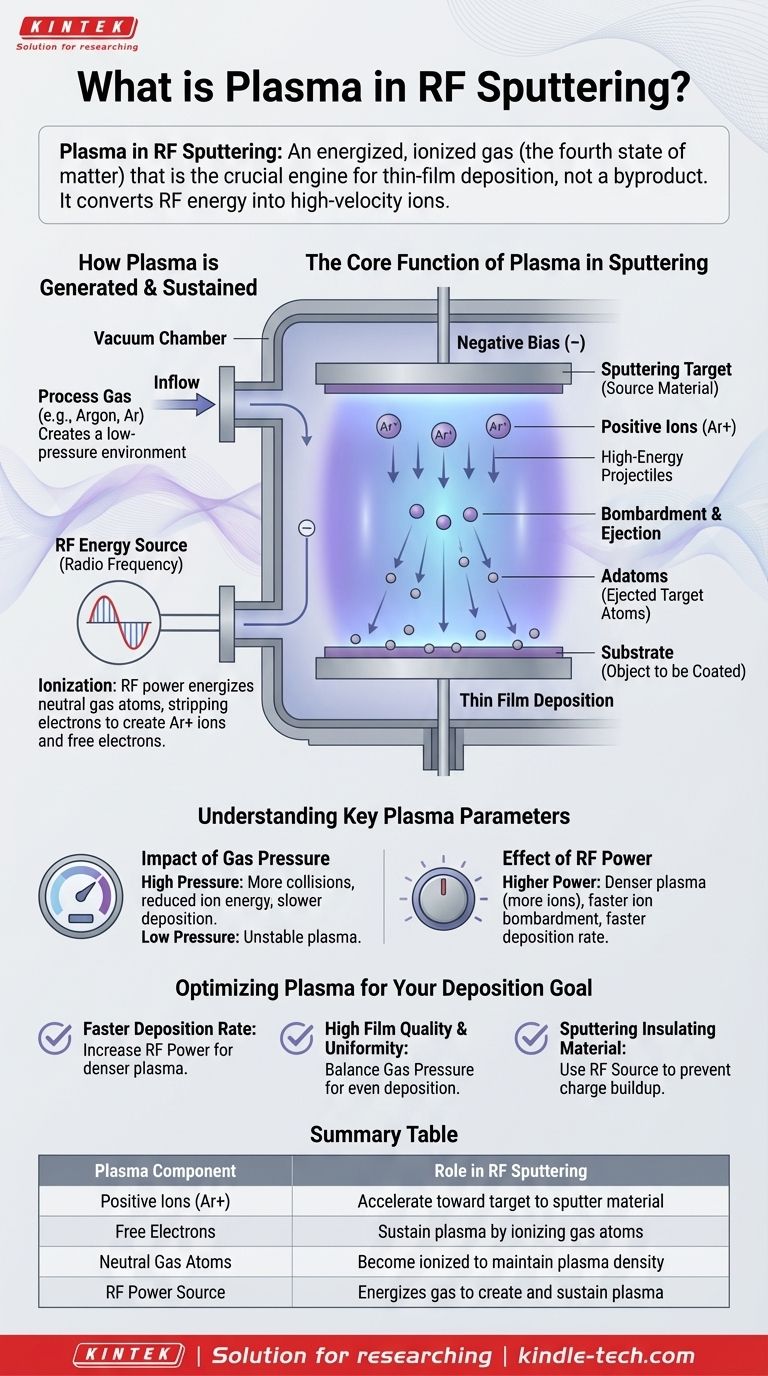
In the context of RF sputtering, plasma is an energized, ionized gas that serves as the crucial medium for the thin-film deposition process. It is often called the "fourth state of matter" and consists of a dynamic mix of positive ions, electrons, and neutral gas atoms, all created by applying a radio frequency (RF) energy source to a low-pressure gas like argon inside a vacuum chamber.
Plasma is not a byproduct of sputtering; it is the engine that drives it. Its primary function is to convert electrical energy from an RF source into high-velocity ions, which act as projectiles to physically knock atoms off a target material and deposit them onto a substrate.

How Plasma is Generated and Sustained
To understand what plasma is, it's essential to know how it's created within the sputtering system. The process involves a controlled environment and a specific energy input.
The Role of the Vacuum Chamber and Process Gas
First, a high vacuum is created in a chamber to remove unwanted atmospheric gases. Then, a small, controlled amount of a high-purity process gas, most commonly argon (Ar), is introduced. This creates a low-pressure environment that is ideal for initiating and sustaining a plasma.
The Function of the RF Energy Source
An RF (radio frequency) power source is applied to an electrode inside the chamber. This alternating electric field energizes the neutral argon atoms, stripping electrons from them. This process, known as ionization, creates a mixture of positively charged argon ions (Ar+) and free electrons, forming the characteristic glow of plasma.
The Core Function of Plasma in Sputtering
Once generated, the plasma becomes the active tool for depositing a thin film. Its components each play a distinct role in a precise sequence of events.
Creating High-Energy Ion Projectiles
The key actors within the plasma are the positive ions (Ar+). The sputtering target, which is the source material for the thin film, is given a negative electrical bias. This potential difference strongly attracts the positively charged argon ions from the plasma, causing them to accelerate directly toward the target.
Bombarding the Sputtering Target
These accelerated ions collide with the surface of the sputtering target with significant kinetic energy. Think of it as a subatomic-scale sandblasting process, where the argon ions are the grains of sand.
Ejecting Target Material for Deposition
The force of this ion bombardment is sufficient to knock atoms or molecules loose from the target material. These ejected particles, now called adatoms, travel through the vacuum chamber and land on the substrate (the object being coated), gradually building up a thin, uniform film.
Understanding Key Plasma Parameters
The characteristics of the plasma directly control the outcome of the deposition. Fine-tuning these parameters is how engineers and scientists control film thickness, quality, and deposition speed.
Impact of Gas Pressure
The pressure of the process gas inside the chamber is a critical variable. Too high a pressure leads to more collisions, which can reduce the energy of the ions hitting the target and slow the deposition rate. Too low a pressure makes it difficult to sustain a stable plasma.
Effect of RF Power
The amount of power supplied by the RF source determines the plasma density. Higher power results in a denser plasma with more ions, which in turn increases the rate of ion bombardment and leads to a faster deposition rate.
Optimizing Plasma for Your Deposition Goal
Controlling the plasma is the key to controlling your sputtering results. The settings you choose should be directly tied to the desired properties of your final thin film.
- If your primary focus is a faster deposition rate: Increase the RF power to generate a denser plasma with a higher concentration of ions.
- If your primary focus is high film quality and uniformity: Carefully optimize the process gas pressure to balance ion energy with the mean free path, ensuring atoms deposit evenly on the substrate.
- If your primary focus is sputtering an insulating material: Using an RF power source is non-negotiable, as its alternating field is necessary to prevent charge buildup and sustain the plasma with non-conductive targets.
Ultimately, mastering the plasma is fundamental to achieving precise and repeatable results in any RF sputtering application.
Summary Table:
| Plasma Component | Role in RF Sputtering |
|---|---|
| Positive Ions (Ar+) | Accelerate toward target to sputter material |
| Free Electrons | Sustain plasma by ionizing gas atoms |
| Neutral Gas Atoms | Become ionized to maintain plasma density |
| RF Power Source | Energizes gas to create and sustain plasma |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your RF sputtering needs. Whether you're working on semiconductor fabrication, optical coatings, or advanced materials research, our expertise ensures you achieve precise plasma control for superior film quality and deposition rates.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















