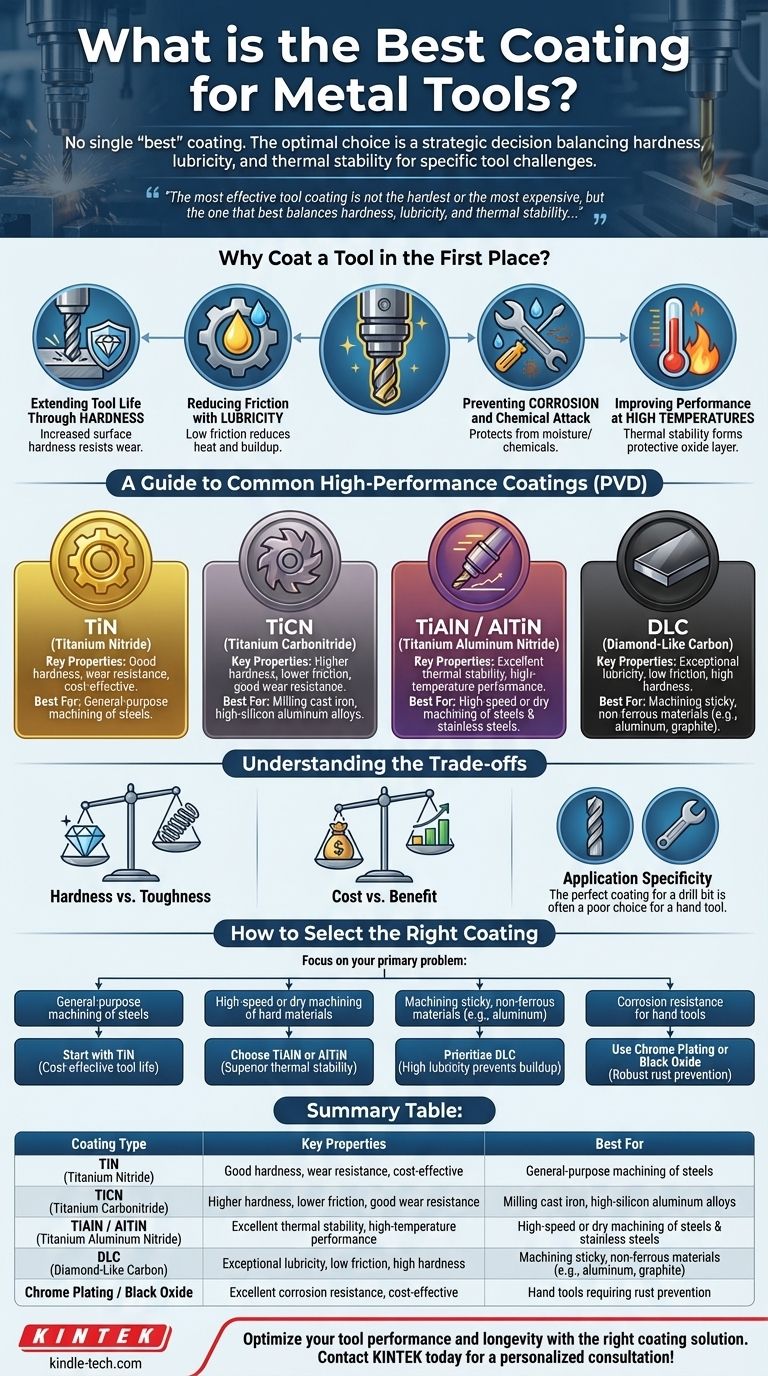
There is no single "best" coating for all metal tools. The optimal choice is a strategic decision based on the tool's material, its intended application, and the specific failure mode you're trying to prevent—be it wear, friction, or corrosion. High-performance cutting tools often rely on PVD coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), while hand tools may only require simple corrosion protection like chrome plating.
The most effective tool coating is not the hardest or the most expensive, but the one that best balances hardness, lubricity, and thermal stability to solve the specific challenges of your task. Understanding this trade-off is the key to improving performance and extending tool life.

Why Coat a Tool in the First Place?
A coating is essentially a micro-thin layer of armor engineered to enhance a tool's surface properties far beyond what its base material can offer. The goal is to address specific points of failure.
Extending Tool Life Through Hardness
The most common reason to coat a tool, especially a cutting tool, is to increase its surface hardness. A harder surface resists abrasive wear far better than an uncoated one.
This is particularly crucial when machining tough or abrasive materials. The coating acts as the first line of defense, preserving the sharp cutting edge underneath.
Reducing Friction with Lubricity
Some coatings are incredibly smooth and slippery, a property known as lubricity. Low friction is critical for several reasons.
First, it reduces the heat generated during cutting operations, which is a primary cause of tool failure. Second, for materials like aluminum, high lubricity prevents the workpiece material from welding itself to the tool, an issue called "built-up edge."
Preventing Corrosion and Chemical Attack
For hand tools or components exposed to the elements, the primary enemy is often rust and corrosion. A coating creates a barrier between the base metal (typically steel) and environmental moisture or chemicals.
