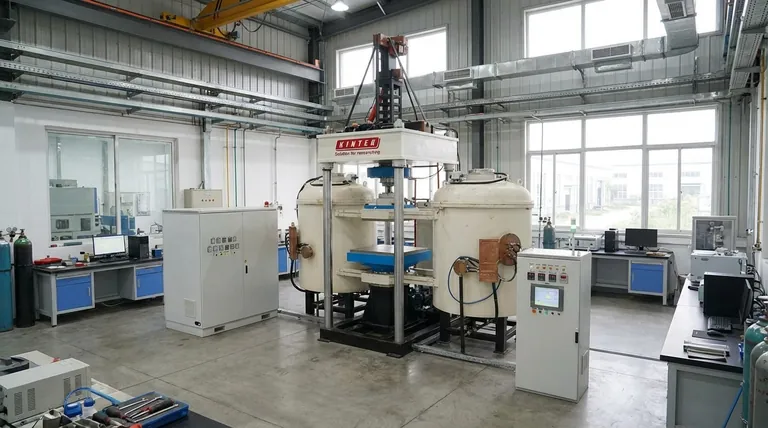
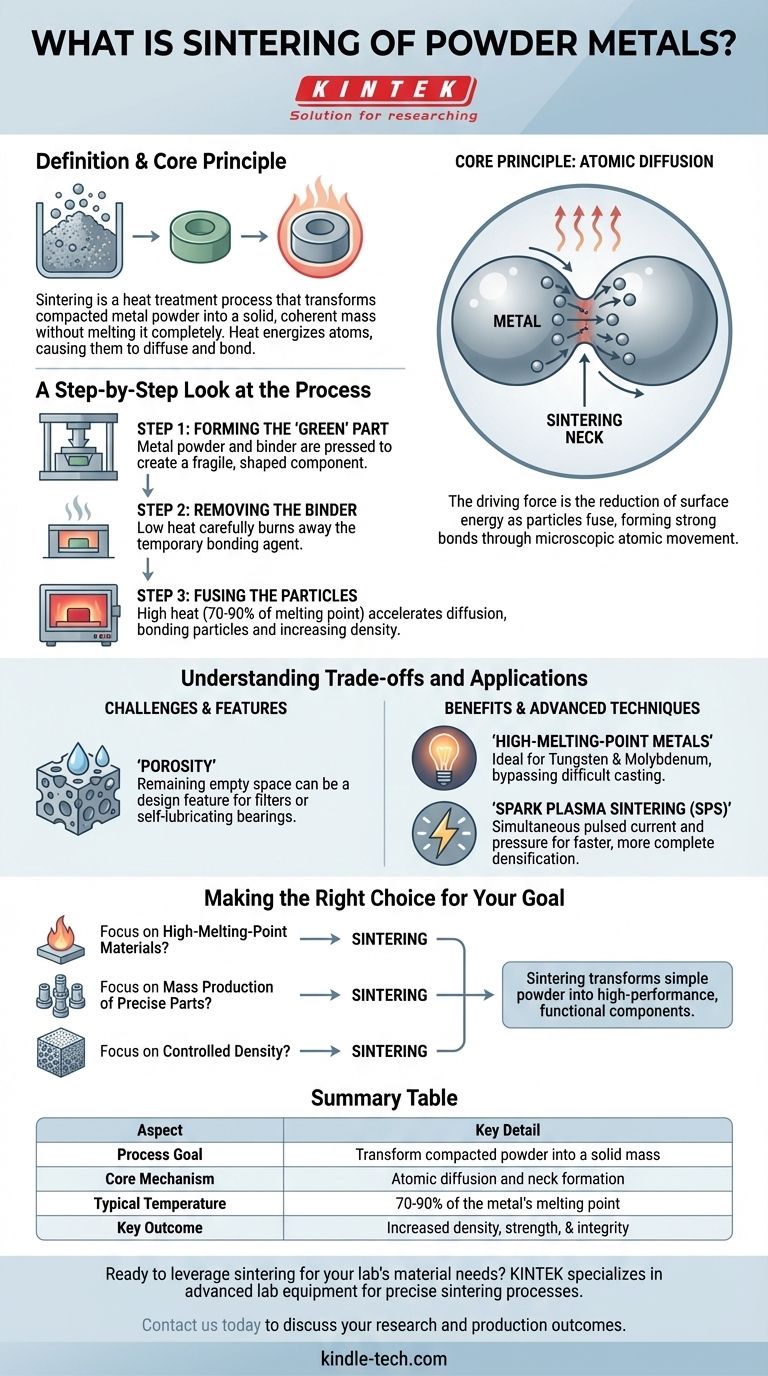
Sintering is a heat treatment process that transforms a compacted metal powder into a solid, coherent mass without melting it completely. By heating the material to a temperature below its melting point, the individual powder particles fuse, creating a strong, dense component with significantly improved mechanical properties.
