For the absolute highest temperatures, the best crucible materials are refractory metals like Tungsten or pure Graphite. These materials can withstand temperatures exceeding 3000°C, but they come with a critical limitation: they must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent rapid oxidation and failure. For high-temperature work in a standard atmosphere, highly stable ceramics like Zirconia are the superior choice.
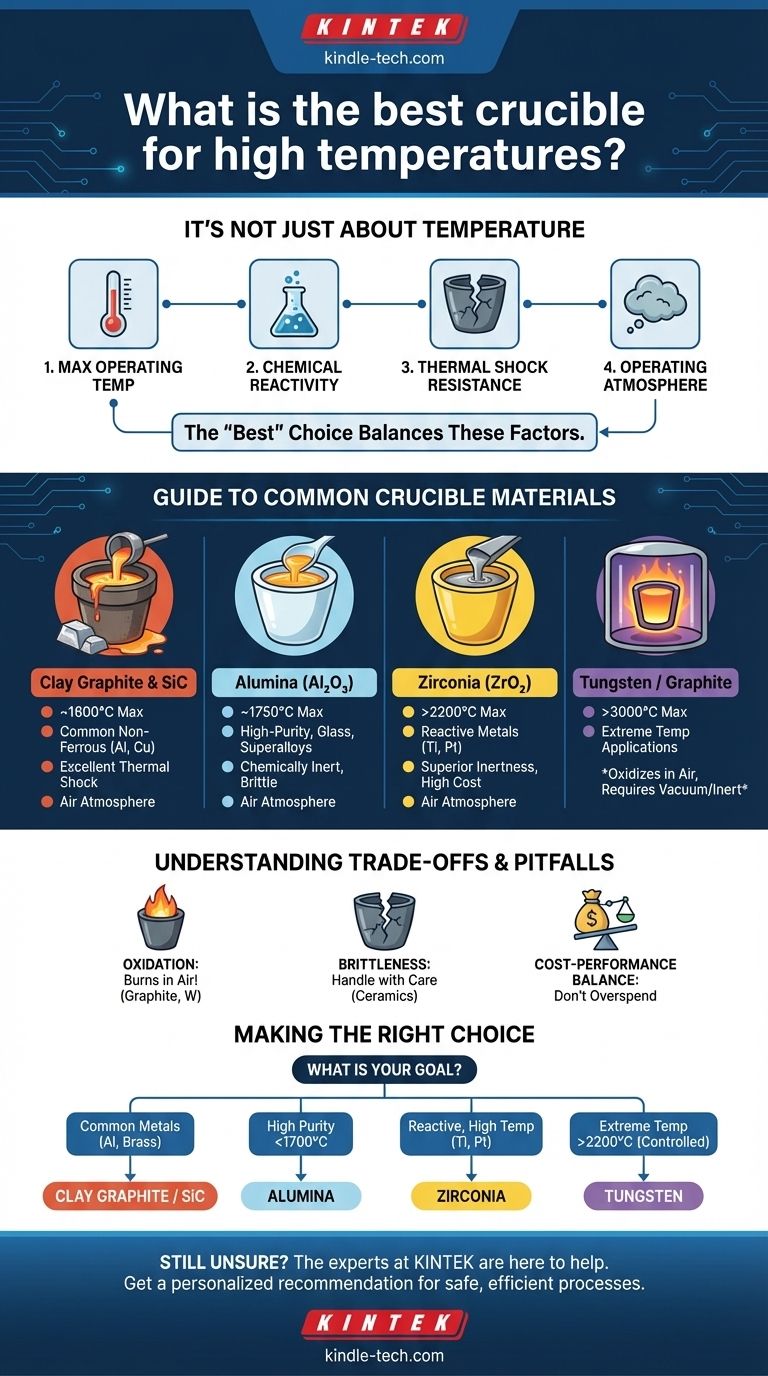
The concept of a single "best" crucible is a misconception. The ideal choice is not determined by temperature alone, but by a balance of four key factors: the maximum temperature, chemical reactivity with your material, resistance to thermal shock, and the operating atmosphere.

Why "Best" Depends On Your Application
Choosing a crucible is a technical decision that directly impacts the success of your process. Overlooking any of the following factors can lead to failed experiments, contaminated melts, or dangerous equipment failure.
