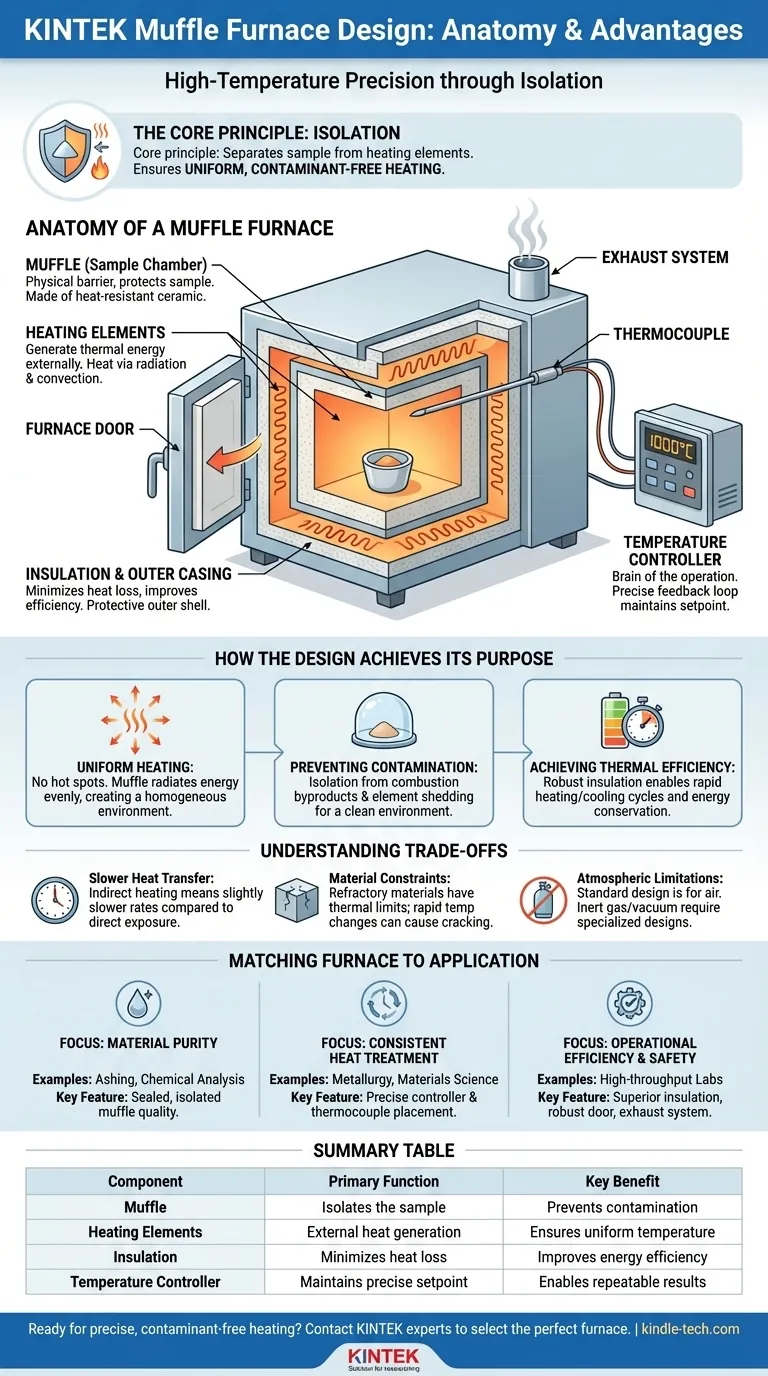
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven designed around a central principle: isolation. Its construction involves a primary heating chamber, known as the muffle, which is heated externally by elements contained within a heavily insulated casing. This entire system is governed by a precise temperature controller, allowing it to achieve uniform and contaminant-free heating for materials placed inside.
The critical design insight of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its construction that intentionally separates the sample from the heating elements. This isolation is the key to preventing contamination and ensuring highly uniform temperature distribution.
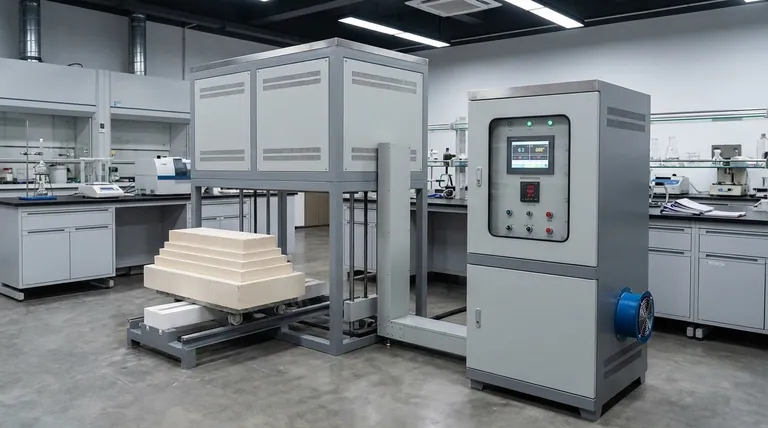

The Anatomy of a Muffle Furnace
To understand the furnace, we must first understand its core components and how they interact. Each part serves a distinct purpose in creating a controlled, high-temperature environment.
