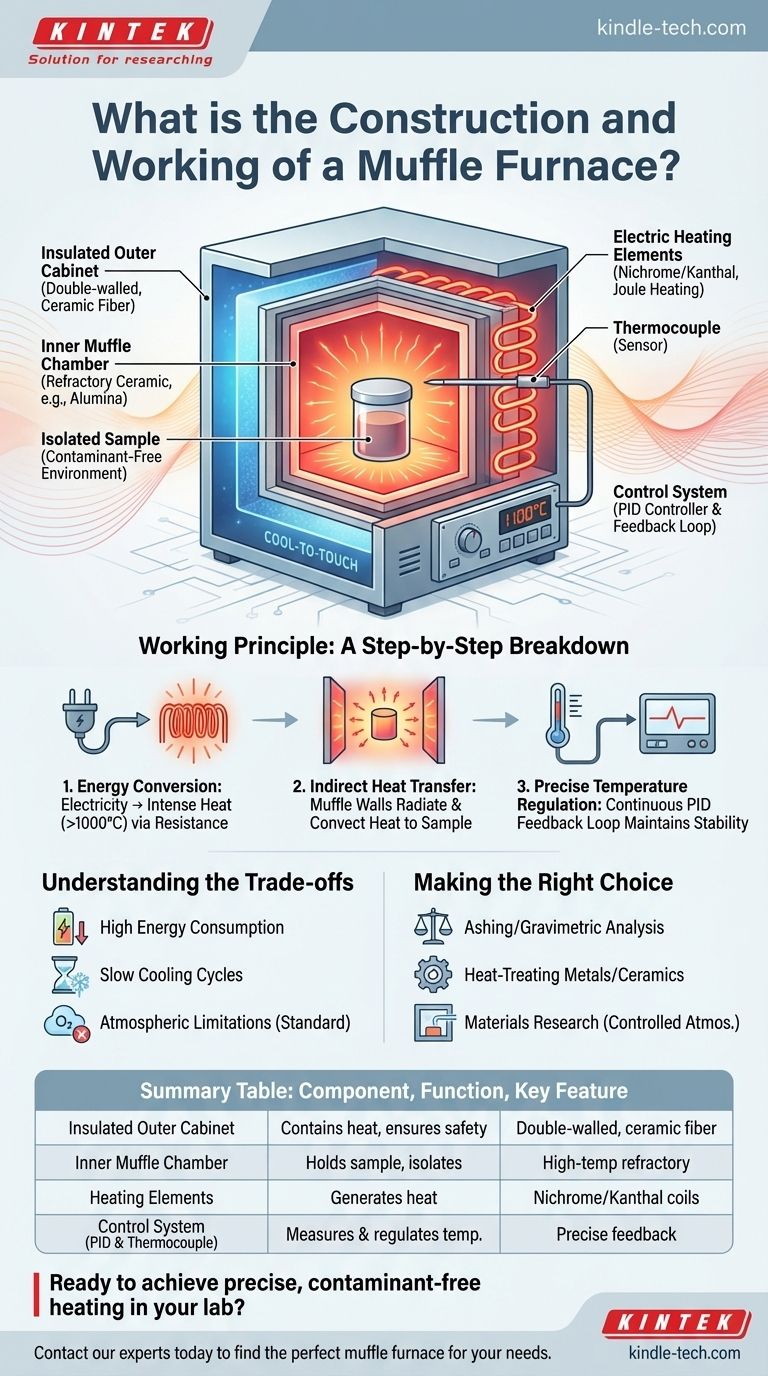
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that isolates the material being heated from the heating elements. Its construction consists of an insulated outer cabinet, an inner chamber made of refractory ceramic (the "muffle"), high-resistance electric heating coils surrounding this chamber, and a digital control system with a temperature sensor. It works by passing electricity through the heating coils, which generate intense heat through resistance, and then transferring this heat into the isolated chamber via radiation and convection.
The essential principle of a muffle furnace is not just to get hot, but to provide a perfectly controlled and contaminant-free high-temperature environment. It achieves this by physically separating the sample from the direct heat source, ensuring uniform and clean heating.

The Core Components and Their Roles
A muffle furnace's design is a model of thermal efficiency. Each part is engineered to generate, contain, and precisely control extreme heat.
