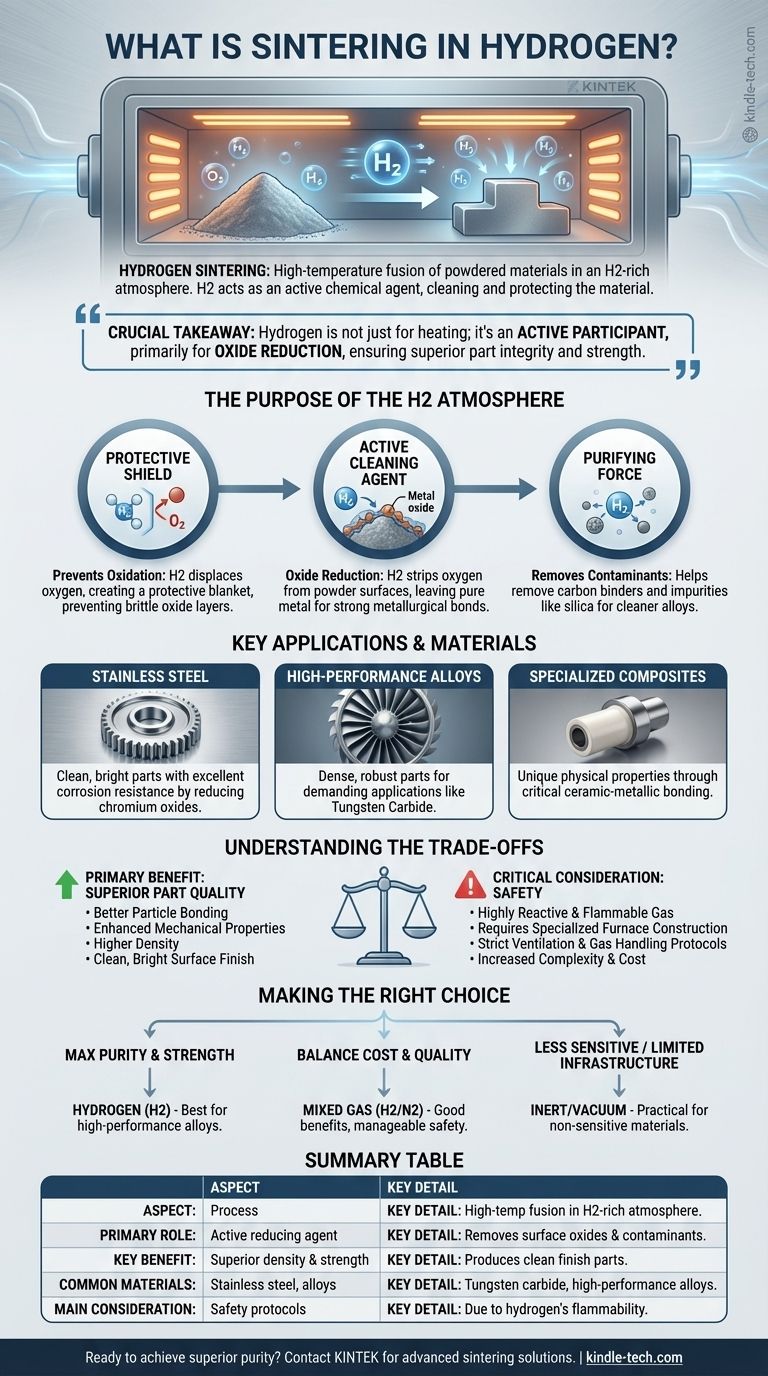
In short, hydrogen sintering is a high-temperature manufacturing process that uses a hydrogen-rich atmosphere to fuse powdered materials into a solid, dense part. Unlike sintering in air or a vacuum, the hydrogen acts as a powerful chemical agent, actively cleaning and protecting the material as it densifies. This results in components with superior mechanical properties and a clean, bright finish.
The crucial takeaway is that hydrogen is not merely an inert environment for heating. It is an active participant in the sintering process, primarily used for its exceptional ability to reduce and remove metal oxides, which are detrimental to the final part's integrity and strength.

