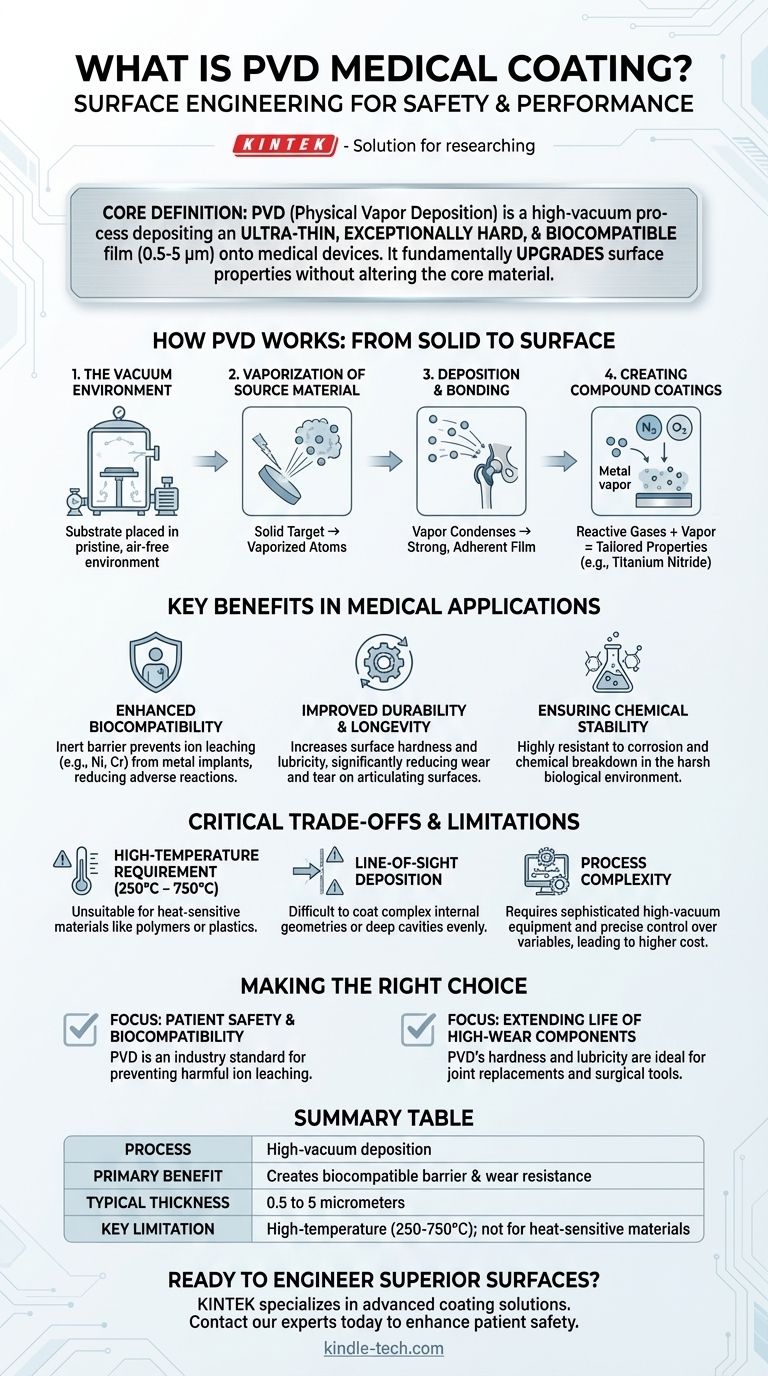
At its core, PVD medical coating is a high-vacuum process that deposits an ultra-thin, exceptionally hard, and biocompatible film onto the surface of a medical device or implant. This technique transforms the surface properties of an instrument or component by adding a new layer, one molecule at a time, to improve its safety and performance within the human body. Key applications include preventing the leaching of metal ions and increasing the wear resistance of surgical implants.
The central purpose of PVD coating in medicine is not just to cover a device, but to fundamentally upgrade its surface. It solves critical challenges of biocompatibility and durability by creating a stable, functional barrier between the device material and the biological environment.

