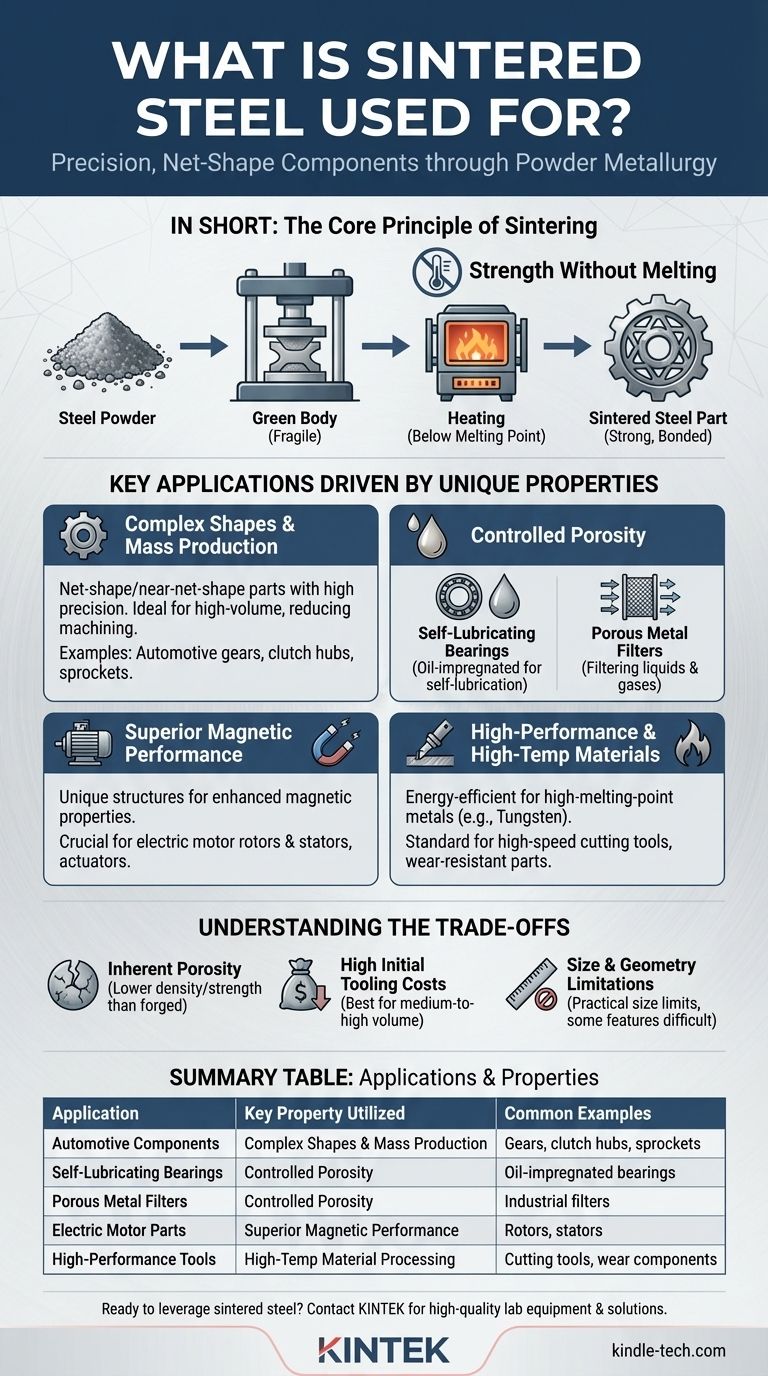
In short, sintered steel is used to create a vast range of precise, net-shape metal components where unique properties like controlled porosity or specific magnetic performance are required. It is a dominant manufacturing method for parts in automotive engines and transmissions, electric motors, self-lubricating bearings, and specialized filters.
The decision to use sintered steel is not about replacing traditional steel manufacturing, but about leveraging a unique process. Sintering creates parts with characteristics that are often difficult, expensive, or impossible to achieve through melting and casting, such as intentional porosity or complex shapes that require no secondary machining.
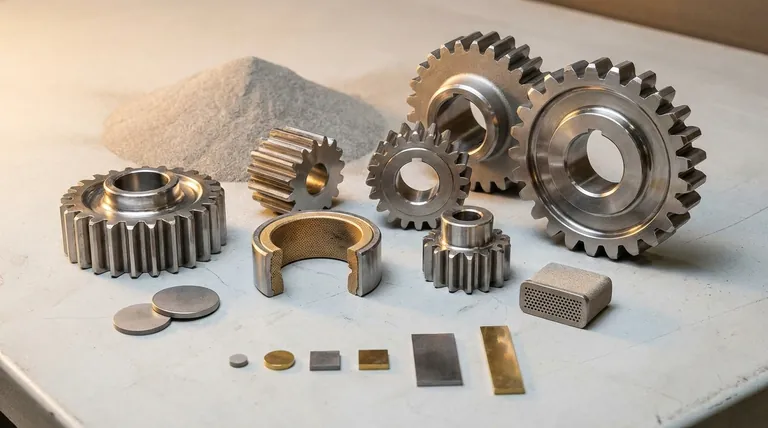

The Core Principle of Sintering: Strength Without Melting
Sintering is a powder metallurgy process. It forges a solid object from metal powder using heat and pressure without melting the material to a liquid state. This fundamental difference is the source of all its unique advantages.