The core principle of sintering is atomic diffusion. It is a form of microscopic welding where heat energizes the atoms in metal particles, causing them to move across particle boundaries and bond together, fundamentally changing loose powder into a robust, engineered part.

The Core Principle: Why Sintering Works
From Powder to Solid
The starting point for sintering is a "green" part—a fragile component made by compressing metal powder into a desired shape, often with a binder. This green part has mechanical integrity but lacks the strength required for most applications. Sintering is the critical step that provides this strength.
The Driving Force: Reducing Energy
Any system in nature seeks its lowest possible energy state. A mass of fine powder has an enormous amount of surface area, which represents a high-energy state.
The sintering process reduces this total surface area as particles fuse together. This reduction in surface energy is the fundamental thermodynamic driving force behind the entire process.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by atomic diffusion. As the compacted powder is heated, the atoms on the surface of the particles become highly mobile.
These energized atoms migrate across the contact points between adjacent particles, forming small connections called sintering necks. As the process continues, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer, reducing the empty space (porosity), and fusing them into a single, solid piece.
A Step-by-Step Look at the Process
Step 1: Forming the "Green" Part
First, a homogenous mixture of metal powder, and sometimes a temporary bonding agent like wax or a polymer, is pressed into a mold. This process, known as forming or compacting, creates the initial shape and density of the final component.
Step 2: Removing the Binder
The fragile green part is then carefully placed in a furnace. In the initial heating stage, the temperature is raised just enough to burn away or evaporate the binder that held the powder together. This must be done carefully to prevent damage to the part.
Step 3: Fusing the Particles
After the binder is removed, the furnace temperature is increased to the sintering point, which is typically 70-90% of the metal's melting temperature.
At this temperature, atomic diffusion accelerates rapidly. The particles bond at their contact points, the part shrinks, its density increases, and its mechanical strength is developed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The Challenge of Porosity
While sintering dramatically increases density, it rarely eliminates all the empty space between particles. The remaining empty space is known as porosity.
This can be a disadvantage if maximum strength is required, but it can also be a key design feature, used to create filters or self-lubricating bearings that hold oil in their pores.
The Benefit for High-Melting-Point Metals
Sintering is especially valuable for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum.
Melting and casting these materials is technically difficult and expensive. Powder metallurgy, with sintering as its final step, allows for the creation of solid parts from these materials at much lower temperatures.
Advanced Techniques: Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Modern methods can enhance the sintering process. In Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), for example, a pulsed electrical current and mechanical pressure are applied simultaneously.
The current activates the particle surfaces and generates intense localized heat, while the pressure aids in compaction. This results in much faster and more complete densification compared to traditional furnace heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use sintering depends entirely on your material, design, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is on high-melting-point materials: Sintering is an ideal choice, as it bypasses the extreme temperatures and challenges associated with traditional melting and casting.
- If your primary focus is on mass production of small, precise parts: The powder metallurgy process culminating in sintering offers excellent repeatability, complex shape capability, and minimal material waste.
- If your primary focus is on controlled density: Sintering provides a unique ability to engineer a specific level of porosity into a component for applications like filters or bearings.
Ultimately, sintering is a powerful manufacturing process that transforms simple powder into high-performance, functional components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Transform compacted metal powder into a solid, coherent mass |
| Core Mechanism | Atomic diffusion and neck formation between particles |
| Typical Temperature | 70-90% of the metal's melting point |
| Key Outcome | Increased density, strength, and structural integrity |
| Common Applications | High-melting-point parts (tungsten, molybdenum), filters, bearings, mass-produced components |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials with high melting points or mass-producing precise components, our solutions ensure accuracy, efficiency, and repeatability.
Contact us today to discuss how our sintering expertise and reliable equipment can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the VAR process for steel? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Structural Integrity
- What causes arcing in vacuum? Prevent Costly System Failures with Proper Material Management
- How does the drying step in a laboratory oven affect the quality of Fe@C nanotubes? Optimize Your Nanomaterial Synthesis
- Why is a vacuum oven required for anhydrous Zinc Phenylphosphate (ZnMPhP-A)? Achieve High Purity & Faster Dehydration
- What is sintering in hydrogen? Achieve Superior Purity and Strength in Metal Parts
- What is the critical role of a vacuum oven in PEO/LiTFSI membrane preparation? Optimize Solid-State Battery Performance
- What industry is brazing used? Critical Joining Process for Aerospace, Medical & Automotive



















