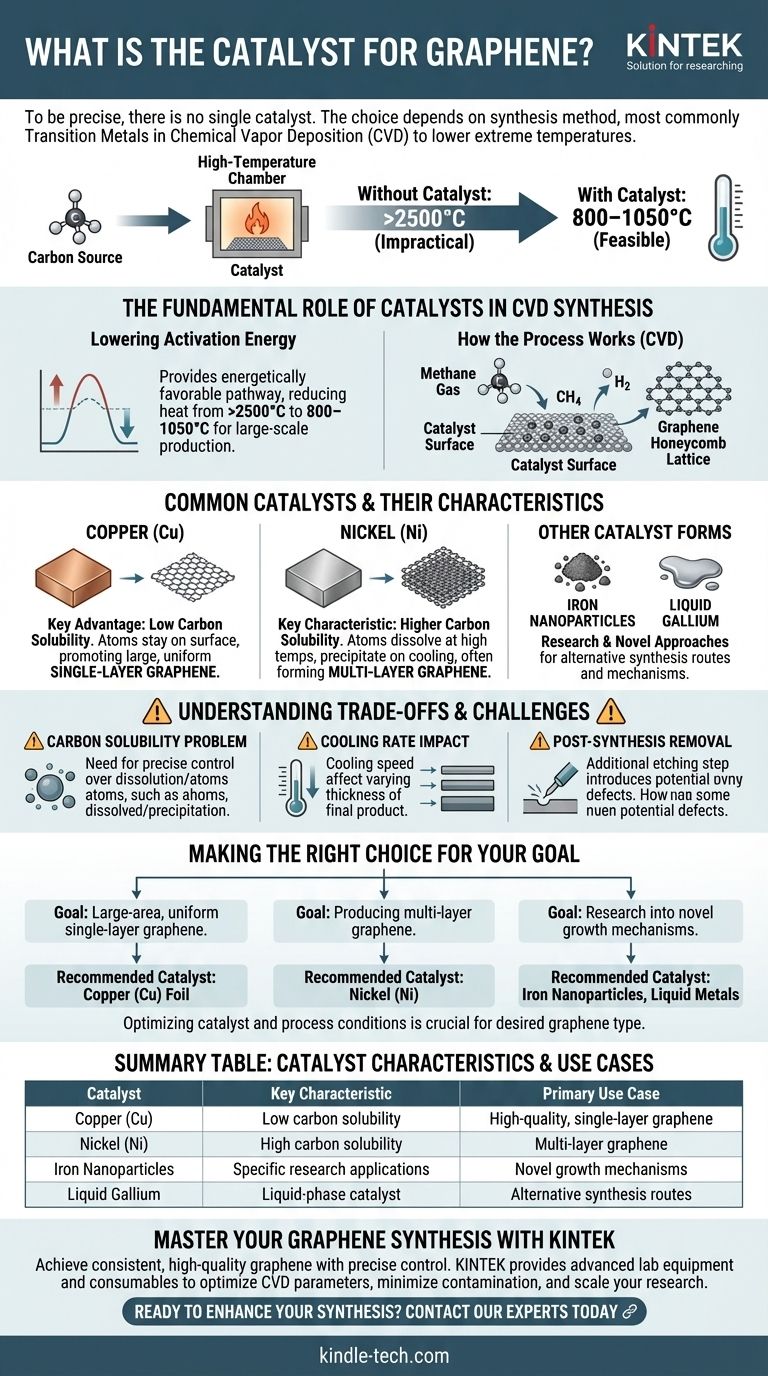
To be precise, there is no single catalyst for graphene. The choice of catalyst depends entirely on the synthesis method, with the most common being transition metals like copper (Cu) and nickel (Ni) used in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Other materials such as iron nanoparticles and liquid gallium are also used in specific production contexts.
The central role of a catalyst in modern graphene production is to make the process viable by drastically reducing the extreme temperatures required for synthesis. However, the catalyst itself introduces critical complexities, such as controlling layer thickness and potential contamination, that define the quality of the final material.

The Fundamental Role of Catalysts in Graphene Synthesis
To understand which catalysts are used, we must first understand why they are necessary. Their primary function is to provide an energetically favorable pathway for carbon atoms to assemble into the desired honeycomb lattice structure.
