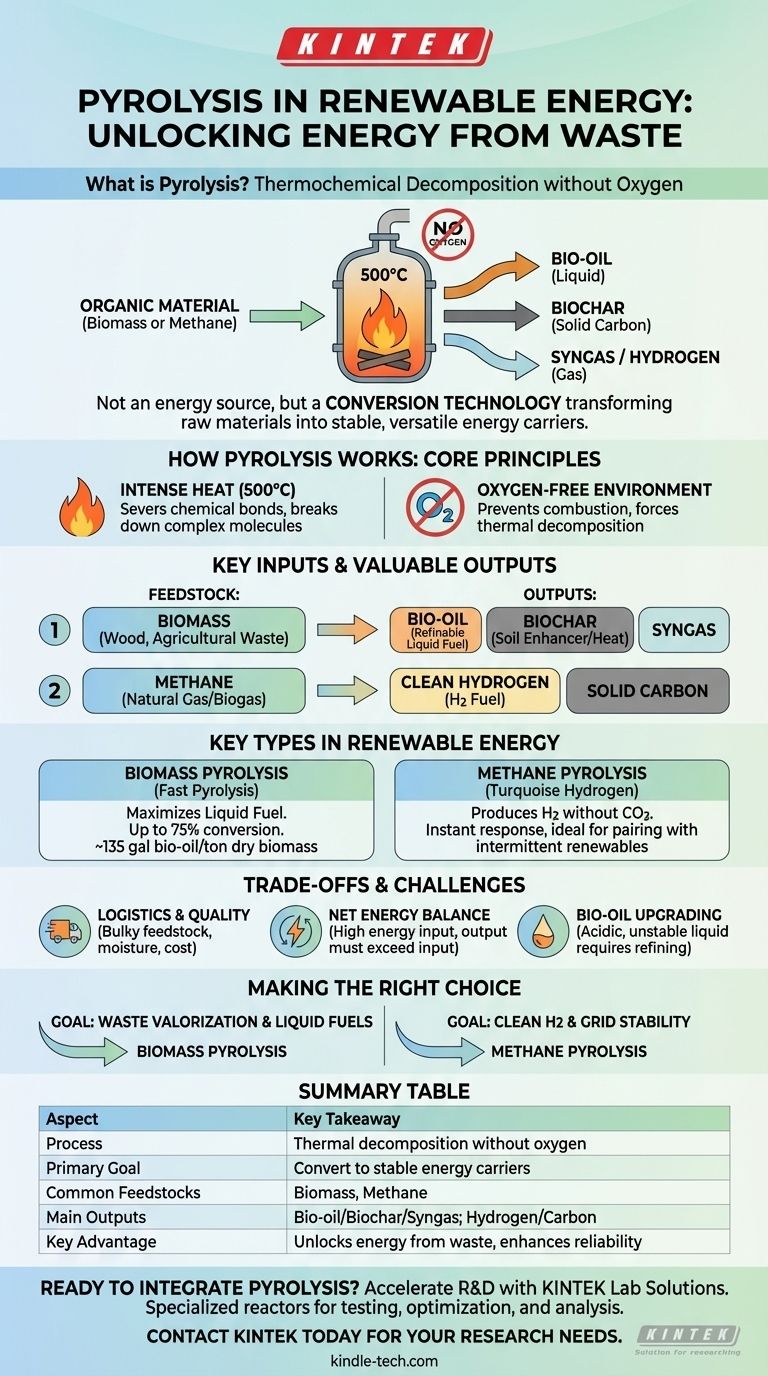
In the context of renewable energy, pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic material at high temperatures—typically around 500°C—in a completely oxygen-free environment. Instead of burning, this process breaks down materials like biomass or methane into more valuable energy products. The primary outputs are a liquid biofuel known as bio-oil, a solid carbon residue called biochar, and a gas mixture (syngas), or in some cases, pure hydrogen.
Pyrolysis is not an energy source itself, but rather a crucial conversion technology. It unlocks the chemical energy stored in raw materials, transforming them into stable, transportable, and more versatile fuels that enhance the reliability of the entire renewable energy system.

How Pyrolysis Works: The Core Principles
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal decomposition. By removing oxygen, we prevent combustion and instead force complex organic molecules to break apart into simpler, more useful ones.
The Role of Heat and an Oxygen-Free Environment
Heating biomass or other feedstocks in the absence of oxygen is the defining characteristic of pyrolysis. Without oxygen, the material cannot catch fire.