The Purpose of the Hydrogen Atmosphere
Sintering in a controlled atmosphere is essential for creating high-quality parts from powdered metal or ceramics. Using hydrogen provides several distinct chemical advantages that go beyond simply preventing unwanted reactions.
A Protective Shield Against Oxidation
The most basic function of the atmosphere is to prevent the powdered material from oxidizing when heated. The presence of pure hydrogen (H2) or a hydrogen-nitrogen mix displaces oxygen, creating a protective blanket around the parts. This ensures the powder particles can fuse together properly without forming brittle oxide layers.
An Active Cleaning Agent
Hydrogen's most significant role is oxide reduction. Many metal powders have a thin layer of oxide on their surface, even before entering the furnace. As the temperature rises, hydrogen gas reacts with these metal oxides, stripping the oxygen away and leaving behind a clean, pure metal surface. This chemical "scrubbing" is critical for achieving strong metallurgical bonds.
A Purifying Force
Beyond removing oxides, a hydrogen atmosphere can help remove other contaminants. It plays a role in carbon control by reacting with residual carbon from binders used to shape the "green" part. It can also help strip away impurities like silica, leading to a cleaner final alloy and improved furnace performance.
Key Applications and Materials
The unique properties of hydrogen sintering make it the preferred method for materials where purity, strength, and surface finish are critical.
Stainless Steel
This is a very common application. Hydrogen sintering is used to produce clean, bright stainless steel parts because it effectively reduces the chromium oxides that naturally form on the powder's surface, ensuring excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
High-Performance Alloys
Materials like tungsten carbide and other advanced alloys demand high-purity processing to achieve their required performance characteristics. Hydrogen provides the reducing environment needed to create dense, robust parts for demanding industrial applications.
Specialized Composites
Certain ceramic-metallic compositions are also processed in hydrogen. The specific atmosphere helps create specialized parts where the bond between the metallic and ceramic components is critical to achieving unique physical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering process involves balancing benefits with practical considerations. While powerful, hydrogen is not the universal solution for every application.
The Primary Benefit: Superior Part Quality
The active chemical cleaning of a hydrogen atmosphere leads directly to parts with superior quality. The result is better particle bonding, which translates to enhanced mechanical properties, higher density, and a clean, bright surface finish that often requires no secondary cleaning operations.
The Critical Consideration: Safety
Hydrogen is a highly reactive and flammable gas. Using it for high-temperature sintering requires significant safety measures, including specialized furnace construction, ventilation, and gas handling protocols. These requirements add complexity and cost compared to sintering in inert atmospheres like pure nitrogen or in a vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the ideal sintering atmosphere depends entirely on the material you are working with and your desired outcome for the final part.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and mechanical strength: Hydrogen's powerful oxide reduction makes it the superior choice for high-performance alloys and demanding stainless steel applications.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost with good quality: A mixed gas, such as a hydrogen/nitrogen blend or dissociated ammonia, can offer many of the benefits of pure hydrogen with a more manageable safety profile.
- If your primary focus is on materials that are not sensitive to oxidation or when safety infrastructure is limited: An inert atmosphere like nitrogen or argon, or sintering in a vacuum, may be a more practical approach.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the atmosphere is key to mastering the final properties of a sintered component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | High-temperature fusion of powdered materials in a hydrogen-rich atmosphere. |
| Primary Role of Hydrogen | Acts as an active reducing agent to remove surface oxides and contaminants. |
| Key Benefit | Produces parts with superior density, mechanical strength, and a clean finish. |
| Common Materials | Stainless steel, tungsten carbide, and high-performance alloys. |
| Main Consideration | Requires stringent safety protocols due to hydrogen's flammability. |
Ready to achieve superior purity and strength in your sintered components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support needed for high-performance sintering processes. Whether you are working with stainless steel, tungsten carbide, or other advanced alloys, our solutions are designed to meet the demanding requirements of your laboratory.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your sintering capabilities and help you produce denser, stronger, and higher-quality parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density



















