In short, PVD coating costs can range from less than a dollar per piece for massive volumes of small items to hundreds of dollars for a single, large, complex component. The final price is not based on the coating material itself but is overwhelmingly determined by the part's size, the quantity being coated per batch, and the labor required for handling.
The most critical concept to understand is that you aren't buying a material; you are renting time and space in a highly specialized vacuum chamber. The cost per piece is fundamentally a calculation of how many of your parts can fit into a single machine cycle.

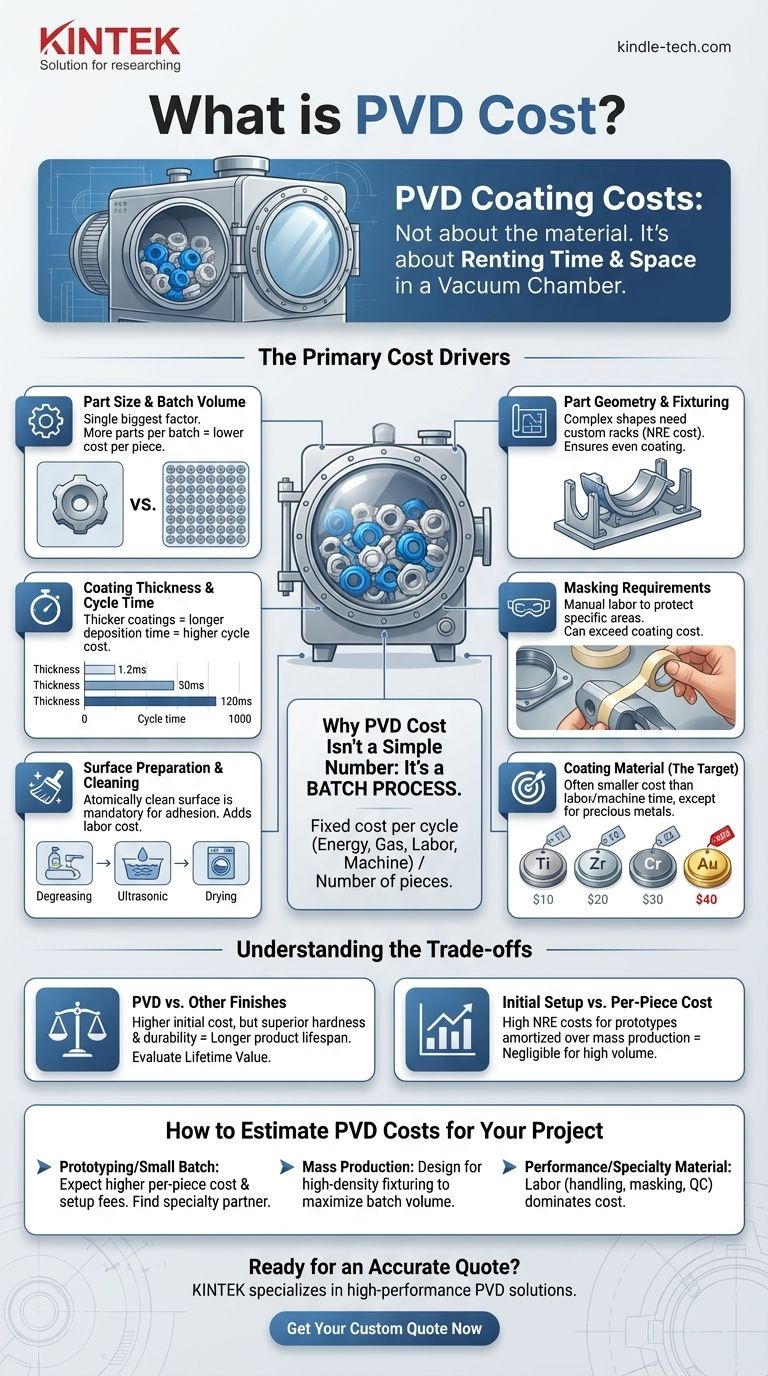
Why PVD Cost Isn't a Simple Number
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a batch process, much like baking in an industrial oven. There is a significant fixed cost to run one complete cycle—this includes energy, inert gases, skilled labor, and machine depreciation.
The final per-piece price is simply that fixed cycle cost divided by the number of pieces that fit into the batch. This is why a single prototype can be expensive, while the 10,000th piece in a production run can be remarkably cheap.
