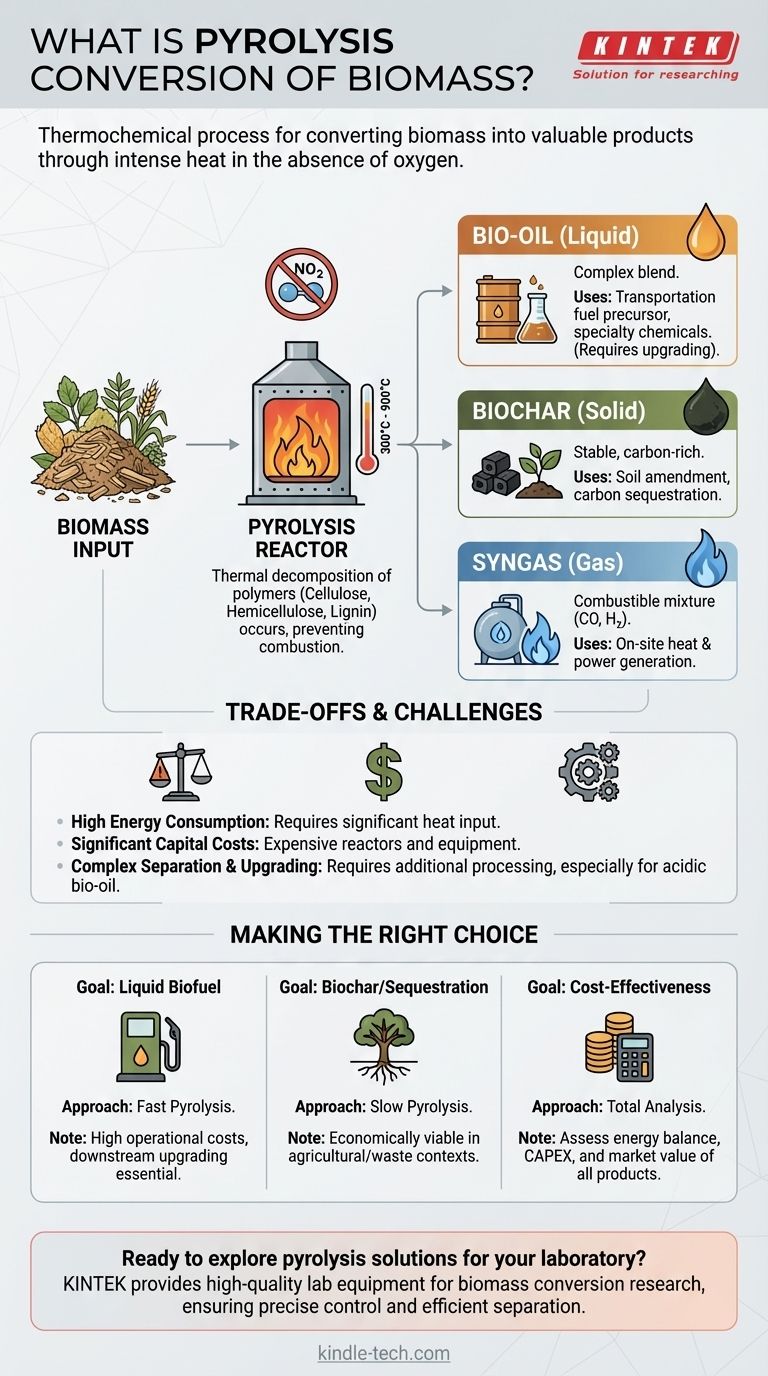
In essence, pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that converts biomass, such as wood, agricultural waste, or organic refuse, into valuable products. It achieves this by heating the material to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen, causing it to thermally decompose rather than burn. The primary outputs are a liquid known as bio-oil, a solid carbon-rich material called biochar, and a combustible gas mixture called syngas.
Pyrolysis offers a promising pathway to convert waste into energy, but it is not a simple solution. The process is defined by a critical trade-off between its potential to create valuable products and its significant energy requirements and high capital costs.

