At its core, a PVD coating machine is a sophisticated system that uses a high-vacuum environment to deposit an extremely thin but incredibly durable film of material onto a product's surface. The machine works by vaporizing a solid source material, such as titanium or chromium, and then depositing that vapor onto a substrate, creating a new, bonded surface layer literally one atom at a time. This process fundamentally enhances the physical properties of the original part.
A PVD machine is not simply for applying color or a simple finish. It is a precision manufacturing tool that uses vacuum physics to create a new, high-performance surface on a product, dramatically increasing its hardness, wear resistance, and lifespan.

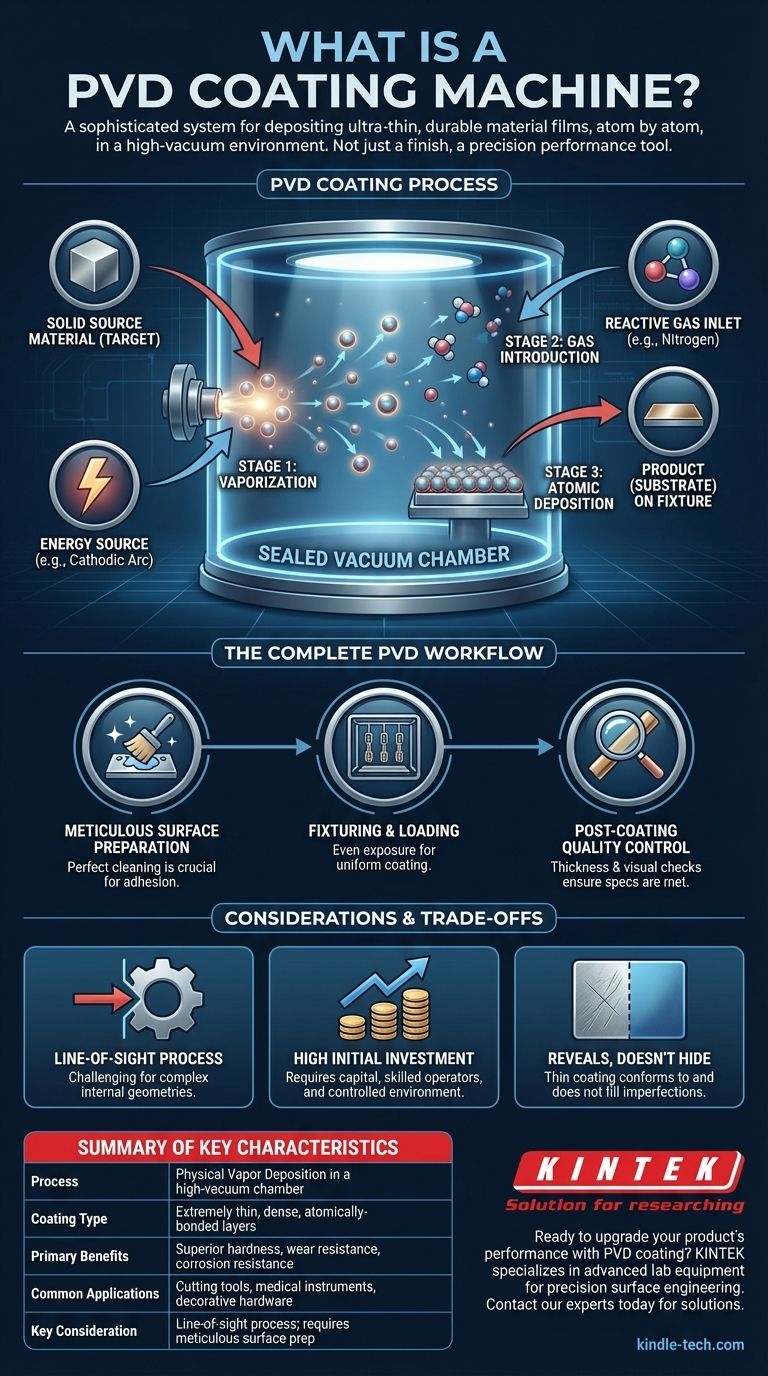
How a PVD Machine Executes the Coating Process
To understand what the machine is, you must first understand the process it facilitates. The entire operation takes place within a sealed vacuum chamber, which is the heart of the machine.
