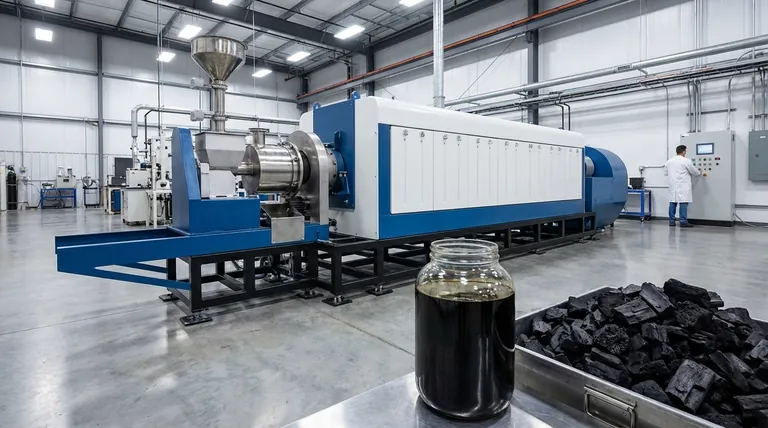
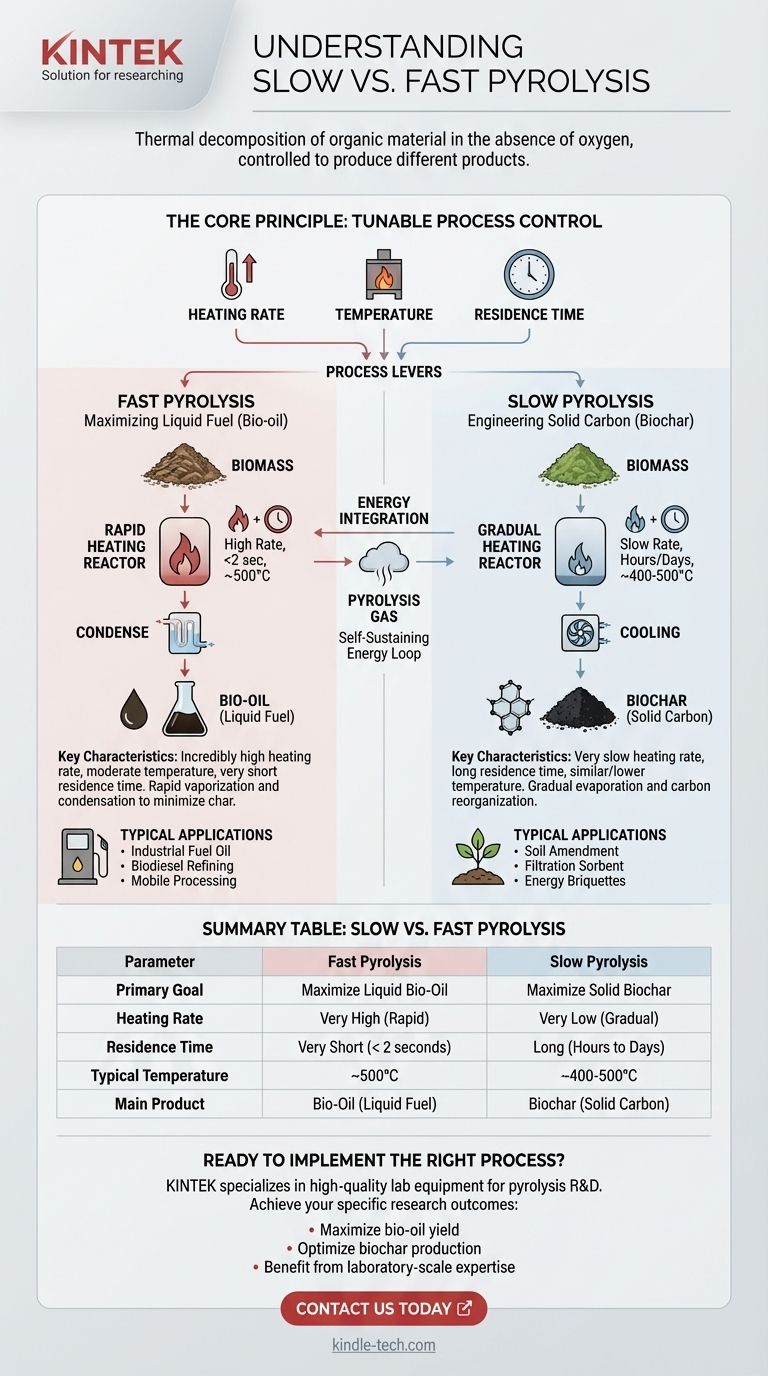
In essence, slow and fast pyrolysis are two methods of thermally decomposing organic material in the absence of oxygen. The fundamental difference lies in the heating rate, process temperature, and time, which are deliberately controlled to produce vastly different primary products. Fast pyrolysis uses rapid heating for a very short time to maximize liquid bio-oil, while slow pyrolysis uses gradual heating over a long period to maximize solid biochar.
