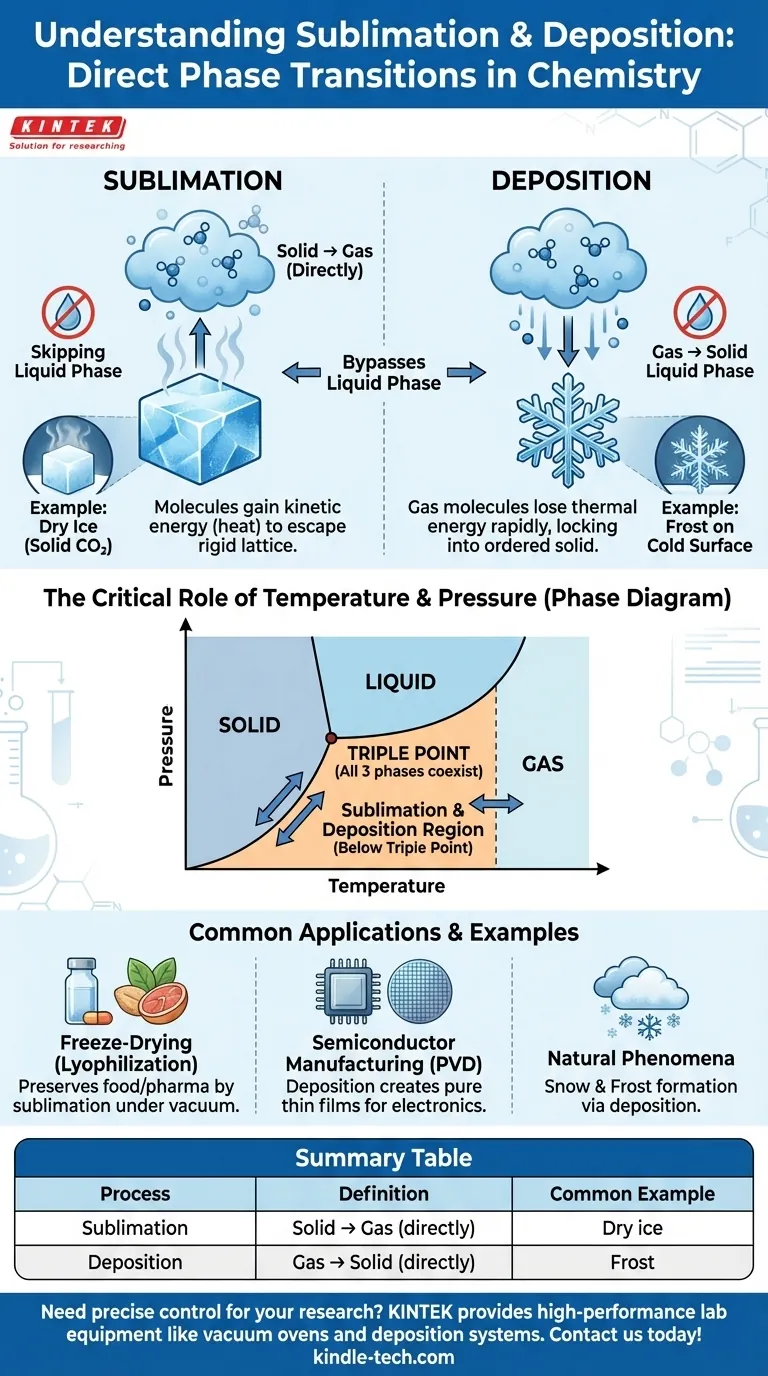
In the study of matter, sublimation and deposition are phase transitions where a substance transitions directly between its solid and gas states, completely bypassing the liquid phase. Sublimation is the direct conversion of a solid into a gas. Deposition is the reverse process, where a gas transforms directly into a solid.
The core principle to understand is that sublimation and deposition are two sides of the same coin. They represent the direct, two-way path between the solid and gas phases that occurs under specific conditions of temperature and pressure, entirely skipping the intermediate liquid state.

The Mechanics of Phase Transitions
To understand why a substance would skip the liquid phase, we must look at the energy and arrangement of its molecules. Phase transitions are fundamentally about changes in molecular energy and freedom of movement.
