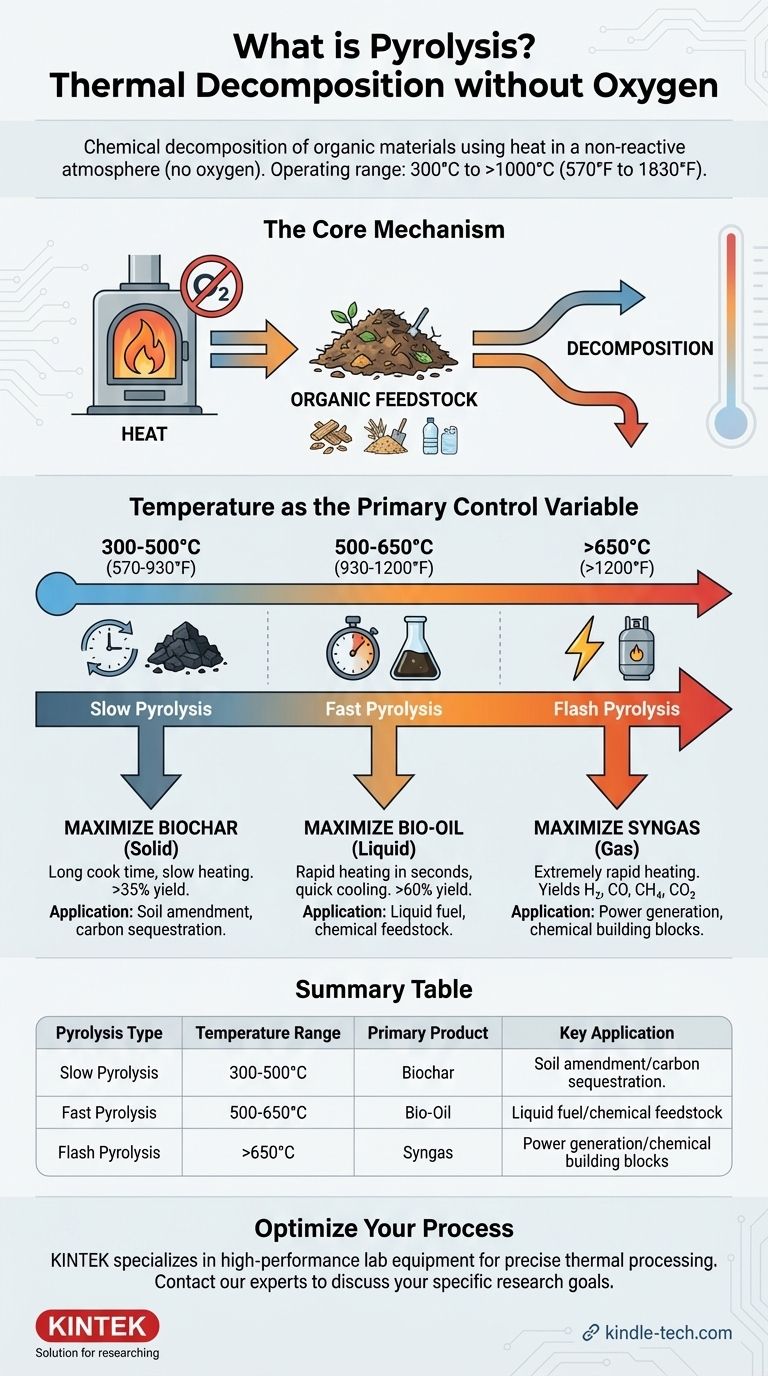
In essence, pyrolysis is the chemical decomposition of organic materials using heat in a non-reactive atmosphere, meaning an environment without oxygen. While there is no single "pyrolysis temperature," the process generally operates in a range from 300°C to over 1000°C (570°F to 1830°F). The specific temperature used is the most critical factor, as it directly determines whether the primary output is a solid (biochar), a liquid (bio-oil), or a gas (syngas).
The core principle to grasp is that pyrolysis isn't just about heating a substance. It's about precisely controlling the temperature and heating rate to selectively break down organic matter into your desired end product: char, oil, or gas.

The Core Mechanism: How Pyrolysis Works
Pyrolysis is a foundational thermochemical process. Understanding its key components is crucial to leveraging it effectively.
The Role of Heat and Absence of Oxygen
In the presence of oxygen, heat causes combustion (burning). By removing oxygen, pyrolysis prevents burning. Instead, the intense heat provides the energy to break the complex chemical bonds within the organic material, decomposing it into simpler, smaller molecules.
The Three Primary Products
This decomposition process typically yields three distinct products in varying proportions:
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid residue, similar to charcoal.
- Bio-oil: A dense, acidic liquid also known as pyrolysis oil or tar.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable, combustible gases including hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH₄), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Temperature as the Primary Control Variable
The final output of pyrolysis is not random; it is a direct function of temperature and the rate of heating. By adjusting these parameters, you can optimize the process to maximize the yield of a specific product.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
This process uses lower temperatures, typically 300-500°C, and a slow heating rate. The material is "cooked" for an extended period, sometimes for hours. These conditions limit the vaporization of compounds, maximizing the output of the solid biochar, which can make up over 35% of the product by weight.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-Oil
To produce liquid fuel, fast pyrolysis is used. It involves very rapid heating to moderate temperatures, around 500-650°C. The organic material is heated in seconds, and the resulting vapors are quickly cooled and condensed. This process is designed to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil, which can be over 60% of the product by weight.
Flash Pyrolysis: Maximizing Syngas
At very high temperatures, typically above 650°C and often exceeding 1000°C, and with extremely rapid heating rates, the process is geared towards gas production. These harsh conditions crack the organic molecules into the smallest possible gaseous components, maximizing the yield of syngas. This gas can then be used to generate electricity or as a chemical building block.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a simple solution. Real-world application requires acknowledging its complexities.
Feedstock Is Critical
The composition of the input material (the "feedstock")—whether it's wood, agricultural waste, plastic, or tires—has a profound impact on the efficiency of the process and the quality of the end products. A system optimized for wood chips will not perform the same way with shredded plastic.
Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an endothermic process, meaning it requires a continuous input of energy to maintain its high operating temperatures. A successful system must be designed so that the energy value of the products is significantly greater than the energy required to run the process.
Product Handling and Upgrading
The raw products of pyrolysis often require further processing. Bio-oil is corrosive and chemically unstable, typically needing to be "upgraded" before it can be used as a drop-in fuel. Syngas must be cleaned of tars and other impurities before it can be used in engines or turbines.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The right pyrolysis method depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the ideal path to maximize biochar production.
- If your primary focus is creating a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock: Fast pyrolysis is the most effective method for producing high yields of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating a combustible fuel gas for power: Flash or high-temperature pyrolysis will maximize your output of syngas.
By treating temperature as a precise control dial, you can effectively transform organic materials into a range of valuable products.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature Range | Primary Product | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | 300-500°C | Biochar (Solid) | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Fast Pyrolysis | 500-650°C | Bio-oil (Liquid) | Liquid fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Flash Pyrolysis | >650°C (often >1000°C) | Syngas (Gas) | Power generation, chemical building blocks |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Whether you're developing new biochar applications, refining bio-oil production, or optimizing syngas yields, our solutions provide the exact temperature control and reliability your laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific pyrolysis research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















