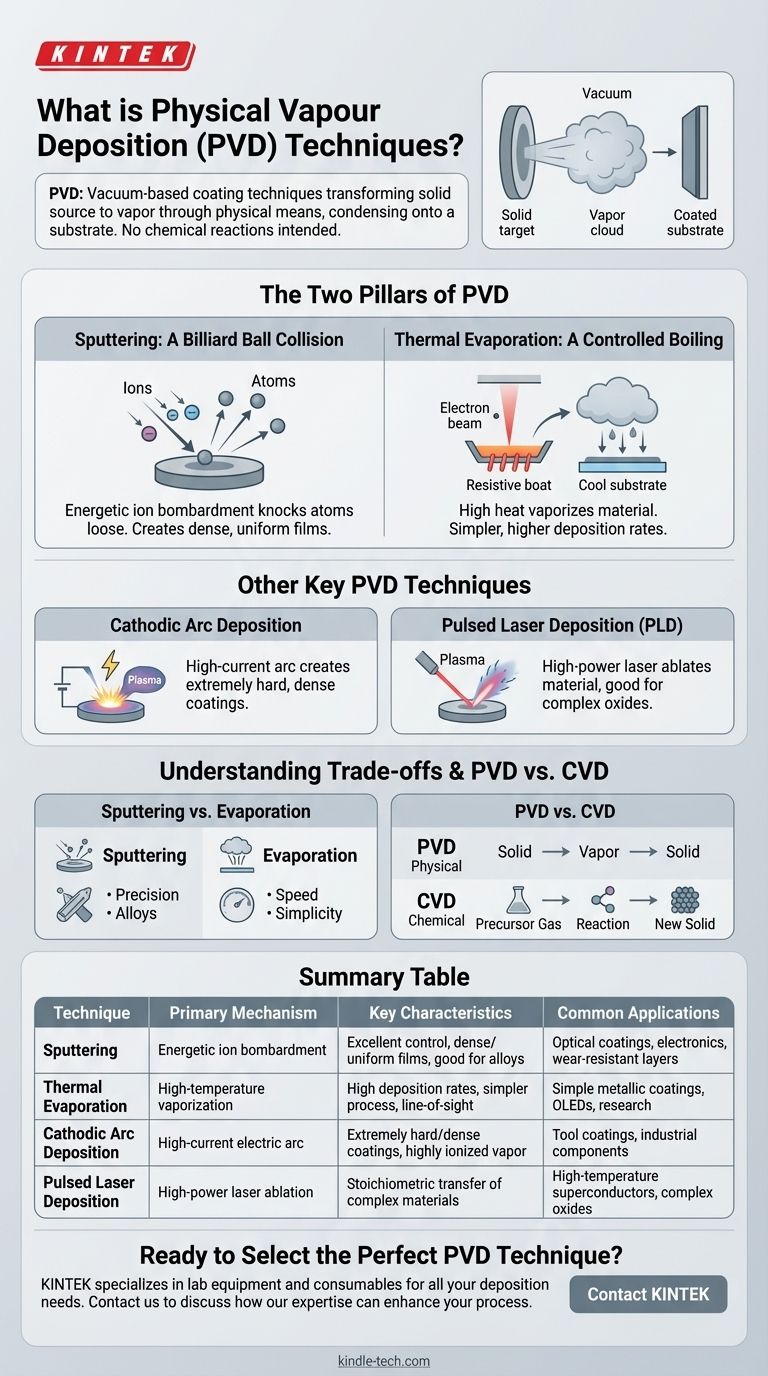
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of vacuum-based coating techniques used to deposit thin, high-performance films onto a substrate. These processes all function by transforming a solid source material into a vapor through purely physical means, transporting it through a vacuum or low-pressure environment, and allowing it to condense onto the target object. The two most fundamental categories of PVD are sputtering, which uses energetic ion bombardment, and thermal evaporation, which uses heat.
The defining principle of all PVD techniques is their reliance on physical mechanisms—like high-energy particle collisions or intense heat—to create a vapor from a source material. Unlike other methods, no fundamental chemical reactions are intended to occur to form the final film on the substrate.