Sublimation: The Solid-to-Gas Transition
In a solid, molecules are locked into a fixed, often crystalline structure, though they still vibrate in place.
When energy (usually in the form of heat) is added, these vibrations increase. In sublimation, the molecules gain enough kinetic energy to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them in their rigid lattice and escape directly as a gas.
A classic example is dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide. At room temperature and standard pressure, it turns directly into gaseous carbon dioxide without ever becoming a liquid puddle.
Deposition: The Gas-to-Solid Transition
Deposition is the opposite of sublimation. It occurs when molecules in the gas phase lose thermal energy rapidly.
This rapid energy loss causes the fast-moving gas molecules to slow down so significantly that they lock directly into an ordered solid structure. They do not have a chance to condense into a liquid first.
The formation of frost on a cold windowpane is a perfect example. Water vapor in the air comes into contact with a surface below freezing and turns directly into ice crystals.
The Critical Role of Temperature and Pressure
Whether a substance sublimes, melts, or boils is not an inherent property of the substance alone. It is determined by the external conditions of temperature and pressure, which are best visualized on a phase diagram.
Introducing the Triple Point
For every substance, there is a specific combination of temperature and pressure called the triple point. This is the unique point where the solid, liquid, and gas phases can coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Why Skipping the Liquid Phase Occurs
Sublimation and deposition occur at temperature and pressure combinations below the triple point.
At these low pressures, the liquid phase is not stable. Adding energy to a solid will push it directly over the boundary into the gas phase (sublimation), and removing energy from a gas will cause it to cross directly into the solid phase (deposition).
Common Applications and Examples
These processes are not just theoretical concepts; they are central to both natural phenomena and critical industrial technologies.
Sublimation in Action: Freeze-Drying
Freeze-drying (lyophilization) is a key method for preserving food and pharmaceuticals. The material is first frozen, and then the surrounding pressure is dramatically reduced, causing the frozen water (ice) to sublimate directly into water vapor, leaving the item dry without heat damage.
Deposition in Technology: Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the tech industry, a process called physical vapor deposition (PVD) is used to create thin films. A solid material is vaporized in a vacuum, and the resulting gas then deposits as a pure, solid film onto a substrate, such as a silicon wafer used for making computer chips.
Natural Phenomena: Snow and Frost
The formation of snow within clouds is a natural example of deposition. Water vapor in the atmosphere cools and deposits directly into intricate ice crystals, forming snowflakes that never existed as liquid raindrops.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these concepts allows you to interpret both natural and industrial processes with greater clarity.
- If your primary focus is visualizing everyday phenomena: Remember that dry ice "smoking" is sublimation, and the frost on your lawn on a cold morning is deposition.
- If your primary focus is understanding industrial processes: Recognize that freeze-drying uses sublimation to remove water gently, while creating advanced electronics often relies on deposition to build components layer by layer.
- If your primary focus is grasping core physical chemistry: Anchor your understanding to the phase diagram, where all behavior below the triple point involves direct solid-gas transitions.
Ultimately, sublimation and deposition demonstrate how the state of matter is a dynamic condition governed by the interplay of energy and pressure.
Summary Table:
| Process | Definition | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sublimation | Solid → Gas (directly) | Dry ice (solid CO₂) turning into gas |
| Deposition | Gas → Solid (directly) | Frost forming on a cold window |
| Key Condition | Occurs at temperatures and pressures below the substance's triple point | - |
Need precise temperature and pressure control for your phase transition research or industrial processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum ovens and deposition systems, to reliably achieve the conditions needed for sublimation and deposition. Let our experts help you select the right tools for your laboratory's unique challenges. Contact us today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Manual Lab Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What are the cost considerations for freeze drying? Uncover the 90% Hidden Operational Expenses
- What are the hazards of evaporators? Manage Chemical, Thermal, and Pressure Risks
- Can you separate the solid and liquid in a solution by filtering? No, and Here's Why
- How does freeze drying compare to conventional freezing for biological material preservation? Achieve Long-Term, Shelf-Stable Preservation
- Why are conventional preservation methods less suitable for biological products? The Critical Risk to Efficacy and Safety



















