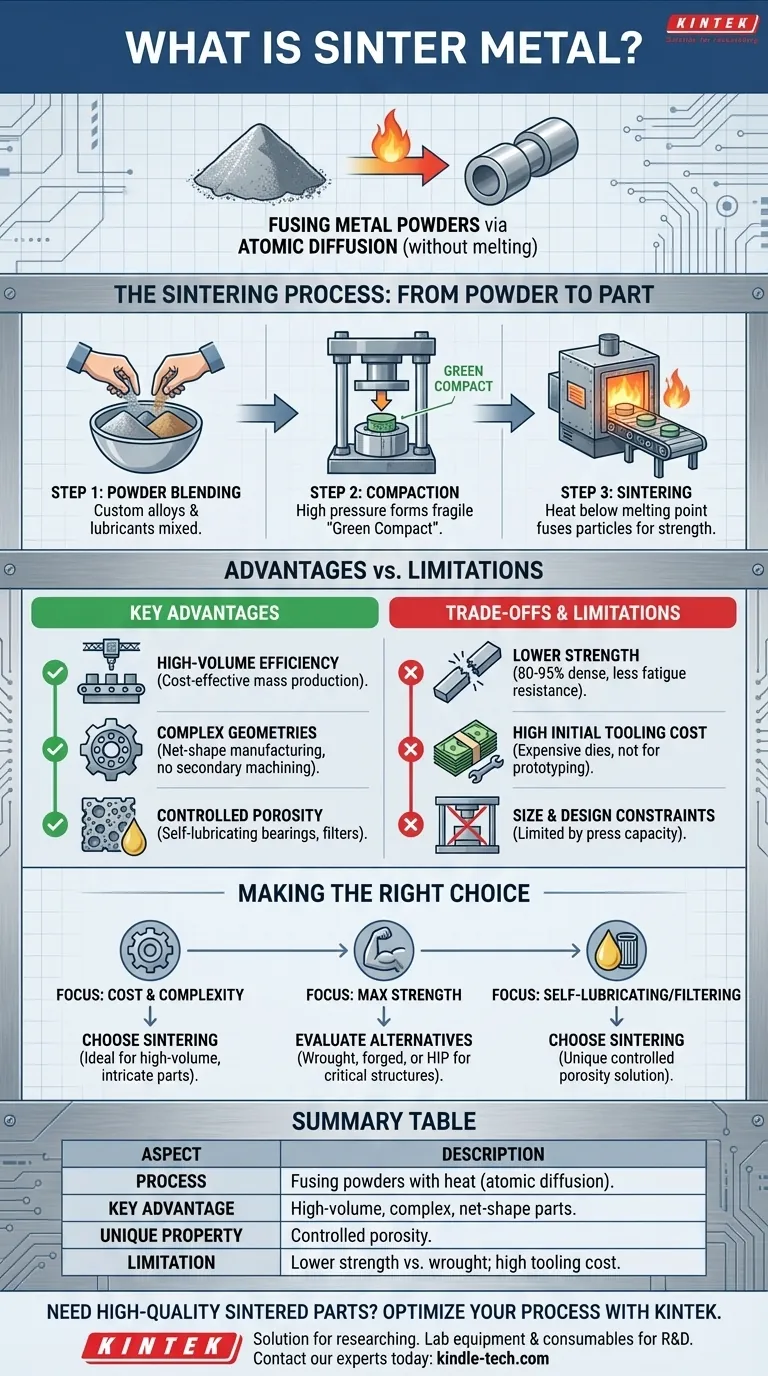
At its core, sinter metal is a material created by fusing metal powders together using intense heat, but without ever melting them. This process, part of a field called powder metallurgy, transforms a compacted powder blank into a solid, functional part with engineered strength and a specific geometry. It is a highly controlled method for creating net-shape or near-net-shape components.
Sintering is not just about creating a solid object; it's a strategic manufacturing choice. It enables the mass production of complex metal parts that are difficult or expensive to create using traditional subtractive methods like machining.
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Part
Understanding sinter metal requires understanding how it is made. The process is a precise, multi-stage journey from raw powder to a finished component.
Step 1: Powder Blending
The process begins by selecting and mixing specific metal powders. This allows for the creation of custom alloys and material composites that might be impossible to produce through melting and casting. Lubricants are also often added to aid in the compaction stage.
Step 2: Compaction
The blended powder is then poured into a high-precision die cavity and compacted under immense pressure, typically at room temperature. This action forms a fragile, weakly bonded part known as a "green compact" which has the desired shape but lacks structural strength.
Step 3: Sintering (The Critical Transformation)
The green compact is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a temperature below the metal's melting point. At this high temperature, the individual metal particles begin to fuse together through a process of atomic diffusion. The particle boundaries blur, forming strong metallurgical bonds, increasing density, and dramatically increasing the part's strength.
Key Advantages of Sintered Metals
Engineers and designers specify sintered parts to solve specific challenges related to cost, complexity, and material properties.
High-Volume Production Efficiency
Once the tooling is created, the sintering process is highly automated and repeatable. This makes it an extremely cost-effective method for producing tens of thousands or millions of identical parts.
Complex Geometries at Low Cost
Sintering excels at producing parts with intricate shapes, internal holes, or varying cross-sections. These features are formed directly in the compaction stage, eliminating the need for expensive and time-consuming secondary machining operations. This is known as net-shape manufacturing.
Controlled Porosity
Unlike fully dense metals, sintered parts possess a degree of controlled, interconnected porosity. While this can be a limitation, it is also a unique advantage. This porosity can be intentionally used to create self-lubricating bearings (by impregnating the pores with oil) or filters.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No manufacturing process is perfect. Objectivity requires acknowledging where sintering may not be the best fit.
Inherent Porosity and Mechanical Strength
Standard sintered parts are typically 80-95% as dense as their wrought (machined from solid bar) counterparts. This inherent porosity means they generally have lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance, making them less suitable for applications with extreme loading or high-impact stress.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The dies required for compaction are made from hardened tool steel and are expensive to design and manufacture. This high initial investment means sintering is not economical for prototypes or low-volume production runs.
Size and Design Constraints
The size of the part is limited by the capacity of the compaction press. Furthermore, features that inhibit the even flow and compaction of the powder, such as undercuts or threads perpendicular to the pressing direction, are very difficult or impossible to produce directly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex parts: Sintering is an exceptional choice, especially for components needed in high volumes where machining would be prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and impact resistance: You should evaluate wrought, forged, or fully dense powder metallurgy methods like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) for critical structural components.
- If your primary focus is creating a self-lubricating or filtering component: The controlled porosity of sintered metal makes it an ideal and often unparalleled solution.
By understanding its unique balance of cost, complexity, and material properties, you can confidently leverage sintering to solve specific manufacturing challenges.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Fusing metal powders with heat, below melting point (atomic diffusion). |
| Key Advantage | High-volume production of complex, net-shape parts at low cost. |
| Unique Property | Controlled porosity for self-lubricating bearings or filters. |
| Best For | Mass production of intricate components where machining is too expensive. |
| Limitation | Lower mechanical strength vs. wrought metals; high initial tooling cost. |
Need high-quality, complex metal parts produced efficiently?
Sintering is a powerful solution for mass production, but selecting the right process and equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and R&D facilities developing or testing sintered metal components.
Our expertise can help you optimize your sintering process for superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory and manufacturing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Achieve 100% Dense Titanium Composites
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets



