The Primary Cost Drivers in Detail
Several key variables directly influence the fixed cost of a PVD cycle and how many parts can be processed within it.
Part Size and Batch Volume
This is the single most dominant factor. The goal of a PVD provider is to maximize the surface area being coated in a single run.
Ten thousand small screws might fit in one cycle, leading to a very low per-piece cost. In contrast, one large automotive wheel might take up that same amount of space, making its coating cost substantially higher.
Part Geometry and Fixturing
How a part is held inside the chamber is critical. Complex shapes may require custom-designed racks or fixturing to ensure the coating is applied evenly.
The cost of designing and fabricating these fixtures (a non-recurring engineering or NRE cost) is factored into the total price, especially for new projects.
Coating Thickness and Cycle Time
A thicker coating requires a longer deposition time inside the chamber. The longer the machine has to run for a single batch, the higher the cycle cost will be.
Most decorative PVD coatings are extremely thin (a few microns), so this is often a larger factor for functional or industrial coatings that demand greater thickness for wear resistance.
Masking Requirements
If only a specific area of your part needs to be coated, the other areas must be physically masked. This is often a meticulous and manual labor process.
The time and skill required for masking can easily become one of the most significant cost components for complex parts, sometimes exceeding the cost of the coating process itself.
Surface Preparation and Cleaning
PVD requires an atomically clean surface for proper adhesion. Parts must go through a multi-stage, rigorous cleaning process before they ever enter the coating chamber.
Any oil, residue, or even fingerprints from handling will cause the coating to fail. This necessary pre-treatment step adds to the labor and overall cost.
Coating Material (The Target)
While important, the cost of the raw coating material (the "target," such as titanium or zirconium) is often a smaller part of the final price than most people assume.
The cost of machine time, energy, and labor typically outweighs the cost of the consumable material, unless you are using precious metals like gold or platinum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Evaluating PVD on price requires looking beyond the per-piece quote and considering the entire manufacturing context.
The Myth of "Expensive" Materials
A coating made from a more "expensive" material may not result in a higher per-piece cost.
If that material deposits more quickly, it could reduce the overall cycle time. The savings from shorter machine time can easily offset the higher raw material cost.
Initial Setup vs. Per-Piece Cost
Be prepared for initial setup fees, especially for custom fixtures. This cost can seem high but is amortized over the life of the production run.
For high-volume production, these NRE costs become a negligible part of the per-piece price. For a short run or prototype, they are a significant factor.
PVD vs. Other Finishes
PVD is often more expensive upfront than processes like painting or electroplating. However, its superior hardness, wear resistance, and chemical stability can result in a much longer product lifespan.
The true cost should be evaluated based on the lifetime value and durability, not just the initial production cost.
How to Estimate PVD Costs for Your Project
To determine if PVD is a financially viable option, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or a small batch: Expect a higher per-piece cost and be prepared for setup fees. The key is to find a coating partner that specializes in small, quick-turnaround runs.
- If your primary focus is mass production: Your design is the biggest cost lever. Design the part and the process to maximize the number of units that can be fixtured into a single PVD batch.
- If your primary focus is performance with a specialty material: While the material itself is a factor, the labor for handling, masking, and quality control for a high-spec part will likely be the dominant cost drivers.
By understanding these core drivers, you can design for manufacturability and make PVD a cost-effective solution for your application.
Summary Table:
| Cost Driver | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Part Size & Batch Volume | Single biggest factor. More parts per batch = lower cost per piece. |
| Part Geometry & Fixturing | Complex shapes may require custom fixtures, adding a setup cost. |
| Masking Requirements | Manual labor to mask specific areas can be a major cost component. |
| Surface Preparation | Rigorous cleaning is mandatory for adhesion, adding to labor costs. |
| Coating Thickness | Thicker coatings require longer cycle times, increasing the cost. |
| Coating Material | Often a smaller factor than labor and machine time, except for precious metals. |
Ready to Get an Accurate Quote for Your PVD Coating Project?
Understanding the cost drivers is the first step. Partnering with the right supplier is the next. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance PVD coating solutions for laboratories and manufacturers.
We help you optimize your design for cost-effective coating, whether you're prototyping a single component or scaling up for mass production. Our expertise ensures you get the durable, high-quality finish your products demand.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and see how we can add value to your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