How the PVD Process Works: From Solid to Surface
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a family of processes, but they all share a common, multi-stage principle that occurs within a high-vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is essential for the purity and quality of the final coating.
The Vacuum Environment
First, the medical component to be coated (the substrate) is placed in a vacuum chamber. All air and impurities are removed to create a pristine environment, ensuring the coating material does not react with contaminants like oxygen or nitrogen unless intended.
Vaporization of the Source Material
A solid source material, known as the target, is converted into a vapor. This is the "Physical Vapor" part of the name. Common methods include evaporation, which uses heat from an electron beam or cathodic arc, and sputtering, which bombards the target with energetic ions to physically knock atoms loose.
Deposition and Bonding
The vaporized atoms travel through the vacuum and condense onto the surface of the medical device, forming a thin, dense, and highly-adherent film. This process often involves bombarding the substrate with positive ions, which promotes a very strong bond between the coating and the device material.
Creating Compound Coatings
During the deposition phase, reactive gases like nitrogen or oxygen can be introduced into the chamber. These gases combine with the metal vapor to form specific ceramic compounds (like Titanium Nitride), allowing for the precise tailoring of the coating's physical and chemical properties.
Key Benefits in Medical Applications
The true value of PVD is realized in how it solves specific problems for devices used inside the human body. The coatings are extremely thin, typically between 0.5 and 5 micrometers, yet they provide significant functional improvements.
Enhancing Biocompatibility
Many high-strength metal alloys used in implants contain elements like nickel or chromium. PVD coatings create an inert barrier that prevents these ions from leaching into the body, which could otherwise cause allergic reactions or other adverse effects.
Improving Durability and Longevity
For high-wear components like the articulating surfaces of joint implants, PVD coatings provide a much harder surface. This "metal to metal" lubricity and enhanced hardness significantly reduces wear and tear, extending the functional life of the implant.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
The human body is a corrosive environment. PVD films are highly resistant to corrosion and chemical breakdown, ensuring the long-term stability and integrity of the device once it has been implanted.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is a specialized process with specific requirements and limitations that must be considered during device design and manufacturing.
High-Temperature Requirement
The PVD process must be performed at high temperatures, typically ranging from 250°C to 750°C. This makes it an excellent choice for robust metals but unsuitable for heat-sensitive materials like most polymers or plastics, which would deform or melt.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
The vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This "line-of-sight" characteristic means that coating complex internal geometries or deep, narrow cavities can be challenging and may result in an uneven film thickness.
Process Complexity
PVD is not a simple dipping or spraying process. It requires sophisticated, high-vacuum equipment and precise control over numerous variables, including pressure, temperature, and gas composition, which makes it a more complex and costly procedure than other surface treatments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating technology depends entirely on the primary problem you need to solve for your medical device.
- If your primary focus is patient safety and biocompatibility: PVD is an industry standard for creating an inert barrier to prevent harmful ion leaching from metallic implants.
- If your primary focus is extending the life of a high-wear component: The exceptional hardness and lubricity of PVD coatings make them ideal for the articulating surfaces of joint replacements and surgical tools.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive or complex geometric part: You must recognize that the high-temperature, line-of-sight nature of PVD may make it unsuitable, requiring the exploration of alternative methods.
Ultimately, PVD coating offers a powerful method to engineer the surface of a medical device, making it safer and more durable without altering its core structure.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | High-vacuum deposition of ultra-thin, hard films. |
| Primary Benefit | Creates a biocompatible barrier and increases wear resistance. |
| Typical Thickness | 0.5 to 5 micrometers. |
| Key Limitation | High-temperature process (250°C - 750°C); not for heat-sensitive materials. |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces for your medical devices?
KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions for the medical industry. Our expertise in PVD processes can help you achieve the critical biocompatibility and durability your implants and surgical tools require. We provide the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise, reliable coating development.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project and enhance patient safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Thermocouple Protection Tube
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition











