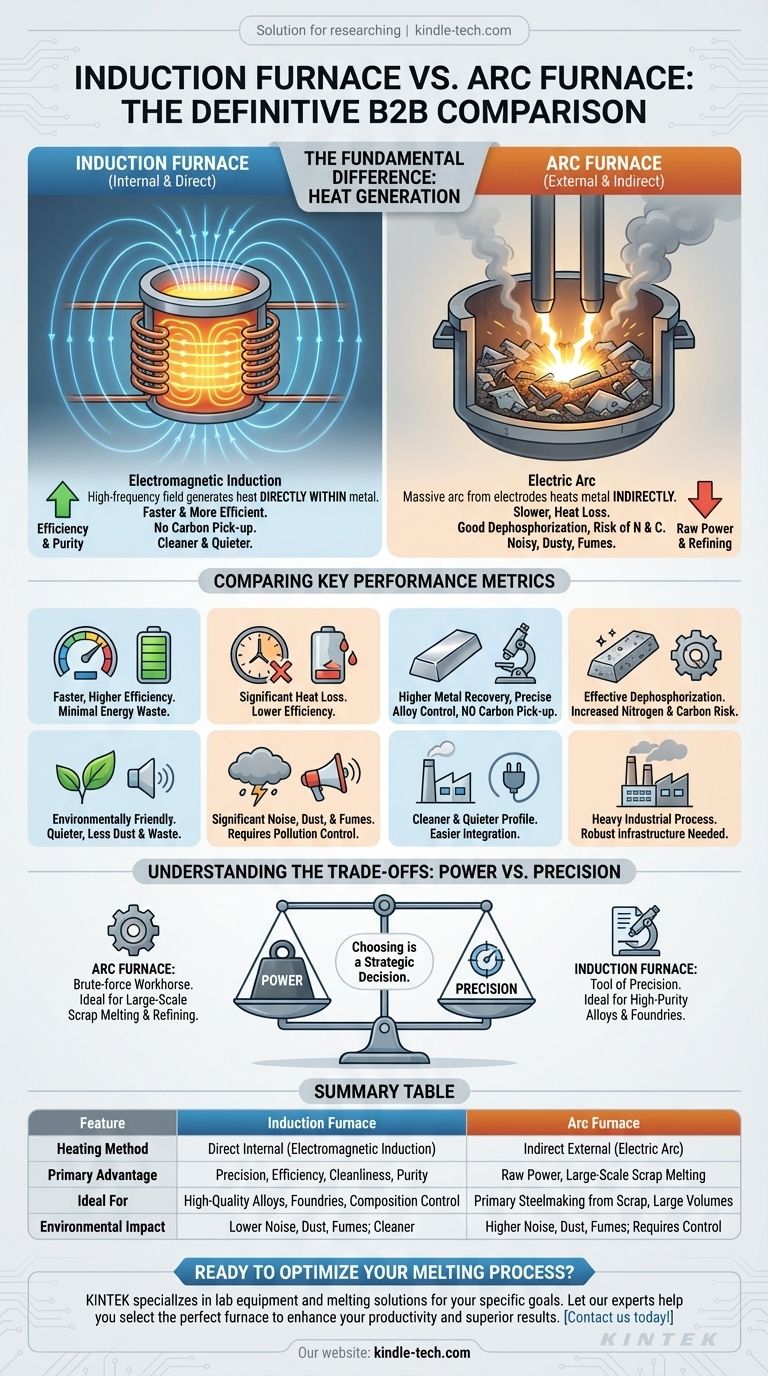
At their core, the fundamental difference is how they generate heat. An induction furnace uses a powerful, high-frequency electromagnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself. In contrast, an electric arc furnace (EAF) uses a massive electric arc that jumps between graphite electrodes and the metal, heating it indirectly from an external source.
Choosing between these furnaces is a strategic decision that trades the raw power and refining capability of an arc furnace against the precision, efficiency, and cleanliness of an induction furnace.