The Two Pillars of PVD: Sputtering and Evaporation
At the heart of PVD are two distinct approaches for turning a solid material into a vapor. Understanding this distinction is key to understanding the entire field.
Sputtering: A Billiard Ball Collision
Sputtering involves bombarding a solid source material, known as the target, with high-energy ions (typically from an inert gas like argon).
This energetic collision is like a cue ball striking a rack of billiard balls. It physically knocks atoms or molecules loose from the target's surface.
These "sputtered" atoms then travel through the vacuum chamber and deposit onto the substrate, building up a thin, often very dense, film.
Thermal Evaporation: A Controlled Boiling
Thermal evaporation is a more intuitive process that uses high temperatures to vaporize the source material inside a vacuum chamber.
The process is analogous to water boiling into steam and condensing on a cold mirror. The vaporized material travels in a straight line until it strikes the cooler substrate, where it condenses back into a solid film.
There are several ways to generate this heat:
- Resistive Heating: An electric current passes through a heat-resistant boat or filament holding the source material.
- Electron-Beam Evaporation: A focused beam of high-energy electrons heats and evaporates the source material with great precision.
- Inductive Heating: Radio frequency (RF) power creates eddy currents that heat a crucible containing the source material.
Other Key PVD Techniques
Beyond the two primary families, several specialized PVD methods have been developed for specific applications.
Cathodic Arc Deposition (Arc-PVD)
This technique uses a high-current, low-voltage electric arc on the surface of the target.
The arc creates a small, intensely hot spot that vaporizes the material, generating a highly ionized vapor that results in extremely hard and dense coatings.
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)
In PLD, a high-power pulsed laser is focused onto the target inside the vacuum chamber.
Each laser pulse ablates, or vaporizes, a small amount of the material, creating a plume of plasma that deposits onto the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single PVD technique is universally superior; the best choice depends entirely on the desired outcome for the film.
The Precision of Sputtering
Sputtering techniques, especially ion beam sputtering, offer exceptional control over film properties.
Because the process is driven by kinetic energy rather than heat, it is excellent for depositing complex alloys or materials with different melting points. The result is often a very smooth, dense, and uniform film.
The Speed and Simplicity of Evaporation
Thermal evaporation is often simpler and can achieve higher deposition rates than sputtering.
However, it can be more difficult to control the film's structure precisely, and it is less suitable for materials that might decompose at high temperatures or for creating complex alloy films.
How PVD Differs from CVD
It is crucial to distinguish PVD from its counterpart, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
PVD is a physical process. The material deposited on the substrate is the same material that left the source target; it has only changed its physical state from solid to vapor and back to solid.
CVD is a chemical process. It introduces precursor gases into a chamber, which then react on the substrate's hot surface to form an entirely new solid material, leaving behind volatile byproducts.
Selecting the Right PVD Approach
Your choice of technique should be driven by the specific properties you need in the final film.
- If your primary focus is maximum control, density, and uniformity: Sputtering, particularly ion beam sputtering, is often the superior choice for creating high-quality optical or electronic films.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate for a simple metallic coating: Thermal or electron-beam evaporation provides an efficient and often more cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely hard, wear-resistant coating: Cathodic Arc Deposition is a leading technique used for tools and industrial components.
Understanding these fundamental mechanisms empowers you to select the precise tool for your specific material and application needs.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Primary Mechanism | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sputtering | Energetic ion bombardment | Excellent control, dense/uniform films, good for alloys | Optical coatings, electronics, wear-resistant layers |
| Thermal Evaporation | High-temperature vaporization | High deposition rates, simpler process, line-of-sight | Simple metallic coatings, OLEDs, research |
| Cathodic Arc Deposition | High-current electric arc | Extremely hard/dense coatings, highly ionized vapor | Tool coatings, industrial components |
| Pulsed Laser Deposition | High-power laser ablation | Stochiometric transfer of complex materials | High-temperature superconductors, complex oxides |
Ready to Select the Perfect PVD Technique for Your Application?
Choosing the right PVD process is critical for achieving the desired film properties in your lab. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. We can help you navigate the trade-offs between sputtering, evaporation, and other PVD methods to find the ideal solution for your specific materials and performance requirements.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our expertise and equipment can enhance your research or production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















