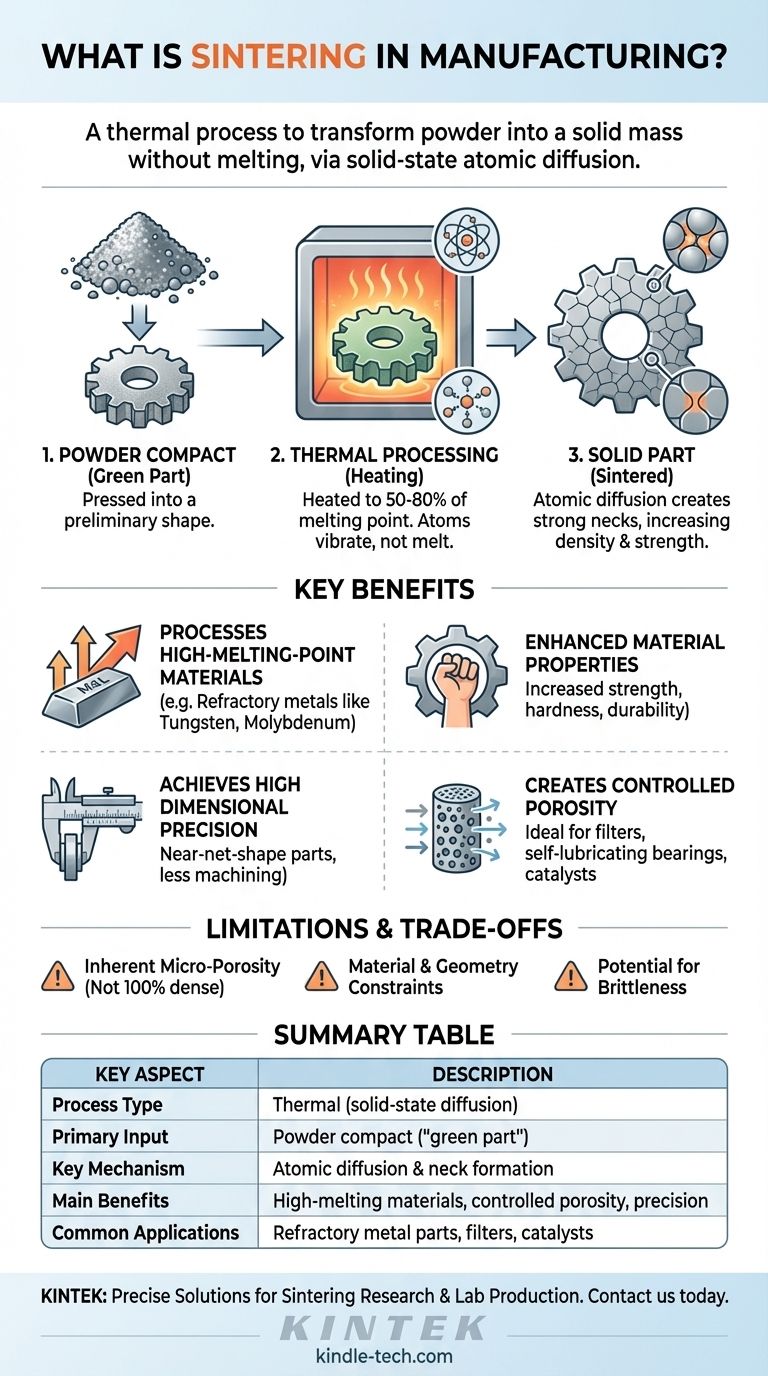
In manufacturing, sintering is a thermal process used to transform a collection of powder particles into a solid, dense mass. By applying heat at a temperature below the material's melting point, sometimes combined with pressure, the atoms in the powder diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together and creating a strong, coherent part.
Sintering is not a melting process; it is a solid-state atomic diffusion process. Its primary purpose is to create dense, functional components from powders, especially for materials like ceramics or refractory metals that are difficult or impossible to process through conventional melting and casting.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering creates a solid object directly from powder, a principle used in everything from traditional pottery to advanced additive manufacturing. The process hinges on encouraging atoms to bond without liquefying the bulk material.
The Starting Point: A Powder Compact
The process begins with a fine powder of the desired material, such as a metal alloy or a ceramic compound. This powder is often mixed with a binder and then pressed into a die to form a preliminary shape, commonly known as a "green compact."
This green part is fragile but holds the desired geometry.
The Role of Heat: Exciting the Atoms
The green compact is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature that is typically 50-80% of the material's absolute melting point. This thermal energy doesn't melt the particles but causes the atoms within them to vibrate vigorously.
This atomic excitement is the driving force behind the entire process.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion and Necking
As the atoms vibrate, they begin to migrate or diffuse across the contact points between individual powder particles. This diffusion builds small "necks" or bridges between particles.
Over time, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer together, reducing the empty space (porosity) between them, and increasing the overall density and strength of the part.
The Key Benefits of Sintering
Sintering is chosen over other manufacturing methods for several distinct advantages that solve specific engineering challenges.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is one of the only viable methods for forming parts from refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum. Their extremely high melting temperatures make traditional casting impractical and prohibitively expensive.
Enhancing Material Properties
The process dramatically improves a material's physical characteristics. By reducing internal pores, sintering significantly enhances strength, hardness, and durability.
It can also be engineered to improve electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and even transparency in certain ceramic materials.
Achieving High Dimensional Precision
Sintering can produce net-shape or near-net-shape parts, meaning the component comes out of the furnace very close to its final dimensions. This minimizes the need for costly secondary machining operations.
Creating Controlled Porosity
While the goal is often to reduce porosity, sintering uniquely allows for its control. This is critical for manufacturing products like self-lubricating bearings, filters, and catalysts, where a strong but porous structure is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. To use sintering effectively, you must understand its inherent limitations.
Inherent Micro-Porosity
It is difficult and often uneconomical to achieve 100% density through sintering alone. Most sintered parts retain some level of residual micro-porosity.
This can make them less suitable than forged or fully-molten parts for applications requiring maximum fatigue resistance or fracture toughness.
Material and Geometry Constraints
The process is limited to materials available in powder form. Furthermore, the ability to create a uniform green compact can restrict the complexity and size of the final part geometry.
Potential for Brittleness
While sintering increases strength, the resulting material, particularly certain ceramics, can be more brittle than its non-sintered counterparts. The bonds between the original particles can sometimes act as initiation points for cracks under high impact loads.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your material, cost constraints, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is processing high-temperature materials: Sintering is the definitive choice for refractory metals like tungsten that are impractical to melt and cast.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Powder metallurgy, which relies on sintering, is an excellent method for producing large volumes of small, complex metal parts with high precision.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity: Sintering is the ideal process for creating functional components like filters or catalysts that require a strong, porous internal structure.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and ductility: For critical applications demanding absolute material integrity, you should consider processes like forging or machining from solid billet, which avoid the issue of residual porosity.
By understanding its core mechanism of atomic diffusion, you can leverage sintering as a powerful tool for creating high-performance parts that other processes simply cannot produce.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Thermal (solid-state diffusion) |
| Primary Input | Powder compact ("green part") |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion and neck formation between particles |
| Main Benefits | Processes high-melting-point materials, creates controlled porosity, achieves high dimensional precision |
| Common Applications | Refractory metal parts, filters, catalysts, net-shape components |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material production?
KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for successful sintering processes. Whether you are working with advanced ceramics or refractory metals, our solutions help you achieve the material properties and dimensional precision your research demands.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your sintering projects and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