The Muffle: The Heart of the Chamber
The central component is the muffle itself—a refractory-lined chamber that houses the samples. It is typically constructed from heat-resistant materials like silica and aluminum ceramics. Its purpose is to act as a physical barrier, protecting the contents from direct contact with the heating elements.
Heating Elements: The Source of Power
Positioned around the outside of the muffle, the heating elements are responsible for generating the thermal energy. By heating the muffle externally, the system ensures that heat is transferred to the sample primarily through radiation and convection, promoting a more even temperature.
Insulation and Outer Casing: Containing the Heat
Multiple layers of high-grade insulation surround the muffle and heating elements. This material is critical for minimizing heat loss, which makes the furnace energy-efficient and allows for rapid heating cycles. The entire assembly is housed within a protective outer casing or shell for safety and structural integrity.
Temperature Control System: The Brains of the Operation
This system is a feedback loop consisting of two parts. A thermocouple (a temperature sensor) sits inside the chamber to measure the exact temperature. This information is fed to an external temperature controller (the control panel), which regulates the power supplied to the heating elements to maintain the desired setpoint with high precision.
Structural and Safety Features: The Practical Details
The design includes practical elements for usability and safety. A furnace door, which can be designed to open in various directions, provides access to the chamber. An exhaust system or release hole is often included to safely vent any gases or fumes produced during the heating process.
How the Design Achieves Its Purpose
The specific construction of a muffle furnace is a direct solution to the challenges of high-temperature material processing. The design directly enables its key functions.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
Because the sample does not have a "hot spot" from a nearby heating element, the muffle design excels at creating a homogeneous thermal environment. The chamber walls heat up and radiate energy evenly inward, ensuring the entire workpiece receives the same thermal treatment.
Preventing Cross-Contamination
This is the most significant advantage of the muffle design. By separating the material being heated from the byproducts of combustion or any potential shedding from the heating elements, the furnace provides an exceptionally clean heating environment.
Achieving Thermal Efficiency
The combination of robust insulation and a self-contained chamber allows the furnace to heat up, recover from temperature drops, and cool down relatively quickly. This makes it an energy-efficient tool for repeated laboratory or industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the muffle furnace design comes with inherent trade-offs that are important to recognize.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The very feature that makes a muffle furnace great—indirect heating—is also a limitation. Because heat must first pass through the muffle wall, the rate of heat transfer can be slightly slower compared to furnaces where elements are directly exposed to the chamber.
Material Constraints
The refractory materials of the muffle have thermal limits. They can be susceptible to thermal shock if heated or cooled too rapidly and have a maximum service temperature. Exceeding these limits can cause cracking and damage to the furnace's core.
Atmospheric Limitations
A standard muffle furnace operates with the air present in the chamber. Creating a specific atmosphere (such as inert gas or a vacuum) requires a more specialized and significantly more complex furnace design.
Matching the Furnace to the Application
Ultimately, the design of a muffle furnace is optimized for specific tasks. Understanding your goal will clarify which design aspects are most important for you.
- If your primary focus is material purity and avoiding contamination: The quality of the sealed, isolated muffle chamber is the most critical design aspect for applications like ashing or chemical analysis.
- If your primary focus is consistent, repeatable heat treatment: A precise temperature controller and a well-placed thermocouple are the key components for metallurgical or materials science applications.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and safety: Look for superior insulation for faster cycle times and a robust door and exhaust system to manage workflow and potential fumes.
By understanding how each component contributes to the furnace's function, you can operate these powerful tools with both confidence and precision.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle | Isolates the sample | Prevents contamination |
| Heating Elements | External heat generation | Ensures uniform temperature |
| Insulation | Minimizes heat loss | Improves energy efficiency |
| Temperature Controller | Maintains precise setpoint | Enables repeatable results |
Ready to achieve precise, contaminant-free heating in your lab?
The robust design of a muffle furnace is ideal for applications requiring high purity and uniform temperatures, such as ashing, heat treatment, and materials testing. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable and efficient solutions.
Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace for your application. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our muffle furnaces can enhance your processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- What is the use of muffle furnace in soil? Analyze Soil Composition with High-Temperature Precision
- What is the theory of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- Can a muffle furnace be used for calcination? Achieve Pure, Controlled Thermal Decomposition



















