In material science and manufacturing, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated coating process that takes place in a high-vacuum environment. Unlike traditional wet plating methods, PVD transforms a solid coating material into a vapor, which then condenses onto a target object atom-by-atom, creating a very thin, highly durable, and high-performance surface layer.
PVD is not a simple paint or dip; it's an advanced surface engineering technique. Its core value lies in creating coatings that are molecularly bonded to the substrate, delivering superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic finishes in an environmentally friendly way.

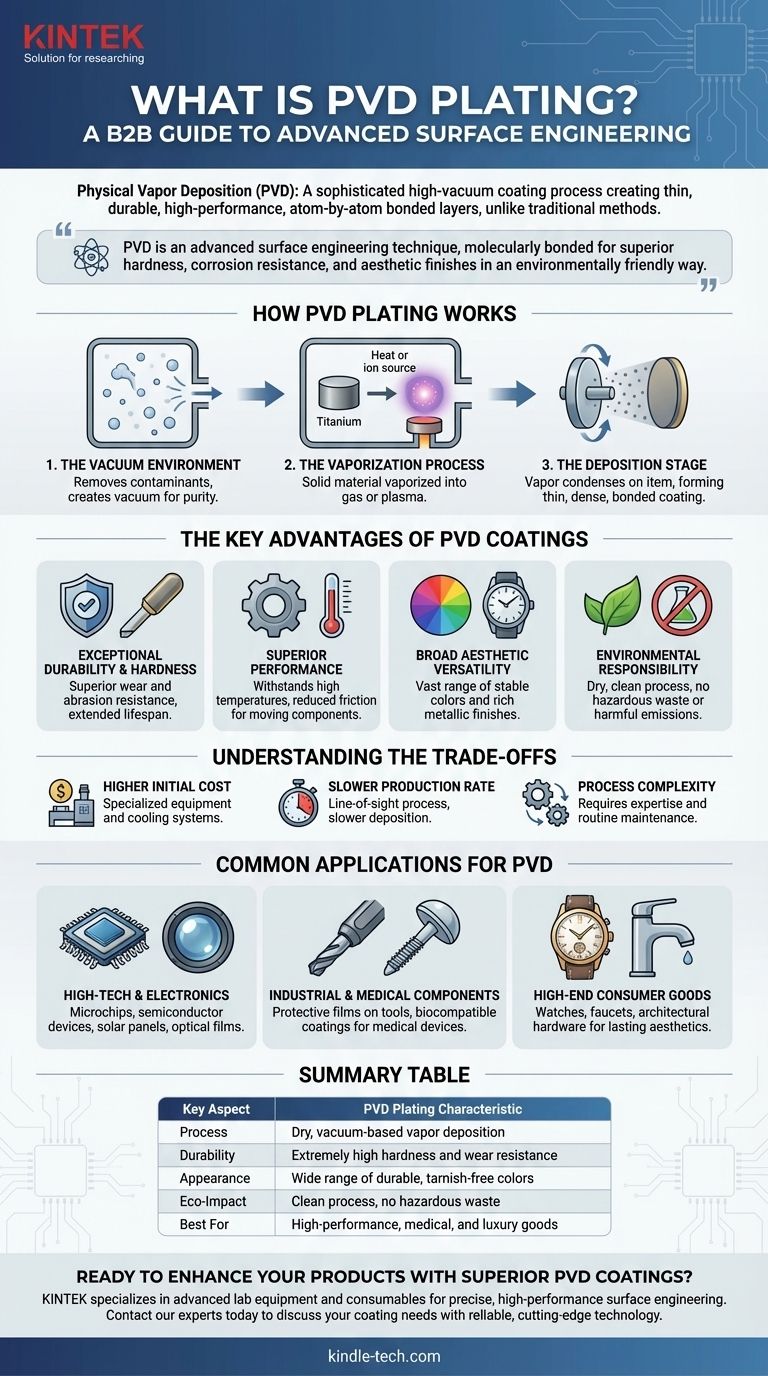
How PVD Plating Works
At its core, the PVD process involves three fundamental stages that occur inside a vacuum chamber. This controlled environment is critical for ensuring the purity and quality of the final coating.