The core principle to understand is that pyrolysis is not a single process, but a tunable one. The choice between "slow" and "fast" is a deliberate engineering decision to target a specific, valuable end-product: liquid fuel from fast pyrolysis or solid carbon from slow pyrolysis.

The Core Principle: Controlling the Reaction
Pyrolysis is a simple concept at its heart. When you heat organic materials like wood, agricultural waste, or plastics without oxygen, they break down rather than burn. This decomposition creates three types of products: a gas, a liquid, and a solid.
The Three Critical Levers
The specific yield of gas, liquid, or solid is not random. It is dictated by three key process parameters that engineers control.
- Heating Rate: This is how quickly the material's temperature is increased. It is the most critical factor distinguishing slow from fast pyrolysis.
- Temperature: This refers to the peak temperature the material reaches inside the reactor.
- Residence Time: This is the total amount of time the material is held at the reaction temperature.
By manipulating these three levers, we can favor the formation of one product over the others.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Fuel (Bio-oil)
The goal of fast pyrolysis is to convert the majority of the biomass into a liquid product known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
The Process Conditions
To achieve this, the conditions are extreme and precise. Biomass is heated at an incredibly high rate to a moderate temperature (around 500°C) for a very short residence time, often less than two seconds.
The Primary Product
This rapid process instantly vaporizes the organic components. These hot vapors are then quickly cooled and condensed, capturing them as a dark, dense liquid—bio-oil. This process intentionally minimizes the chemical reactions that would lead to solid char formation.
Typical Applications
The resulting bio-oil can be used as an industrial fuel oil or further refined into transportation fuels like biodiesel. The process can be implemented in smaller, mobile reactors that process biomass near its source, reducing transportation costs.
Slow Pyrolysis: Engineering Solid Carbon (Biochar)
The objective of slow pyrolysis is the exact opposite: to maximize the yield of the solid product, known as biochar or coke.
The Process Conditions
This process involves a very slow heating rate over a much longer residence time, lasting several hours or even days. The peak temperatures are often similar to or slightly lower than those in fast pyrolysis.
The Primary Product
Gradually heating the material allows the volatile components to slowly evaporate while the carbon structure reorganizes itself into a stable, carbon-rich solid. This controlled "roasting" is designed to create high-quality biochar while minimizing the liquid yield.
Typical Applications
Biochar is a valuable product used for soil amendment in agriculture, as a filtration medium (sorbent), or pressed into briquettes for energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis method involves balancing product goals with operational complexity.
Product Yield vs. Process Speed
Fast pyrolysis is quick and efficient at producing liquid fuel, but it requires more sophisticated and precisely controlled reactors (such as fluidized-bed or ablative reactors) to manage the rapid heat transfer.
Slow pyrolysis is a much longer process, but it can often be accomplished in simpler equipment like kilns or retorts, making it more accessible for smaller-scale biochar production.
Energy Integration
In both processes, the non-condensable pyrolysis gas that is produced is a valuable byproduct. It is almost always captured and used to provide the heat energy required to run the pyrolysis plant itself, creating a self-sustaining energy loop.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use slow or fast pyrolysis is entirely dependent on the desired end product.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuel (bio-oil): Fast pyrolysis is the correct pathway, designed specifically to maximize liquid yield.
- If your primary focus is creating a stable solid carbon product (biochar): Slow pyrolysis is the superior method for maximizing the quantity and quality of this solid.
- If your primary focus is generating fuel gas (syngas): A third variation, "gasification," which involves higher temperatures and a controlled amount of oxygen, would be the most appropriate choice.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between these processes allows you to intentionally engineer a specific, valuable outcome from raw biomass.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Fast Pyrolysis | Slow Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize Liquid Bio-Oil | Maximize Solid Biochar |
| Heating Rate | Very High (Rapid) | Very Low (Gradual) |
| Residence Time | Very Short (< 2 seconds) | Long (Hours to Days) |
| Typical Temperature | ~500°C | ~400-500°C |
| Main Product | Bio-Oil (Liquid Fuel) | Biochar (Solid Carbon) |
Ready to implement the right pyrolysis process for your lab's biomass conversion goals?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are optimizing for bio-oil or biochar production, our reliable reactors and systems are designed to deliver precise control over heating rates, temperature, and residence time.
Let us help you achieve your specific research outcomes:
- Maximize bio-oil yield with our fast pyrolysis systems.
- Optimize biochar production with our controlled slow pyrolysis equipment.
- Benefit from our expertise in laboratory-scale thermal processing.
Contact us today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds


















