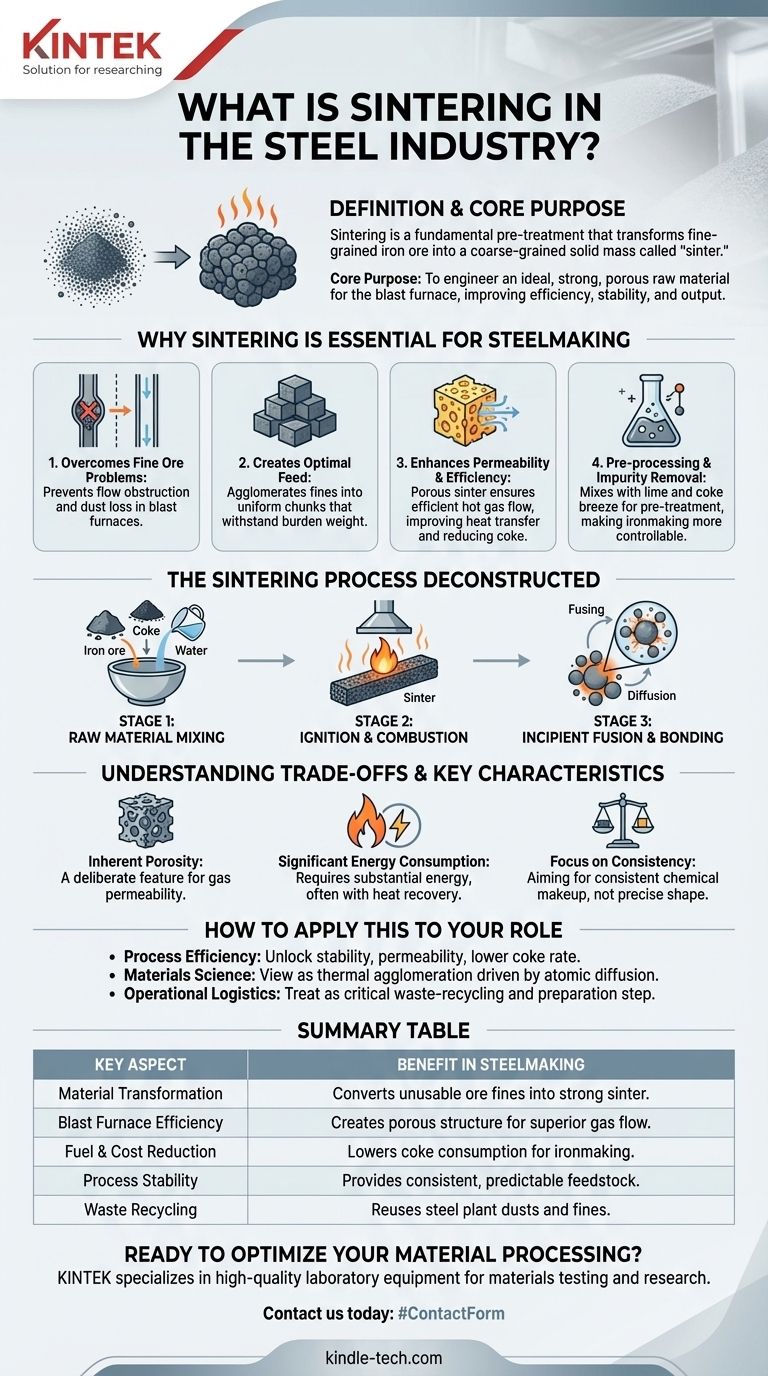
In the steel industry, sintering is a fundamental pre-treatment process that transforms fine-grained iron ore and other materials into a coarse-grained, solid mass called "sinter." This is achieved by heating the raw material mix to a high temperature, just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together. The resulting sinter is the primary feedstock for the blast furnace, where it is converted into iron.
The core purpose of sintering is not simply to create a solid lump, but to engineer an ideal raw material for the blast furnace. It transforms otherwise unusable fine ore powders into a strong, porous feed that dramatically improves the efficiency, stability, and output of the entire ironmaking operation.

Why Sintering is Essential for Steelmaking
The modern blast furnace cannot efficiently process raw, fine-grained iron ore. Sintering is the critical step that converts these fine materials into a product with the precise physical and chemical properties needed for high-performance iron production.
