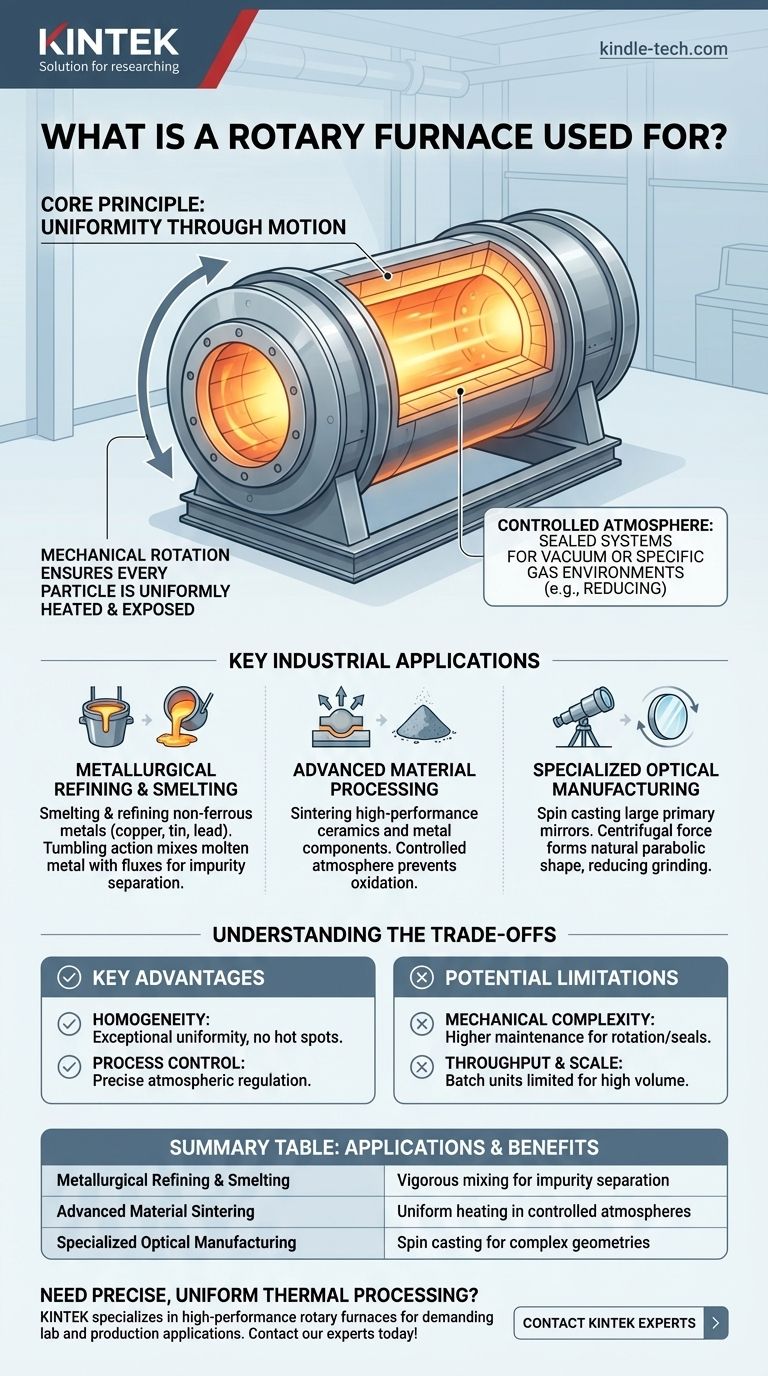
At its core, a rotary furnace is a high-temperature industrial furnace used for processes that require continuous mixing, uniform heat transfer, and controlled atmospheric conditions. Its primary applications span metallurgy, advanced materials processing, and specialized manufacturing, including the smelting of metals like copper and tin, the sintering of high-performance materials, and even the creation of large optical mirrors.
The defining feature of a rotary furnace is its ability to use mechanical rotation to ensure every particle of the material being processed is uniformly heated and exposed to the desired chemical environment. This makes it indispensable for tasks where homogeneity is critical.

The Core Principle: Uniformity Through Motion
The fundamental advantage of a rotary furnace comes from its rotating cylindrical design. Unlike a static furnace where material can sit unmixed, the constant tumbling action guarantees process consistency.
How It Works
A rotary furnace is essentially a cylindrical shell that rotates on its horizontal axis. The inside is lined with refractory materials—heat-resistant bricks or cements—to protect the steel shell from extreme temperatures, which can exceed 1000°C.
Material is fed into one end, and the rotation causes it to tumble and move progressively toward the other end, ensuring every part of the load is exposed to the heat source and internal atmosphere.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Many designs, particularly rotary tube furnaces, are sealed systems. This allows for precise control over the internal environment, enabling processes that must occur in a vacuum or under a specific gas, such as a reducing atmosphere, to prevent oxidation.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique combination of heat, mixing, and atmosphere control makes the rotary furnace versatile for several demanding applications.
Metallurgical Refining and Smelting
This is a primary use case. Rotary furnaces are used to smelt and refine non-ferrous metals. The tumbling action is crucial for mixing molten metal with fluxes, which helps separate impurities into a slag layer.
This process is effective for producing materials such as low-impurity bullion, copper matte, and various lead or tin alloys.
Advanced Material Processing
For materials science, the rotary furnace is ideal for sintering. This process uses heat to fuse powders into a solid mass without melting them.
The controlled atmosphere is critical here, as it prevents unwanted chemical reactions (like oxidation) that could compromise the final material's properties. This is vital for producing high-performance ceramics and metal components.
Specialized Optical Manufacturing
In a highly specialized application, rotary furnaces are used in a process called spin casting to create large primary mirrors for telescopes.
Molten glass is spun inside the furnace. Centrifugal force pushes the glass up the walls, naturally forming a parabolic surface—the precise shape needed for a telescope mirror, which dramatically reduces the need for later grinding and polishing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to proper application.
Key Advantage: Homogeneity
The single greatest benefit is the exceptional uniformity of the final product. The constant mixing eliminates hot spots and ensures consistent chemical reactions throughout the entire batch.
Key Advantage: Process Control
The ability to seal the chamber allows for unparalleled control over the processing atmosphere, which is impossible in many open-hearth or static furnace designs.
Potential Limitation: Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the drive system and seals, adds mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. This can lead to higher maintenance requirements to ensure reliable operation.
Potential Limitation: Throughput and Scale
While large continuous-feed rotary furnaces exist for bulk material processing, highly specialized batch units (like those for mirror casting) are by nature limited in throughput. The design must be matched to the required production volume.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is metal refining or separating impurities: The vigorous mixing action of a rotary furnace is ideal for ensuring complete interaction between molten metal and refining agents.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced powders or ceramics: The combination of uniform heating and precise atmosphere control is essential for sintering materials without contamination or oxidation.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing large, uniquely shaped glass or ceramic parts: The spin-casting capability offered by a rotating furnace provides a distinct advantage in forming complex geometries like parabolic mirrors.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace excels in any high-temperature process where consistency and uniformity are fundamental requirements for a successful result.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Metallurgical Refining & Smelting | Vigorous mixing for impurity separation |
| Advanced Material Sintering | Uniform heating in controlled atmospheres |
| Specialized Optical Manufacturing | Spin casting for complex geometries (e.g., telescope mirrors) |
| General High-Temperature Processing | Exceptional product homogeneity and consistency |
Need precise, uniform thermal processing for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including rotary furnaces designed for demanding applications like metal refining, material sintering, and advanced ceramics. Our solutions ensure the controlled atmosphere and consistent results your research or manufacturing requires. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research



