While high-performance PVD coatings offer this benefit, simpler and more cost-effective methods like chrome plating, nickel plating, or even powder coating are often sufficient for this purpose.
Improving Performance at High Temperatures
High-speed machining generates extreme heat at the cutting edge. Many standard tool steels will soften (anneal) at these temperatures, causing the edge to dull instantly.
Specialized coatings like TiAlN are designed to thrive in this heat. They form a protective, ceramic-like oxide layer at high temperatures, effectively using the heat to create an even tougher shield.
A Guide to Common High-Performance Coatings
Most advanced tool coatings are applied using Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), a process that bonds a micro-thin layer of ceramic material to the tool's surface in a vacuum.
TiN (Titanium Nitride)
TiN is the classic, general-purpose PVD coating, easily identified by its bright gold color. It provides a good balance of increased hardness and wear resistance at a very reasonable cost.
It's an excellent, cost-effective starting point for improving the life of drills, mills, and inserts used on common steels.
TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride)
TiCN is a step up from TiN in terms of hardness and wear resistance. Its lower coefficient of friction also helps when cutting gummy materials.
This coating is ideal for applications where abrasive wear is the primary concern, such as milling cast iron or high-silicon aluminum alloys. It performs best with good lubrication.
TiAlN / AlTiN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride)
These are high-performance coatings designed for high-temperature applications. When heated, the aluminum in the coating forms a nano-layer of aluminum oxide, which is exceptionally hard and thermally stable.
This makes TiAlN or AlTiN the top choice for high-speed or dry machining of steels, stainless steels, and other high-temperature alloys.
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon)
DLC coatings are prized for their exceptional lubricity. They have one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any coating, making them incredibly slick.
This makes DLC the perfect solution for machining non-ferrous materials like aluminum and graphite, where sticking is a major problem. Its hardness also provides excellent wear resistance in abrasive applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a coating is never about finding a single "best" option. It's about navigating a series of compromises to fit your specific goal.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Dilemma
Extremely hard coatings can also be more brittle. While they resist abrasive wear, a sharp impact or vibration (chatter) can cause the thin coating to micro-chip.
In applications with unstable setups or interrupted cuts, a slightly softer but tougher coating might outperform a harder, more brittle one.
The Cost Factor
Advanced coatings add significant cost to a tool. For a hobbyist or small shop, coating a standard drill bit may not be worth the expense.
For a production environment where a 50% increase in tool life saves thousands of dollars in downtime and tool changes, the investment is easily justified.
Application Specificity
The perfect coating for a drill bit is often a poor choice for a hand tool. A PVD coating like TiAlN on a wrench is expensive overkill.
For hand tools, corrosion resistance and grip are more important. Simple chrome plating offers excellent rust prevention and a cleanable surface, while a black oxide finish provides mild corrosion resistance and a non-reflective finish.
How to Select the Right Coating
Focus on the problem you are trying to solve, and the choice becomes clear.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose machining of steels: Start with TiN for a cost-effective and noticeable improvement in tool life.
- If your primary focus is high-speed or dry machining of hard materials: Choose TiAlN or AlTiN for their superior thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is machining sticky, non-ferrous materials like aluminum: Prioritize a high-lubricity coating like DLC to prevent material buildup.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance for hand tools: Use simple, robust finishes like chrome plating or black oxide instead of expensive PVD coatings.
By matching the coating's strengths to your application's demands, you transform a good tool into the perfect instrument for the job.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| TiN (Titanium Nitride) | Good hardness, wear resistance, cost-effective | General-purpose machining of steels |
| TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride) | Higher hardness, lower friction, good wear resistance | Milling cast iron, high-silicon aluminum alloys |
| TiAlN / AlTiN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) | Excellent thermal stability, high-temperature performance | High-speed or dry machining of steels & stainless steels |
| DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) | Exceptional lubricity, low friction, high hardness | Machining sticky, non-ferrous materials (e.g., aluminum, graphite) |
| Chrome Plating / Black Oxide | Excellent corrosion resistance, cost-effective | Hand tools requiring rust prevention |
Optimize your tool performance and longevity with the right coating solution.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced coating technologies. Whether you're in a production environment needing thermally stable TiAlN coatings or a research lab requiring the superior lubricity of DLC, our expertise ensures you get the perfect solution to reduce wear, prevent corrosion, and boost efficiency.
Let our specialists help you select the ideal coating to transform your tools. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the optical properties of CVD diamond? Unlock Unmatched Performance for Demanding Applications
- How are thin films used in semiconductors? Building the Digital World, One Atomic Layer at a Time
- What is a thin film device? Unlocking the Power of Nanoscale Materials
- What materials are used in thin film? A Guide to Metals, Semiconductors, and Ceramics
- What is sputtering target for semiconductors? The Engineered Source for High-Purity Thin Films
- What do optical coatings do? Control Light for Superior Optical Performance
- What are sputtering targets for semiconductors? Essential High-Purity Materials for Thin Film Deposition
- Are carbon nanotubes hard to make? Mastering the Challenge of Scalable, High-Quality Production



