The Vacuum Environment
First, all the air and contaminants are removed from a chamber to create a vacuum. This step is essential because it prevents airborne particles from reacting with the coating material, ensuring an extremely pure and clean deposition.
The Vaporization Process
Next, a solid, high-purity coating material (such as titanium or chromium) is vaporized. This is typically achieved using heat or by bombarding the material with ions, turning the solid directly into a gas or plasma.
The Deposition Stage
The vaporized material then travels through the vacuum chamber and deposits onto the surface of the item being coated. This process forms a thin, dense, and tightly bonded film on the object's surface, creating the final PVD coating.
The Key Advantages of PVD Coatings
PVD is preferred in many industries because its resulting coatings offer a combination of functional and aesthetic benefits that traditional methods struggle to match.
Exceptional Durability and Hardness
PVD coatings are significantly harder and more corrosion-resistant than coatings applied by processes like electroplating. This results in excellent resistance to wear and abrasion, extending the lifespan of the coated part.
Superior Performance Characteristics
These coatings can withstand high temperatures and impacts. They also often provide a reduced coefficient of friction, which improves the efficiency and performance of moving components.
Broad Aesthetic Versatility
The process allows for a wide range of inorganic materials to be used, enabling a vast spectrum of colors and finishes. The resulting surfaces are fine, smooth, and have a rich metallic luster that is both attractive and long-lasting.
Environmental Responsibility
PVD is a dry, environmentally friendly process. Unlike electroplating or painting, it does not produce hazardous chemical waste or emit harmful substances, making it a much cleaner coating technology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not the universal solution for every application. Its primary limitations are related to cost, speed, and complexity.
Higher Initial Cost
The sophisticated equipment required for PVD, including vacuum chambers and cooling systems, makes it a more expensive process compared to traditional coating methods.
Slower Production Rate
PVD is a line-of-sight process that can have a slower rate of deposition or "yield" than batch processes like electroplating. This can limit its feasibility for very high-volume, low-cost manufacturing.
Process Complexity
Operating a PVD system requires specialized knowledge and routine maintenance. The reliance on a stable vacuum and a reliable cooling system adds layers of operational complexity.
Common Applications for PVD
The unique properties of PVD coatings make them indispensable in fields where performance, purity, and reliability are critical.
High-Tech and Electronics
PVD is used to create the incredibly thin, pure films necessary for manufacturing microchips, semiconductor devices, solar panels, and optical lenses.
Industrial and Medical Components
The technology is applied to create durable protective films on tools and machine parts, enhancing their lifespan. In medicine, it's used for coating medical devices where cleanliness, durability, and biocompatibility are essential.
High-End Consumer Goods
The combination of extreme durability and premium aesthetic finishes makes PVD a popular choice for luxury goods like watches, high-end faucets, and architectural hardware where a lasting, beautiful finish is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if PVD is the appropriate solution, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and performance: PVD is a superior choice for applications where wear, corrosion, and heat resistance are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is a premium, long-lasting aesthetic: PVD offers a vast range of stable, high-quality metallic finishes that will not tarnish or fade like traditional coatings.
- If your primary focus is environmental responsibility: PVD stands out as a significantly cleaner and more sustainable process than traditional methods like electroplating.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost on a mass-produced item: The higher cost and slower production rate of PVD may make traditional coating methods a more practical choice.
Ultimately, PVD plating represents a modern approach to surface engineering where performance, durability, and precision are the highest priorities.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | PVD Plating Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process | Dry, vacuum-based vapor deposition |
| Durability | Extremely high hardness and wear resistance |
| Appearance | Wide range of durable, tarnish-free colors |
| Eco-Impact | Clean process, no hazardous waste |
| Best For | High-performance, medical, and luxury goods |
Ready to enhance your products with superior PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise, high-performance surface engineering. Whether you're in medical device manufacturing, electronics, or luxury goods, our solutions deliver the durability and aesthetic quality your products demand. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your coating needs with reliable, cutting-edge technology.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















