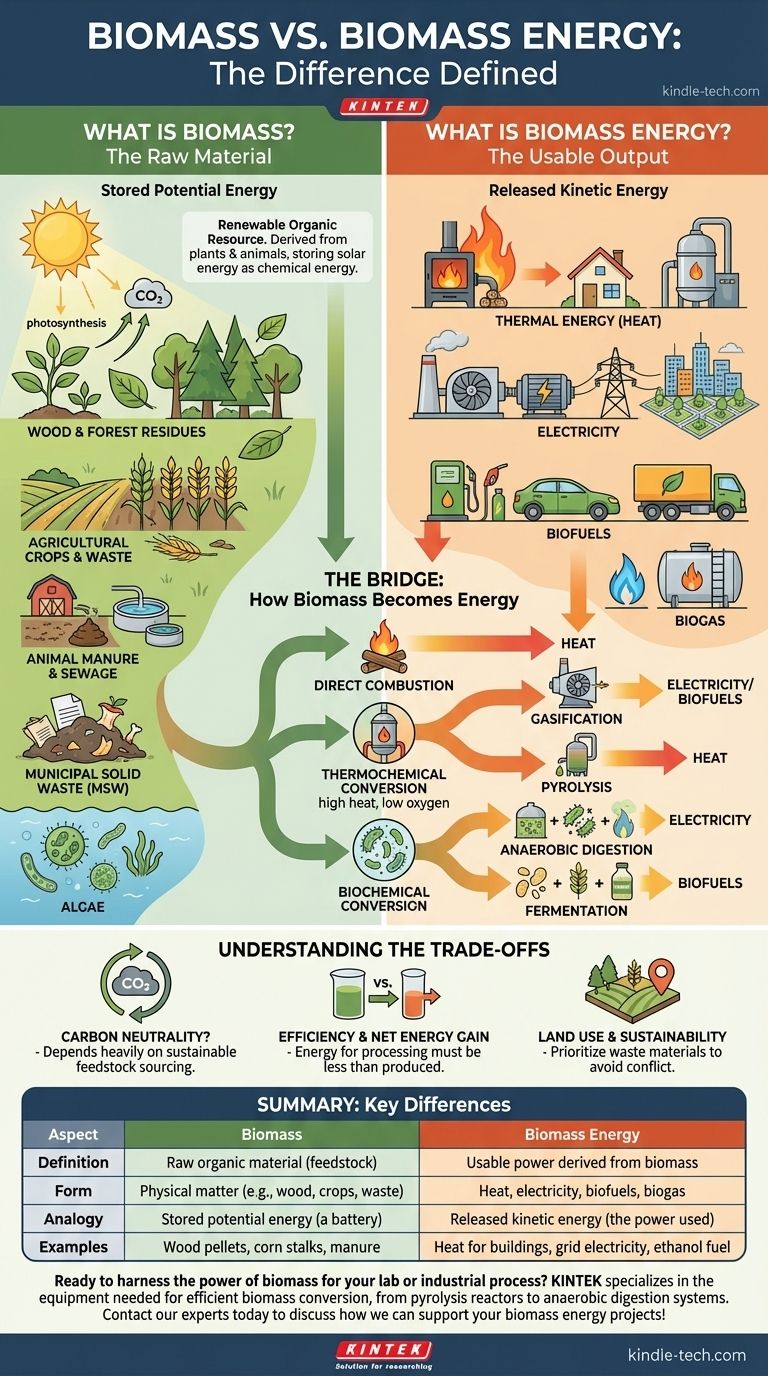
In short, biomass is the raw organic material, while biomass energy is the usable power—such as heat or electricity—that is generated from that material. Think of biomass as the physical fuel, like wood pellets or corn stalks, and biomass energy as the result of converting that fuel into a form we can use to power our homes and industries.
The core distinction is one of potential versus kinetic energy. Biomass is the stored chemical potential energy in organic matter. Biomass energy is the kinetic energy—heat, light, and electricity—released when that potential is unlocked through conversion.
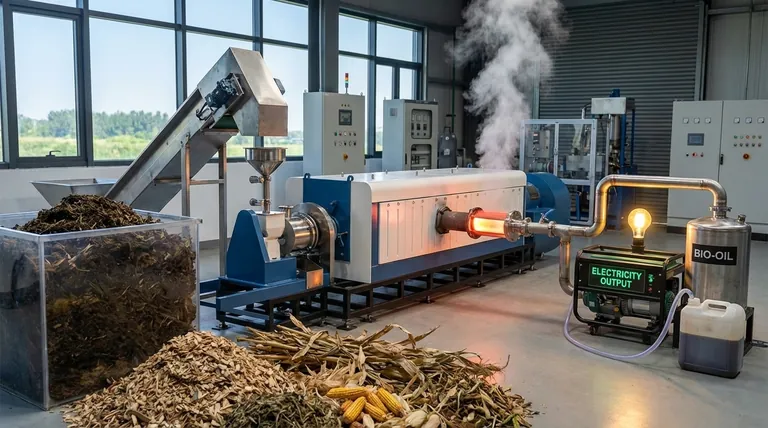

What is Biomass? The Raw Material
Biomass is a renewable organic resource. At its core, it is any material derived from plants or animals.
Defining Biomass: Stored Solar Energy
Plants capture the sun's energy through photosynthesis, converting it into chemical energy stored within their structure. This stored energy is the essence of biomass.
