, making it a responsible choice for modern manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a PVD-coated product means you are choosing an enhanced version of stainless steel. Your final decision should be guided by your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and unique color: PVD offers a durable and consistent way to achieve finishes that standard stainless steel cannot provide.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability in a high-wear environment: Seek out products with PVD coatings specifically engineered for hardness, as they offer superior protection against scratches and abrasion.
- If your primary focus is a long-lasting, low-maintenance finish: The excellent tarnish and corrosion resistance of PVD makes it ideal for items like watches, fixtures, and hardware that are frequently handled.
Ultimately, PVD elevates stainless steel, transforming it into a material that is not only strong but also precisely tailored in color and resilience for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Property | PVD Stainless Steel | Standard Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Hardness | Extremely High | High |
| Scratch Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Color Options | Wide Range (Black, Gold, Bronze, etc.) | Metallic Silver Only |
| Coating Durability | Molecular Bond, Won't Chip/Flake | N/A |
Ready to enhance your products with durable, vibrant PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface treatment R&D and quality control. Our solutions help you achieve perfect PVD finishes. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's coating and material testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