The Problem with Raw Iron Ore Fines
Fine powders, when charged directly into a blast furnace, create significant problems. They obstruct the flow of hot gases required for the chemical reactions and can be blown out of the furnace as dust, leading to material loss and operational instability.
Creating an Optimal Blast Furnace Feed
Sintering agglomerates these fine particles into larger, more uniform chunks. This ensures that the material can withstand the immense weight of the furnace burden without being crushed into dust, guaranteeing a smooth descent through the furnace.
Enhancing Permeability and Efficiency
The sinter produced is not only strong but also highly porous. This porosity creates clear pathways for hot gases to ascend through the furnace charge, ensuring efficient heat transfer and chemical reduction of the iron ore. This directly improves the furnace's utilization coefficient and reduces the amount of expensive coke fuel required.
Pre-processing and Impurity Removal
The sintering process involves mixing iron ore fines with fluxing agents like lime and a carbon-based fuel like coke breeze. Heating this mixture begins the process of impurity removal, which will be completed in the blast furnace. This pre-treatment makes the subsequent ironmaking process more predictable and controllable.
The Sintering Process Deconstructed
While the concept is simple—heating a material until its particles stick together—the industrial process is a carefully controlled, multi-stage operation.
Stage 1: Raw Material Mixing
A precise recipe of iron ore fines, recycled steel plant dusts, coke breeze (for fuel), and lime (as a flux) is blended together with a small amount of water. This creates a homogenous mixture with a texture similar to damp soil.
Stage 2: Ignition and Combustion
This mixture is spread in a layer on a large, slow-moving permeable grate called a sinter strand. The top surface of this bed passes under an ignition hood, which ignites the coke particles on the surface.
Stage 3: Incipient Fusion and Bonding
As the strand moves forward, air is pulled down through the bed. This draws the narrow, high-temperature combustion zone downwards through the entire layer of material. This heat wave causes the surfaces of the iron ore particles to become semi-molten or "sticky." The atoms at these surfaces diffuse across particle boundaries, fusing them into a single, porous mass.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Characteristics
Sintering is an optimized solution, not a perfect one. Understanding its inherent characteristics is key to appreciating its role.
Inherent Porosity is a Feature, Not a Flaw
The goal of sintering is not to create a fully dense, non-porous solid. The micro-porosity of the final sinter product is a deliberate and crucial feature that ensures excellent gas permeability within the blast furnace.
Significant Energy Consumption
As a high-temperature process, sintering consumes a substantial amount of energy, primarily from the combustion of coke breeze. Modern plants incorporate extensive heat recovery and gas recycling systems to mitigate this operational cost and environmental impact.
Focus on Consistency, Not Final Shape
Unlike powder metallurgy, where sintering is used to create a precise final part, the goal in steelmaking is bulk material preparation. The focus is on producing sinter with consistent chemical makeup, strength, and porosity, not on achieving a specific final dimension.
How to Apply This to Your Role
Your perspective on sintering will depend on your specific focus within the industry.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: View sintering as the key to unlocking blast furnace stability, superior gas permeability, and a lower coke consumption rate.
- If your primary focus is materials science: Recognize sintering as a thermal agglomeration process driven by atomic diffusion, creating a strong, porous aggregate without reaching the material's full melting point.
- If your primary focus is operational logistics: Treat sintering as a critical waste-recycling and raw material preparation step that makes previously unusable fine ores a valuable asset.
Ultimately, the sintering process is the essential bridge between inconsistent raw materials and the high-performance demands of modern ironmaking.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit in Steelmaking |
|---|---|
| Material Transformation | Converts unusable ore fines into a strong, coarse-grained sinter. |
| Blast Furnace Efficiency | Creates a porous structure for superior gas flow and heat transfer. |
| Fuel & Cost Reduction | Lowers the amount of expensive coke required for ironmaking. |
| Process Stability | Provides a consistent, predictable feedstock for the blast furnace. |
| Waste Recycling | Allows for the reuse of steel plant dusts and other fine by-products. |
Ready to Optimize Your Material Processing?
Just as sintering is vital for preparing raw materials for the blast furnace, having the right lab equipment is critical for developing and controlling your industrial processes. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables for materials testing and research, helping you achieve the precision and consistency your operations demand.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can support your sintering research, quality control, and process optimization. Let KINTEK be your partner in enhancing efficiency and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