When animals consume plants, they incorporate this energy into their own bodies and waste. Therefore, biomass is effectively a natural, living battery for solar energy.
Common Examples of Biomass Feedstocks
The term "biomass" covers a wide range of materials, often called feedstocks. These are typically grouped into a few key categories:
- Wood and Forest Residues: This includes everything from firewood and wood pellets to sawdust, bark, and dead trees.
- Agricultural Crops & Waste: These are energy crops grown specifically for fuel (like switchgrass or corn for ethanol) and agricultural byproducts (like corn cobs, wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse).
- Animal Manure and Human Sewage: Organic waste from livestock farms and wastewater treatment plants can be a rich source of biomass.
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): This includes organic materials like paper, food scraps, and yard waste that are diverted from landfills.
- Algae: These microscopic aquatic organisms are a promising future source of biomass due to their rapid growth and high energy content.
What is Biomass Energy? The Usable Output
Biomass energy is the useful power we derive from a biomass feedstock. It is not the material itself but the end product of a conversion process.
The Key Forms of Biomass Energy
This energy can be harnessed in several distinct forms, each suited for different applications:
- Thermal Energy (Heat): The most direct use. Burning biomass in a stove, furnace, or boiler generates heat for warming buildings or for industrial processes like making steam.
- Electricity: Biomass can be burned to heat water, creating steam that spins a turbine and drives a generator to produce electricity for the grid.
- Biofuels: Biomass can be converted into liquid fuels. The two most common are ethanol (an alcohol fuel, often from corn) and biodiesel (from vegetable oils or animal fats), which can power vehicles.
- Biogas: When organic matter decomposes without oxygen (anaerobic digestion), it produces biogas, which is mostly methane. This gas can be captured and burned to generate heat or electricity.
The Bridge: How Biomass Becomes Energy
The critical link between the raw material and the usable energy is the conversion technology. There are three primary pathways to unlock the energy stored in biomass.
Direct Combustion
This is the oldest and simplest method: burning the biomass. It is efficient for generating heat but can be less efficient for electricity production and can release air pollutants if not properly controlled.
Thermochemical Conversion
This involves heating biomass in low-oxygen or zero-oxygen environments.
- Gasification: Produces a flammable gas mixture called "syngas," which can be burned to generate electricity or further processed into liquid biofuels.
- Pyrolysis: Produces a liquid called "bio-oil" or "pyrolysis oil," which can be used as a fuel for boilers or refined into other products.
Biochemical Conversion
This pathway uses microorganisms to break down the organic matter.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Bacteria break down wet organic waste (like manure or sewage) in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas.
- Fermentation: Yeast and other microbes convert the sugars in crops like corn and sugarcane into ethanol.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a valuable renewable resource, using biomass for energy is not without its complexities and challenges.
The Question of Carbon Neutrality
The idea behind biomass is that it is "carbon neutral"—the carbon dioxide released when it's burned is offset by the CO2 absorbed by the plants as they grew. However, this depends heavily on the feedstock. Using waste wood is very different from clearing a mature forest for fuel, which results in a net increase in atmospheric carbon for decades.
Efficiency and Net Energy Gain
The energy required to grow, harvest, transport, and convert the biomass must be less than the energy it ultimately produces. Some processes, particularly for certain biofuels, have a low or even negative net energy gain, making them impractical without subsidies.
Land Use and Sustainability
Growing energy crops on a large scale can compete with food production for land and water resources. The most sustainable biomass strategies prioritize the use of waste materials that do not create these conflicts.
Making the Right Distinction for Your Goal
Understanding the difference between the material and the energy is crucial for making informed decisions in the renewable energy sector.
- If your primary focus is sourcing and sustainability: Your analysis should center on the biomass itself—its origin, carbon lifecycle, and impact on land and water use.
- If your primary focus is power generation: Your concern is biomass energy—specifically the conversion efficiency, the cost per kilowatt-hour, and the reliability of the output.
- If your primary focus is transportation: You are interested in a specific form of biomass energy, namely biofuels, and the processes used to create them from feedstocks like corn or algae.
Ultimately, distinguishing between the fuel and the power it produces is the first step toward accurately evaluating the role biomass can play in a clean energy future.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Biomass | Biomass Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw organic material (feedstock) | Usable power derived from biomass |
| Form | Physical matter (e.g., wood, crops, waste) | Heat, electricity, biofuels, biogas |
| Analogy | Stored potential energy (a battery) | Released kinetic energy (the power used) |
| Examples | Wood pellets, corn stalks, manure | Heat for buildings, grid electricity, ethanol fuel |
Ready to harness the power of biomass for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in the equipment needed for efficient biomass conversion, from pyrolysis reactors to anaerobic digestion systems. Whether you're researching biofuels or scaling up renewable energy production, our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get the precise, reliable tools for your work. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your biomass energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using laboratory centrifuges and drying equipment in Pd1Ni catalyst testing? Ensure Stability.
- What types of plastic can be used for pyrolysis? Transform Low-Value Waste into High-Value Resources
- What are the challenges of large-scale biomass energy use? The Hidden Hurdles to a Green Energy Source
- How does reactive sputtering work? Master Thin Film Deposition for Superior Coatings
- What temperature is glass sintering? Master the Precise Thermal Window for Your Glass
- What temperature should brazing be? Master the Key to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the laboratory apparatus for mixing? Choose the Right Tool for Your Sample Volume and Viscosity
- How is a laboratory drying oven used for moisture determination in biomass? Precision Analysis & Energy Metrics