The Core Mechanism: How Pyrolysis Works
Pyrolysis fundamentally changes the chemical structure of organic material through intense heat in a controlled environment. Understanding this core mechanism is key to evaluating its applications.
The Role of Heat and Oxygen Deprivation
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is heating biomass in the absence of oxygen. This is crucial because it prevents combustion (burning). Instead of burning away, the complex organic polymers within the biomass—cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—break down into smaller, simpler molecules.
This process occurs at temperatures ranging from 300°C to over 900°C, depending on the desired outcome.
The Three Primary Products
The thermal decomposition of biomass yields a mixture of products in three different states:
- Bio-oil (Liquid): A dark, dense liquid often called pyrolysis oil. It is a complex blend of oxygenated organic compounds and can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used to produce specialty chemicals.
- Biochar (Solid): A stable, carbon-rich solid that resembles charcoal. It can be used as a soil amendment to improve fertility and water retention or as a method for long-term carbon sequestration.
- Syngas (Gas): A mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂). This gas can be burned on-site to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction, improving the process's overall energy efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While scientifically sound, the practical implementation of pyrolysis on a commercial scale faces several significant hurdles. These challenges must be factored into any serious evaluation of the technology.
High Energy Consumption
The process is inherently energy-intensive. Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for decomposition consumes a substantial amount of energy. While the syngas produced can offset some of this demand, the initial energy input remains a major operational cost.
Significant Capital Costs
Pyrolysis reactors and the associated equipment needed to handle feedstocks and process the outputs are expensive. The high capital investment required can make the technology inaccessible, particularly for smaller-scale applications or in regions with limited financial resources.
Complex Product Separation and Upgrading
The raw output of a pyrolysis reactor is a mixed stream of gas, liquid, and solid. Separating these components efficiently requires additional equipment and energy, adding to the overall cost and complexity.
Furthermore, the raw bio-oil is often acidic, unstable, and has a lower energy density than conventional fossil fuels. It typically requires significant and costly refining or upgrading before it can be used as a direct substitute for gasoline or diesel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating pyrolysis requires aligning the process with your specific objective, as different goals demand different approaches and present unique economic challenges.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuel: You will need a "fast pyrolysis" setup, but must be prepared for the high operational costs and the absolute necessity of a downstream bio-oil upgrading facility.
- If your primary focus is creating biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: A "slow pyrolysis" process is more suitable, as it maximizes the solid yield and can be more economically viable in agricultural or waste management contexts.
- If your primary focus is overall cost-effectiveness: You must perform a rigorous analysis of the total energy balance, capital expenditure, and the market value of all three product streams (bio-oil, biochar, and syngas).
By understanding these fundamental principles and their associated trade-offs, you can make an informed decision on whether pyrolysis is the correct technological path for your objectives.
Summary Table:
| Product | State | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-oil | Liquid | Transportation fuel precursor, specialty chemicals |
| Biochar | Solid | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Syngas | Gas | On-site heat generation, process energy |
Ready to explore pyrolysis solutions for your laboratory or project? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research. Whether you're developing new pyrolysis processes or optimizing existing ones, our reliable equipment helps you achieve precise temperature control and efficient product separation. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sustainable energy goals with tailored laboratory solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is the density of plasma matter? Exploring the Universe's Widest Range of Densities
- What are the problems with electric arc furnace? Balancing High Costs with Unmatched Flexibility
- What is RF sputtering of oxide materials? A Guide to Depositing High-Quality Insulating Films
- Why is a high-precision constant temperature stirring reaction device necessary for functionalized BNNS grafting?
- What features do ultra-low temperature freezers typically include? Ensuring Absolute Sample Security
- What is the difference between electric arc furnace and plasma arc furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Heat Processing Needs
- What is the process of pyrolysis in the lab? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- What are the different types of nitriding process? Gas, Salt Bath, or Plasma?



