The Critical Vacuum Environment
The process must occur in a vacuum to eliminate any foreign particles or gases, such as oxygen or water vapor. This pristine environment ensures the deposited coating is pure and adheres perfectly to the substrate without risk of contamination.
Stage 1: Vaporization of the Source Material
A solid, pure metal, known as a 'target', is placed inside the chamber. The machine then uses a high-energy method, such as a cathodic arc or sputtering, to bombard this target. This action vaporizes the solid material, dispersing its atoms throughout the chamber.
Stage 2: Introduction of Reactive Gases
To create even harder ceramic coatings (like titanium nitride), the machine introduces precisely controlled reactive gases, most commonly nitrogen. The vaporized metal atoms react with this gas mid-flight, forming a new compound before they even reach the product.
Stage 3: Atomic-Level Deposition
The vaporized metal or metal-ceramic compound then condenses onto the surfaces of the parts placed in the chamber. Because this happens atom-by-atom, the new layer is exceptionally dense, uniform, and strongly bonded to the substrate, making it almost impossible to remove.
Beyond the Machine: The Complete PVD Workflow
A PVD machine does not operate in isolation. It is the central component of a multi-stage industrial process that demands precision at every step.
Meticulous Surface Preparation
The final coating is only as good as the surface it is applied to. Before entering the PVD machine, parts must be perfectly cleaned, and any old coatings or impurities must be stripped away. A flawless substrate is non-negotiable for proper adhesion.
Fixturing and Loading
Parts are carefully mounted on specialized racks or fixtures inside the machine. This step is critical to ensure all relevant surfaces are evenly exposed to the vapor source for a uniform coating.
Post-Coating Quality Control
After the cycle is complete, the coated parts undergo inspection. This often includes thickness measurements and visual checks to ensure the coating meets all quality and performance specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, PVD technology has specific characteristics that make it suitable for some applications more than others.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the vapor travels in a relatively straight line from the source to the substrate, it can be challenging to uniformly coat highly complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes. Parts must be fixtured to expose all critical surfaces.
High Initial Investment
PVD machines and their supporting equipment represent a significant capital investment. The process requires a controlled environment, skilled operators, and a robust quality control workflow, which must be factored into the cost.
The Coating Reveals, Not Hides
A PVD coating is extremely thin and will conform to the existing surface texture. It is not a thick layer that can hide scratches, tool marks, or other surface imperfections. The initial surface finish of the part must be exactly what you want the final finish to be.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Deciding to use PVD coating is a strategic choice based on your product's performance requirements and market position.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of functional components: PVD is the definitive choice for adding superior hardness and wear resistance to items like drill bits, surgical tools, and engine parts.
- If your primary focus is a decorative, highly durable finish: PVD provides a long-lasting and tarnish-resistant surface for products like faucets, door hardware, and jewelry that is far superior to traditional plating.
- If your primary focus is environmental and worker safety: PVD is a clean, dry vacuum process that produces no hazardous waste, making it an excellent and responsible alternative to chemical-based processes like chrome plating.
Ultimately, integrating PVD technology is a decision to fundamentally upgrade the physical value and engineered performance of your products.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition in a high-vacuum chamber |
| Coating Type | Extremely thin, dense, atomically-bonded layers |
| Primary Benefits | Superior hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical instruments, decorative hardware |
| Key Consideration | Line-of-sight process; requires meticulous surface prep |
Ready to upgrade your product's performance with PVD coating?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precision surface engineering. Our expertise can help you integrate PVD technology to achieve superior hardness, durability, and a competitive edge for your products.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD solutions can meet your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