Lowering the Activation Energy
Without a catalyst, forming graphene from a carbon source requires immense heat—over 2500°C. This makes the process impractical and expensive.
A catalyst provides a surface that dramatically lowers this required temperature to a more manageable range of 800–1050°C, making large-scale production feasible.
How the Process Works (CVD)
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the most common synthesis method, a carbon-containing gas like methane is introduced into a high-temperature chamber.
The hot gas decomposes, and the catalyst's surface acts as a template. Carbon atoms adsorb onto the metal surface and arrange themselves into the stable, hexagonal structure of graphene.
Common Catalysts and Their Characteristics
The behavior of the catalyst directly impacts the quality and properties of the graphene produced. The most common choices are transition metals, each with distinct advantages.
Copper (Cu)
Copper is arguably the most popular catalyst for producing high-quality, single-layer graphene.
Its key advantage is its very low carbon solubility. This means carbon atoms stay on the surface rather than dissolving into the bulk copper, promoting the growth of large, uniform sheets.
Nickel (Ni)
Nickel is another widely used catalyst. However, it has a higher carbon solubility compared to copper.
At high temperatures, carbon atoms can dissolve into the nickel. As it cools, these atoms precipitate back to the surface, which can result in the formation of multi-layer graphene. This can be an advantage or disadvantage depending on the desired outcome.
Other Catalyst Forms
Research continues to explore alternative catalysts. Iron nanoparticles have been used, and novel approaches even utilize liquid gallium vapor to facilitate graphene growth, highlighting the flexibility of the synthesis process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, the use of catalysts introduces significant process control challenges that engineers and researchers must manage carefully.
The Problem of Carbon Solubility
As mentioned with nickel, the tendency of carbon to dissolve into the catalyst at high temperatures is a critical variable.
This dissolution and subsequent precipitation during cooling can lead to unwanted carbon deposition or non-uniform graphene thickness, making precise control difficult.
The Impact of the Cooling Rate
The rate at which the system cools is a crucial parameter that directly affects the final product.
Different cooling rates can alter the thickness and quality of the graphene as it precipitates from the catalyst. This adds another layer of complexity to achieving consistent, repeatable results.
Post-Synthesis Removal
After synthesis, the metallic catalyst often needs to be removed from the graphene film. This typically involves an etching process, which is an additional step that can introduce defects or contaminants if not performed carefully.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal catalyst and process conditions are not universal; they are dictated by the specific type of graphene you need to produce.
- If your primary focus is large-area, uniform single-layer graphene: A low-solubility catalyst like copper foil is the industry-standard choice.
- If your primary focus is producing multi-layer graphene: A catalyst with higher carbon solubility, such as nickel, is often more suitable, but requires precise control over the cooling process.
- If your primary focus is research into novel growth mechanisms: Exploring alternative catalysts like liquid metals or nanoparticles can yield different and potentially valuable results.
Ultimately, mastering graphene synthesis requires a deep understanding of the interplay between the catalyst, carbon source, and the precise physical conditions of the reaction.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | Low carbon solubility | High-quality, single-layer graphene |
| Nickel (Ni) | High carbon solubility | Multi-layer graphene |
| Iron Nanoparticles | Specific research applications | Novel growth mechanisms |
| Liquid Gallium | Liquid-phase catalyst | Alternative synthesis routes |
Master Your Graphene Synthesis with KINTEK
Choosing the right catalyst is just the first step. Achieving consistent, high-quality graphene requires precise control over the entire synthesis process, including temperature management and post-processing.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science research. Whether you are developing new CVD processes or scaling up production, our expertise and reliable products can help you:
- Optimize your CVD parameters for superior graphene quality.
- Minimize contamination and defects in your final material.
- Scale your research from the lab to pilot production.
Ready to enhance your graphene synthesis? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
People Also Ask
- What is the carbon footprint of diamond mining? Uncovering the True Environmental and Ethical Cost
- What are the environmental issues with diamond mining? Uncover the True Ecological and Human Cost
- What are some ethical issues with diamond mining? Uncover the Hidden Costs of Your Gemstone
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What are the raw materials for CVD diamonds? A seed, a gas, and the science of crystal growth.














