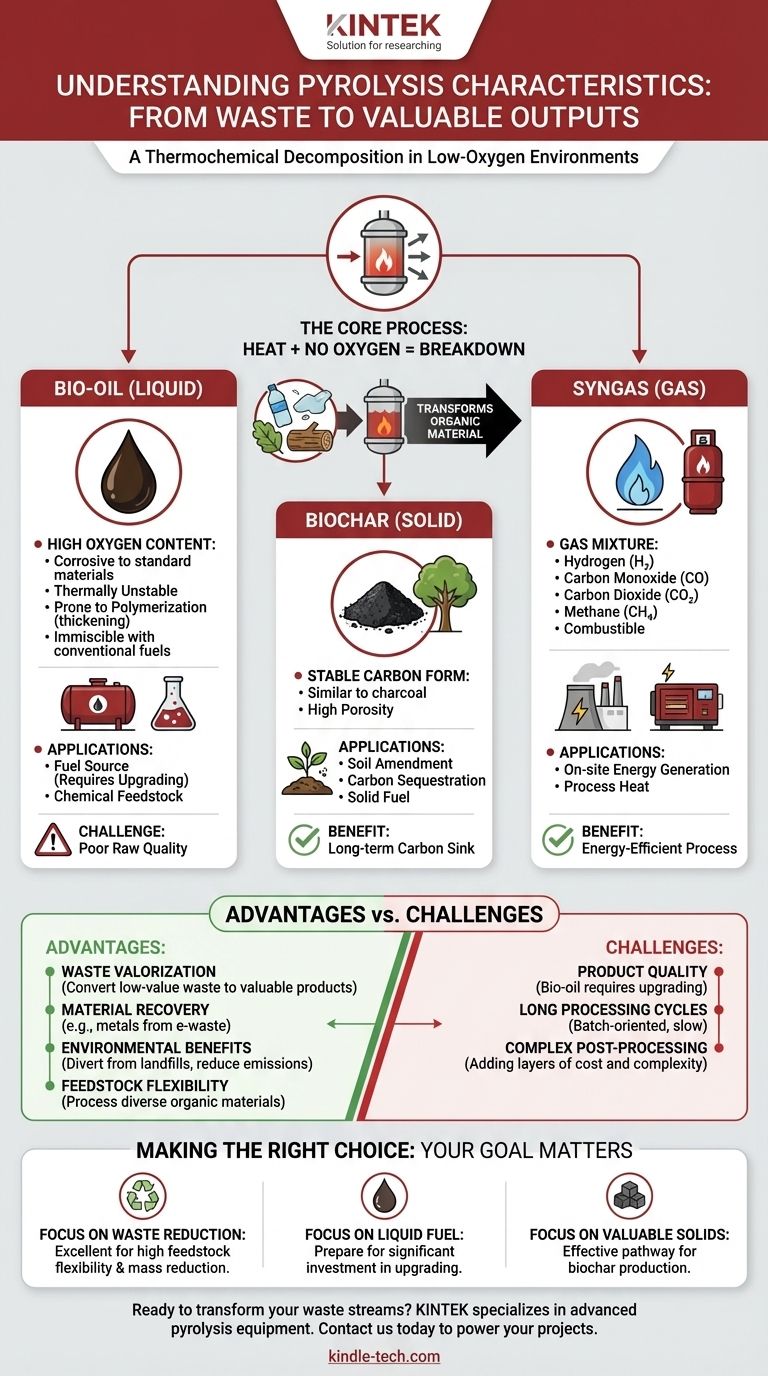
In essence, pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition process where organic material is heated at high temperatures in a low-oxygen or completely oxygen-free environment. This process transforms waste materials like wood, plastic, or biomass into valuable outputs. Instead of burning the material, the heat breaks down its molecular structure, resulting in solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Pyrolysis is a powerful tool for converting waste into resources, but its primary characteristic is this duality: it creates valuable outputs (like fuel and char) while also presenting significant technical challenges, particularly in the quality and stability of its liquid product, bio-oil.

The Core Process: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Defining Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is not burning. It is the thermal degradation of a substance in an inert atmosphere, meaning an environment with very little or no oxygen.