The Insulated Outer Cabinet
The furnace's external body is a double-walled steel box. The space between the walls is packed with high-grade ceramic fiber insulation.
This insulation is critical for preventing heat from escaping, which ensures energy efficiency and keeps the outer surface safe to touch.
The Inner Muffle Chamber
This is the heart of the furnace. It's a box made from a molded, high-temperature refractory material like alumina.
This chamber is where you place your samples. Its material is designed to withstand thermal shock and radiate heat evenly onto the contents within it. Crucially, it creates a barrier between the heating elements and your sample.
The Electric Heating Elements
Positioned outside the muffle chamber but inside the insulated cabinet, these elements do the actual work.
They are typically coils made from a high-resistance alloy like Nichrome or Kanthal. When a high electrical current is passed through them, they glow red-hot, a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
The Control System
Modern furnaces rely on a precise feedback loop for control. This system includes a thermocouple, a PID controller, and a power regulator.
The thermocouple is a sensor that extends into the heating chamber to measure the real-time temperature. The PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller is the "brain" that compares this reading to your set temperature and intelligently adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to maintain it with extreme accuracy.
The Working Principle: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Understanding how the components work together reveals the furnace's simple but effective operation.
Step 1: Energy Conversion
The process begins when you set a temperature and turn the unit on. The controller sends electrical energy to the heating elements.
Due to their high resistance, the elements convert this electrical energy directly into thermal energy (heat), glowing intensely and reaching temperatures well over 1000°C.
Step 2: Indirect Heat Transfer
The heat generated by the elements is transferred to the outer walls of the muffle chamber.
The chamber's walls absorb this energy and then radiate it uniformly into the chamber's interior. Heat is also transferred through natural convection of the air inside, ensuring the sample is heated evenly from all sides without any hot spots.
Step 3: Precise Temperature Regulation
The thermocouple constantly measures the internal temperature and feeds this information back to the PID controller.
If the temperature is too low, the controller increases power to the elements. If it's too high, it cuts the power. This continuous feedback loop allows the furnace to hold a set temperature with remarkable stability, often within a single degree.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, muffle furnaces are not without their operational considerations.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1100°C or higher requires a significant amount of electrical power. This is a primary operational cost.
Slow Cooling Cycles
The same high-efficiency insulation that keeps the furnace hot also prevents it from cooling down quickly. This can be a bottleneck in processes that require rapid cycling.
Atmospheric Limitations
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air. Heating certain materials in the presence of oxygen can cause unwanted oxidation. For these applications, a specialized furnace with ports for introducing inert gas like argon or nitrogen is required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application dictates the type of furnace you need. Understanding its working principle helps you select the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing or gravimetric analysis: A standard muffle furnace is perfect, as it provides the stable, high-temperature, and contaminant-free environment needed for complete combustion.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating metals or ceramics: Prioritize a model with an advanced PID controller for programmable, multi-step heating cycles to achieve specific material properties.
- If your primary focus is materials research in a controlled atmosphere: You require a specialized furnace with sealed chambers and gas inlet/outlet ports to prevent oxidation or introduce reactive gases.
By understanding its construction, you can effectively leverage the muffle furnace for any application demanding precise, repeatable, and clean high-temperature processing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Insulated Outer Cabinet | Contains heat, ensures safety and efficiency | Double-walled steel with ceramic fiber insulation |
| Inner Muffle Chamber | Holds the sample, provides contaminant-free environment | Made of high-temperature refractory material (e.g., alumina) |
| Heating Elements | Generates heat via electrical resistance | Coils made of Nichrome or Kanthal |
| Control System (PID & Thermocouple) | Precisely measures and regulates temperature | Maintains set temperature with high stability |
Ready to achieve precise, contaminant-free heating in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for applications like ashing, heat treatment, and materials research. Our furnaces offer the precise temperature control and clean environment your work demands.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific laboratory needs and enhance your high-temperature processing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why refractory materials are used in furnaces? Ensure Safety, Efficiency, and Process Purity
- What are the hazards of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Critical Risks for Lab Safety
- Why ceramics can withstand high temperature? Unlock the Secrets of Atomic Structure
- How do you make biochar in a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Pyrolysis
- What is the difference between a crucible and a furnace? Understanding the Heat Source and Container Partnership



