Maximum Operating Temperature
This is the first and most obvious specification. Every material has a maximum service temperature, beyond which it will soften, melt, or degrade.
Always select a crucible with a temperature rating significantly higher than your intended operating temperature to ensure a margin of safety.
Chemical Reactivity
A crucible must be a neutral container. It cannot react with or contaminate the material being heated.
For example, a graphite crucible is excellent for melting aluminum but will contaminate molten steel by introducing carbon into the alloy, fundamentally changing its properties. A ceramic crucible like Alumina would be required instead.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when its temperature changes rapidly. Poor resistance can cause a crucible to crack or shatter.
Materials like clay graphite and silicon carbide are known for excellent thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for processes with fast heating and cooling cycles. High-purity ceramics are often more susceptible to cracking.
Operating Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is a critical, often overlooked, factor. The presence of oxygen dramatically changes material performance at high temperatures.
Graphite, Tungsten, and Molybdenum will literally burn away in an oxygen-rich atmosphere at high heat. They are only suitable for vacuum or inert gas (e.g., argon) furnaces.
A Guide to Common Crucible Materials
Each crucible material offers a unique profile of strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these profiles is the key to making an informed choice.
Clay Graphite & Silicon Carbide (SiC)
These are the workhorses for melting most common non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and copper. They offer an excellent balance of cost, durability, and outstanding resistance to thermal shock. Their maximum temperature is typically around 1600°C.
Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina is a high-purity, chemically inert ceramic capable of handling temperatures up to around 1750°C. It is an excellent choice for melting glass, high-purity metals, and superalloys where contamination is a major concern. Its primary weakness is a relative brittleness and lower resistance to thermal shock.
Zirconia (ZrO₂)
Zirconia is a step above Alumina in performance, with a maximum use temperature often exceeding 2200°C. It is exceptionally stable and non-reactive, making it one of the best choices for melting highly reactive materials like titanium or platinum group metals. This performance comes at a significantly higher cost.
Tungsten & Molybdenum
These are refractory metals, not ceramics. Tungsten has one of the highest melting points of any element (3422°C) and is used for the most extreme temperature applications. Both materials are strong and durable but will oxidize catastrophically in air, requiring a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Every material choice involves a compromise. Being aware of these limitations prevents costly mistakes.
The Oxidation Problem
This is the most critical pitfall for ultra-high-temperature work. Materials like graphite and tungsten seem ideal on paper due to their melting points, but they are completely unsuitable for use in an open-air furnace. Always verify atmospheric compatibility.
Brittleness vs. Durability
Ceramic crucibles like Alumina and Zirconia are very hard but also brittle, much like a dinner plate. They can easily be fractured by mechanical impact or severe thermal shock. In contrast, a silicon carbide or clay graphite crucible is far more resilient to rough handling.
The Cost-Performance Balance
The highest-performing material is not always the right choice. A Zirconia crucible can cost many times more than an Alumina one. For processes that don't require its extreme temperature resistance or reactivity profile, it is an unnecessary expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct crucible, match the material's properties directly to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass): Choose a Clay Graphite or Silicon Carbide crucible for the best balance of cost and durability.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melts or reactive metals below 1700°C: Choose an Alumina crucible for its excellent chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is melting platinum, titanium, or other reactive alloys at very high temperatures: A Zirconia crucible is the superior and necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving extreme temperatures (above 2200°C) in a controlled atmosphere: You must use a refractory metal crucible like Tungsten.
Ultimately, selecting the right crucible is about understanding your specific process and choosing the tool designed to meet those demands.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp (°C) | Key Strengths | Ideal For | Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten/Graphite | >3000°C | Extreme temperature resistance | Ultra-high temp applications | Vacuum/Inert Only |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | >2200°C | Excellent chemical inertness | Reactive metals (Ti, Pt) | Air |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | ~1750°C | High purity, chemically inert | Glass, superalloys | Air |
| Clay Graphite/SiC | ~1600°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Common non-ferrous metals | Air |
Still unsure which crucible is right for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing crucibles from leading manufacturers to meet your exact temperature, material, and atmospheric requirements. Contact our technical team today for a personalized recommendation to ensure your high-temperature processes are safe, efficient, and contamination-free.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- How much heat can a ceramic crucible withstand? A Guide to Material-Specific Temperature Limits



