By preventing combustion, the process breaks down large organic molecules into smaller, simpler ones, which are then captured as new products.
The Three Primary Products
The output of pyrolysis is always a mix of three distinct forms:
- Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil): A dark, viscous liquid.
- Biochar: A solid, carbon-rich residue, similar to charcoal.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable gases.
The ratio of these three products depends heavily on the feedstock material, temperature, and processing time.
Characteristics of Pyrolysis Products
Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil)
The liquid product of pyrolysis is often the most sought-after, but it has challenging characteristics. Due to its high oxygen content, it is fundamentally different from petroleum fuels.
This high oxygen content makes the oil:
- Corrosive to standard pipes and containers.
- Thermally unstable, meaning it can degrade or change with heat.
- Prone to polymerization (thickening and solidifying) when exposed to air.
- Immiscible with conventional hydrocarbon fuels, making it difficult to blend.
Biochar
The solid product, biochar, is a stable form of carbon. It is the same principle behind making charcoal from wood.
This material can be used as a solid fuel or, more increasingly, as a valuable soil amendment in agriculture to improve water retention and sequester carbon.
Syngas
The gaseous product, syngas, is a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane. This gas has fuel value and can be combusted on-site to provide the energy needed to run the pyrolysis process itself, making the system more energy-efficient.
Advantages of the Pyrolysis Process
Waste Valorization
The core advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to convert low-value or negative-value organic waste (like plastic, tires, or agricultural residue) into valuable products like fuels and chemicals.
Material Recovery
Pyrolysis is an effective method for recovering valuable materials from a mixed waste stream. For example, it can separate carbon black and steel from old tires or recover valuable metals from electronic waste.
Environmental Benefits
By diverting waste from landfills and creating fuel from renewable sources, pyrolysis can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When the biochar is used in soil, it acts as a long-term carbon sink.
Feedstock Flexibility
Pyrolysis furnaces are highly flexible and can be designed to process a wide range of organic materials, from wood and crops to plastics and sewage sludge.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Product Quality and Stability
The most significant challenge is the poor quality of the raw pyrolysis oil. As noted, it is corrosive, unstable, and cannot be directly used in modern engines or refineries without significant, and often expensive, upgrading.
Long Processing Cycles
Depending on the specific technology and application, such as thermal debinding in manufacturing, pyrolysis can be a slow, batch-oriented process with long cycle times compared to other methods.
Complex Post-Processing
The direct outputs of pyrolysis rarely represent the final product. The oil needs upgrading, the char may need to be processed into pellets, and the gas may need cleaning, adding layers of complexity and cost to the overall system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if pyrolysis is the right solution, you must first clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis is an excellent choice due to its high feedstock flexibility and ability to dramatically reduce the mass of organic waste.
- If your primary focus is liquid fuel production: Be prepared for significant investment in post-processing and upgrading equipment to handle the corrosive and unstable nature of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable solids: Pyrolysis is a highly effective and direct pathway for producing biochar for agriculture or specialized carbon products.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a transformative technology, but its success depends on a clear-eyed understanding of both its powerful benefits and its inherent material challenges.
Summary Table:
| Product | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil) | Dark, viscous liquid; high oxygen content; corrosive and unstable | Fuel source (requires upgrading), chemical feedstock |
| Biochar | Solid, carbon-rich residue; stable | Solid fuel, soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Syngas | Mixture of H₂, CO, CO₂, CH₄; combustible | On-site energy generation, process heat |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis equipment and consumables, tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're focused on waste reduction, fuel production, or material recovery, our solutions ensure efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can power your pyrolysis projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What is the major product of pyrolysis? Tailoring the Output for Your Specific Needs
- What is calcination mainly used for? Purify and Transform Materials with High-Temp Processing
- What is the use of biochar from pyrolysis? Unlock its potential as fuel, material, and soil amendment
- What is the structure of a rotary hearth furnace? A Guide to Continuous, Uniform Heating
- What are the factors affecting biochar production? Key Variables to Engineer Biochar for Your Application
- Which catalyst used in biomass pyrolysis for production of bio-oil? Select the Right Catalyst for Your Bio-Oil



