How Sintering Works
The process begins by compressing steel powder in a die to form a fragile, pre-shaped part known as a "green body" or "green compact." This part is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, the metal particles fuse together through atomic diffusion, creating a strong, solid metallic bond and a finished component.
The Power of the "Green Body"
The ability to form a complex shape in its initial "green" state is a primary driver for using sintering. It allows manufacturers to produce net-shape or near-net-shape parts, which require little to no subsequent machining. This dramatically reduces waste and manufacturing time, especially for high-volume production.
Key Applications Driven by Unique Properties
The use cases for sintered steel are not random; they are directly tied to the specific engineering advantages the process offers over alternatives like casting or forging.
For Complex Shapes & Mass Production
Sintering excels at producing small, intricate structural parts with high precision and repeatability. The high initial cost of tooling (dies and presses) is offset by the low per-piece cost in large production runs.
This makes it a cornerstone of the automotive industry for components like gears, clutch hubs, sprockets, and engine valve guides.
For Controlled Porosity
Unlike fully dense molten metal, sintering allows for precise control over the final density and porosity of the part. This property is exploited in two opposite ways.
First, it's used to create self-lubricating bearings. Pores are intentionally left in the metal structure and then impregnated with oil. During operation, the bearing heats up, and the oil flows out to provide lubrication exactly where it's needed.
Second, it's used to produce porous metal filters. The interconnected network of pores is the functional feature of the part, used for filtering liquids and gases in various industrial applications.
For Superior Magnetic Performance
The powder metallurgy process allows for the creation of unique alloys and material structures that deliver enhanced magnetic properties. Sintered soft magnetic materials are crucial for high-performance electromagnetic components like the rotors and stators in modern electric motors and actuators.
For High-Performance & High-Temperature Materials
For metals with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or molybdenum (which can be alloyed with steel), melting them is incredibly energy-intensive. Sintering provides a more energy-efficient path to creating solid parts, making it the standard for applications like high-speed cutting tools and certain wear-resistant components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the solution for every steel component. Its advantages come with specific limitations that are critical to understand.
Inherent Porosity and Strength
Unless secondary operations like hot isostatic pressing (HIP) are performed, sintered parts typically have a lower density than their forged or wrought counterparts. This residual porosity can result in lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance, making them unsuitable for certain high-stress applications.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The dies and presses required for powder compaction represent a significant upfront investment. This makes sintering most economical for medium-to-high-volume production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized over thousands or millions of parts.
Size and Geometry Limitations
There are practical limits to the size of parts that can be produced via sintering. Furthermore, certain geometric features, such as undercuts or holes perpendicular to the pressing direction, can be difficult or impossible to form directly and may require secondary machining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Component
Selecting the right manufacturing process requires aligning your primary goal with the core strengths of the technology.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of complex small parts: Sintering is a leading candidate, especially if it can eliminate costly machining steps.
- If your primary focus is creating a part with controlled porosity: Sintering is the ideal and often only method for creating self-lubricating bearings or specialized metal filters.
- If your primary focus is specialized electromagnetic performance: Sintered soft magnetic composites offer superior and more isotropic properties for components like motor stators and rotors.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue resistance: You should carefully compare sintering with alternatives like forging or machining from bar stock, as they often provide superior mechanical properties for critical structural parts.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine when sintering is not just an alternative, but the optimal solution for your engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Property Utilized | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Components | Complex Shapes & Mass Production | Gears, clutch hubs, sprockets, valve guides |
| Self-Lubricating Bearings | Controlled Porosity | Oil-impregnated bearings for machinery |
| Porous Metal Filters | Controlled Porosity | Industrial filters for liquids and gases |
| Electric Motor Parts | Superior Magnetic Performance | Rotors, stators, soft magnetic composites |
| High-Performance Tools | High-Temperature Material Processing | Cutting tools, wear-resistant components |
Ready to leverage sintered steel for your lab or manufacturing needs? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for advanced materials processing, including sintering applications. Whether you're developing new components or optimizing your production process, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements with precision equipment and expert solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of using metal? Understanding Corrosion, Weight, and Cost Challenges
- Where is soldering commonly used? From Everyday Electronics to Industrial Applications
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are the advantages disadvantages and uses of sheet metal? The Ultimate Guide to Material Selection
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM



