Instead, the intense heat severs the chemical bonds within the material, breaking down large, complex molecules into smaller, lighter ones that are collected as liquid (bio-oil) and gas (syngas). What remains is a solid, carbon-rich substance called biochar.
Key Inputs: Feedstocks
The versatility of pyrolysis allows it to process a wide range of inputs. The most common feedstocks include:
- Biomass: Organic matter like wood, corn stover, perennial grasses, and agricultural waste.
- Methane (CH₄): Natural gas or biogas can be split into hydrogen and solid carbon.
Valuable Outputs: Energy Carriers
The outputs of pyrolysis depend on the feedstock and process conditions. The primary products are valuable energy carriers.
From biomass, you get bio-oil, a liquid that can be refined into transportation fuels, and biochar, a charcoal-like solid that can improve soil health or be burned for heat.
From methane, the primary output is clean hydrogen (H₂) fuel and solid, inert carbon.
Key Types of Pyrolysis in Renewable Energy
While the core principle remains the same, different applications of pyrolysis serve distinct goals within the renewable energy landscape.
Biomass Pyrolysis: Creating Liquid Bio-oil
This is the most common form, often using a method called fast pyrolysis to maximize liquid fuel production.
The biomass is heated and cooled very rapidly, a process that can convert up to 75% of the input biomass into bio-oil. This yields approximately 135 gallons of bio-oil for every ton of dry biomass processed, turning low-value waste into a high-density liquid fuel.
Methane Pyrolysis: Generating Clean Hydrogen
This emerging technology offers a pathway to "turquoise hydrogen"—hydrogen produced without carbon dioxide emissions.
Using methods like microwave-powered reactors, methane (CH₄) is split into hydrogen gas (H₂) and solid carbon. A key advantage is its responsiveness; it can be turned on instantly with no ramp-up time, making it ideal for pairing with intermittent renewables like wind and solar to produce hydrogen whenever there is excess electricity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. It is essential to understand its limitations to assess its practical viability.
Feedstock Logistics and Quality
Biomass is often bulky, has high moisture content, and can be expensive to collect and transport to a processing facility. Variations in feedstock quality can also impact the efficiency of the process and the consistency of the final products.
Net Energy Balance
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires significant heat input. For the technology to be sustainable, the energy value of the outputs must be significantly greater than the energy required to run the process itself. This net energy balance is a critical factor in its economic feasibility.
Bio-oil Requires Upgrading
The bio-oil produced from biomass pyrolysis is not a "drop-in" replacement for gasoline or diesel. It is typically acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable. It must undergo further refining, known as upgrading, before it can be used in conventional engines or existing infrastructure, which adds cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deploying pyrolysis effectively means aligning the technology with a specific strategic objective.
- If your primary focus is on waste valorization and liquid fuels: Biomass pyrolysis is the ideal path for converting agricultural or forestry residues into a dense, storable, and transportable bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is on producing clean hydrogen and stabilizing the grid: Methane pyrolysis offers a highly scalable and responsive method for generating hydrogen on-demand, complementing intermittent renewable power sources perfectly.
Ultimately, pyrolysis serves as a critical bridge technology, transforming raw, often low-value materials into high-value energy carriers that make the renewable energy ecosystem more robust and flexible.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition of organic material in the absence of oxygen. |
| Primary Goal | Convert raw materials into stable, transportable energy carriers. |
| Common Feedstocks | Biomass (wood, agricultural waste), Methane (natural gas, biogas). |
| Main Outputs | Bio-oil, Syngas, Biochar (from biomass); Hydrogen & Carbon (from methane). |
| Key Advantage | Unlocks chemical energy from waste, enhancing renewable energy reliability. |
Ready to Integrate Pyrolysis Technology into Your Energy Strategy?
Whether you're developing a process for waste valorization or clean hydrogen production, having the right equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory reactors and systems that are essential for research, development, and optimization of pyrolysis processes.
We provide the precise, reliable lab equipment you need to:
- Test and characterize different feedstocks.
- Optimize process parameters like temperature and residence time.
- Analyze the quality and yield of your bio-oil, syngas, or hydrogen outputs.
Let our expertise in lab equipment and consumables support your renewable energy innovation. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your R&D and help you build a more sustainable future.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