The Fundamental Difference: Heating Mechanism
The method of generating heat is the single most important distinction between these two technologies, influencing everything from efficiency to the quality of the final product.
Induction Furnace: Direct Internal Heating
An induction furnace operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Coils surrounding the crucible create a powerful magnetic field.
This field induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense and rapid heat from the inside out.
A key benefit of this process is the electromagnetic stirring effect, which naturally mixes the molten metal, ensuring a highly uniform temperature and a homogeneous final product.
Arc Furnace: Indirect External Heating
An electric arc furnace melts metal using the immense energy of an electric arc.
This high-current arc is struck between large graphite electrodes and the metal scrap inside the furnace. The arc itself can reach temperatures of thousands of degrees Celsius.
This heat is then transferred—largely through a layer of slag—to the metal. This is an indirect heating method, as the heat is generated outside the metal and must be transferred to it.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The differences in heating methods lead to vastly different outcomes in efficiency, material quality, and environmental impact.
Thermal Efficiency and Speed
Because heat is generated directly within the charge material, induction furnaces are faster and have a much higher thermal efficiency. There is very little wasted energy.
Arc furnaces suffer from significant heat loss through the furnace walls, roof, and exhaust gases. The indirect transfer of heat from the arc to the steel is inherently less efficient.
Material Quality and Composition
Arc furnaces are very effective at dephosphorization, a critical refining step in primary steelmaking. However, the process can increase the nitrogen content in the steel.
Induction furnaces provide more control over the melt. They result in a higher metal recovery rate and less burn-off of expensive alloy elements. A critical advantage is the absence of graphite electrodes, which eliminates the risk of carbon pick-up in the melt.
Environmental Impact and Cleanliness
Induction furnaces are significantly more environmentally friendly. They are quieter and produce far less dust, waste residue, and exhaust gas.
Arc furnaces are known for producing significant noise, dust, and fumes. They require extensive pollution control systems to manage their environmental footprint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is universally superior; they are tools designed for different scales and purposes. The choice involves balancing power against precision.
The Power vs. Precision Dilemma
The electric arc furnace is a brute-force workhorse. It is ideal for melting down large volumes of raw materials like scrap steel, and its ability to handle impurities and perform key refining steps makes it the backbone of many steel mills.
The induction furnace is a tool of precision. It excels in applications where purity and exact alloy composition are critical, such as in foundries producing high-quality castings and specialty steel manufacturers.
Operational Footprint
Operating an arc furnace is a heavy industrial process. The noise, dust, and high energy consumption demand a robust infrastructure to support it.
Induction furnaces have a much cleaner and quieter operational profile, making them more suitable for integration into a wider variety of manufacturing facilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision hinges entirely on your primary objective, whether it is large-scale raw material processing or high-purity alloy production.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap with strong refining needs: The electric arc furnace is superior due to its power and effective dephosphorization capabilities.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality, specialized alloys with precise composition: The induction furnace offers better control, higher efficiency, and a cleaner melting process.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and operational cleanliness: The induction furnace is the clear choice, generating significantly less noise, dust, and waste.
Ultimately, understanding these core differences empowers you to select not just a furnace, but the optimal process for your specific material and business goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct internal heating via electromagnetic induction | Indirect external heating via electric arc |
| Primary Advantage | Precision, efficiency, cleanliness, and material purity | Raw power, large-scale scrap melting, and refining capability |
| Ideal For | High-quality alloys, foundries, precise composition control | Primary steelmaking from scrap, large-volume production |
| Environmental Impact | Lower noise, dust, and fumes; cleaner operation | Higher noise, dust, and fumes; requires pollution control |
Ready to optimize your melting process? The choice between an induction furnace and an arc furnace is critical for your product quality, efficiency, and operational costs. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with the right melting solutions for your specific materials and goals. Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace to enhance your productivity and ensure superior results. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results



















